Abstract
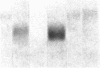
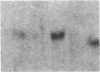
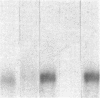
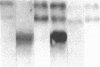
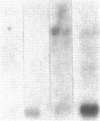
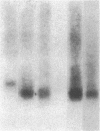
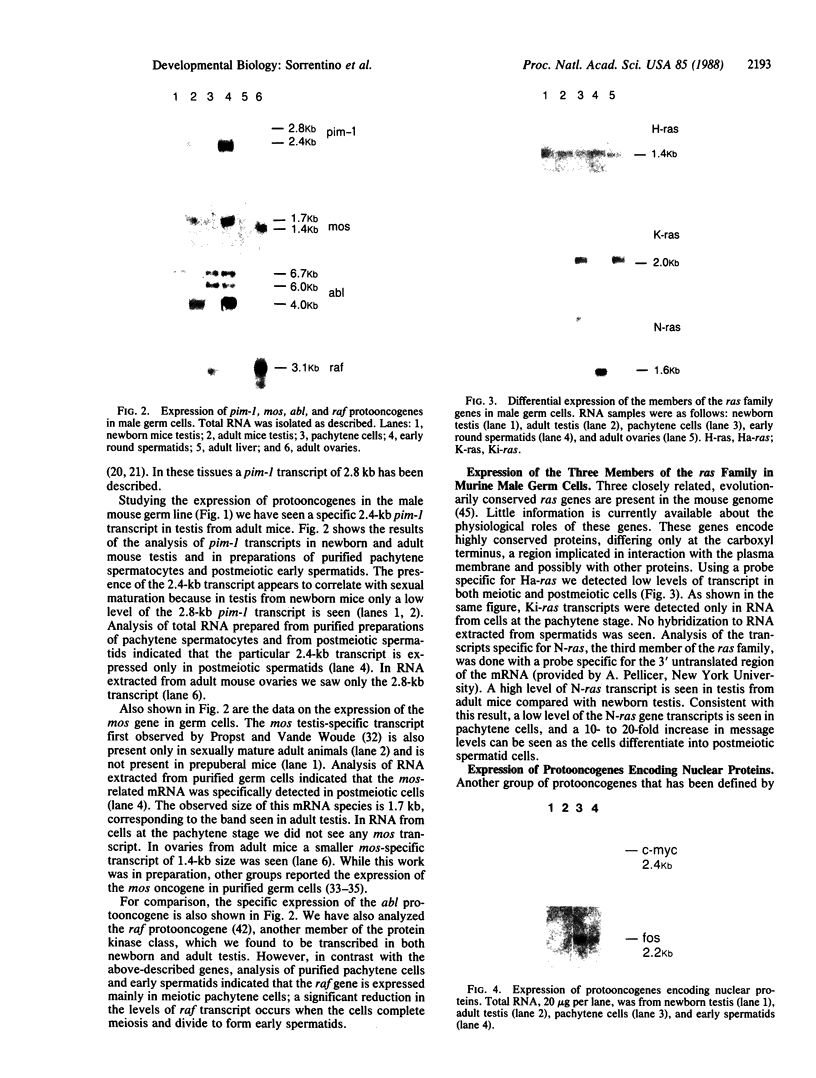
We report that a 2.4-kilobase (kb) pim-1 transcript is expressed in the germ cells of mouse testis. Analysis of purified populations of spermatogenic cell types indicates that the 2.4-kb transcript is selectively expressed in haploid postmeiotic early spermatids. The evidence for a developmentally regulated expression of pim-1 in haploid spermatids suggests a possible developmental role for this protooncogene product. The 2.4-kb pim-1 transcript present in postmeiotic cells differs in size from the 2.8-kb transcript usually detected in somatic tissues. Similar testis-specific transcripts have been seen for mos and abl genes. These data suggest specificity in transcription or processing of certain genes in haploid male germ cells. We have also analyzed other representative protooncogenes, including examples of protein kinases, the ras family, and the "nuclear" protooncogenes. The results indicate that additional protooncogenes are preferentially expressed in either meiotic pachytene cells or postmeiotic early spermatids. These findings suggest a differential regulation of gene expression in these two developmental stages of germ cells. In particular, analysis of expression of the three members of the ras gene family indicates a distinct temporal differential regulation in the expression of the Harvey, Kirsten, and N-ras genes in these germ cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemà S., Casalbore P., Agostini E., Tatò F. Differentiation of PC12 phaeochromocytoma cells induced by v-src oncogene. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):557–559. doi: 10.1038/316557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of the ras oncogene protein into PC12 cells induces morphological differentiation. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. I., Gall A. M., Southard J. L., Sidman R. L. Abnormal spermiogenesis in quaking, a myelin-deficient mutant mouse. Biol Reprod. 1971 Aug;5(1):30–58. doi: 10.1093/biolreprod/5.1.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Determinants of messenger RNA stability. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Cole M. D. Constitutive c-myc oncogene expression blocks mouse erythroleukaemia cell differentiation but not commitment. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):760–763. doi: 10.1038/320760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G., Quint W., Zijlstra M., Maandag E. R., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Melief C., Berns A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrovsky E., Kuehl W. M., Hollis G. F., Kirsch I. R., Bender T. P., Segal S. Expression of a transfected human c-myc oncogene inhibits differentiation of a mouse erythroleukaemia cell line. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):748–750. doi: 10.1038/322748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Devare S. G., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A., Antoniades H. N. Simian sarcoma virus onc gene, v-sis, is derived from the gene (or genes) encoding a platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.6304883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Defeo D., Shih T. Y., Gonda M. A., Young H. A., Tsuchida N., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. The p21 src genes of Harvey and Kirsten sarcoma viruses originate from divergent members of a family of normal vertebrate genes. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):506–511. doi: 10.1038/292506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcone G., Tatò F., Alemà S. Distinctive effects of the viral oncogenes myc, erb, fps, and src on the differentiation program of quail myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):426–430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gizang-Ginsberg E., Wolgemuth D. J. Expression of the proopiomelanocortin gene is developmentally regulated and affected by germ cells in the male mouse reproductive system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1600–1604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P., Gilboa E., Witte O. N., Baltimore D. Structure of the Abelson murine leukemia virus genome and the homologous cellular gene: studies with cloned viral DNA. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. S., Kiessling A. A., Millette C. F., Cooper G. M. Expression of c-mos RNA in germ cells of male and female mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht N. B., Kleene K. C., Distel R. J., Silver L. M. The differential expression of the actins and tubulins during spermatogenesis in the mouse. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jul;153(1):275–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90472-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits A., Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E., Martin G. R. Two proto-oncogenes implicated in mammary carcinogenesis, int-1 and int-2, are independently regulated during mouse development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7806–7810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Millette C. F. Expression of proenkephalin messenger RNA by mouse spermatogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5015–5018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleene K. C., Distel R. J., Hecht N. B. cDNA clones encoding cytoplasmic poly(A)+ RNAs which first appear at detectable levels in haploid phases of spermatogenesis in the mouse. Dev Biol. 1983 Aug;98(2):455–464. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90375-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman H. M., Hatton K. S., Skoultchi A. I., Schildkraut C. L. c-myc mRNA levels in the cell cycle change in mouse erythroleukemia cells following inducer treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5323–5327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon J., Guerrero I., Pellicer A. Differential expression of the ras gene family in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1535–1540. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistrich M. L., Longtin J., Brock W. A., Grimes S. R., Jr, Mace M. L. Purification of rat spermatogenic cells and preliminary biochemical analysis of these cells. Biol Reprod. 1981 Dec;25(5):1065–1077. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod25.5.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutter G. L., Wolgemuth D. J. Distinct developmental patterns of c-mos protooncogene expression in female and male mouse germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5301–5305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Curran T., Müller D., Guilbert L. Induction of c-fos during myelomonocytic differentiation and macrophage proliferation. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):546–548. doi: 10.1038/314546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Slamon D. J., Tremblay J. M., Cline M. J., Verma I. M. Differential expression of cellular oncogenes during pre- and postnatal development of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):640–644. doi: 10.1038/299640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peschon J. J., Behringer R. R., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Spermatid-specific expression of protamine 1 in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5316–5319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Wolgemuth D. J. Haploid expression of a unique c-abl transcript in the mouse male germ line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1791–1794. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst F., Rosenberg M. P., Iyer A., Kaul K., Vande Woude G. F. c-mos proto-oncogene RNA transcripts in mouse tissues: structural features, developmental regulation, and localization in specific cell types. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1629–1637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst F., Vande Woude G. F. Expression of c-mos proto-oncogene transcripts in mouse tissues. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):516–518. doi: 10.1038/315516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Goldsborough M. D., Mark G. E., Bonner T. I., Groffen J., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Structure and biological activity of v-raf, a unique oncogene transduced by a retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4218–4222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijsewijk F., Schuermann M., Wagenaar E., Parren P., Weigel D., Nusse R. The Drosophila homolog of the mouse mammary oncogene int-1 is identical to the segment polarity gene wingless. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Berns A. Proviral activation of the putative oncogene Pim-1 in MuLV induced T-cell lymphomas. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1793–1798. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Boelens W., Robanus-Maandag E., Verbeek J., Domen J., van Beveren C., Berns A. The primary structure of the putative oncogene pim-1 shows extensive homology with protein kinases. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):603–611. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90886-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to postmeiotic male germ cells and the neural tube of mid-gestational embryos. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90665-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino V., Drozdoff V., McKinney M. D., Zeitz L., Fleissner E. Potentiation of growth factor activity by exogenous c-myc expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8167–8171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino V., Drozdoff V., Zeitz L., Fleissner E. Increased radiation-induced transformation in C3H/10T1/2 cells after transfer of an exogenous c-myc gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4131–4134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Dorsal, an embryonic polarity gene in Drosophila, is homologous to the vertebrate proto-oncogene, c-rel. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):692–694. doi: 10.1126/science.3118464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Bellvé A. R., Leder P. Transcription and promoter usage of the myc gene in normal somatic and spermatogenic cells. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):707–710. doi: 10.1126/science.6494906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villasante A., Wang D., Dobner P., Dolph P., Lewis S. A., Cowan N. J. Six mouse alpha-tubulin mRNAs encode five distinct isotypes: testis-specific expression of two sister genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2409–2419. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters S. H., Distel R. J., Hecht N. B. Mouse testes contain two size classes of actin mRNA that are differentially expressed during spermatogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1649–1654. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Viviano C. M., Gizang-Ginsberg E., Frohman M. A., Joyner A. L., Martin G. R. Differential expression of the mouse homeobox-containing gene Hox-1.4 during male germ cell differentiation and embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5813–5817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]