Abstract
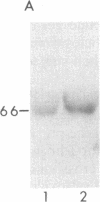
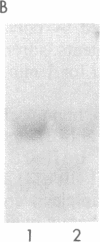
We have generated a monospecific antibody to a synthetic peptide encoded by an RNA complementary to the mRNA for angiotensin II (AII) and determined whether this antibody recognizes the AII receptor. We demonstrate that the antibody competes specifically with 125I-labeled AII for the same binding site on rat adrenal membranes. Furthermore, we show that this antibody inhibits the secretion of aldosterone from cultured rat adrenal cells, suggesting that the antibody recognizes the biologically relevant AII receptor. Finally, we demonstrate that antibody to the complementary peptide can be used to immunoaffinity-purify a protein of Mr 66,000 that specifically binds radiolabeled AII.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blalock J. E., Bost K. L. Binding of peptides that are specified by complementary RNAs. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):679–683. doi: 10.1042/bj2340679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bost K. L., Blalock J. E. Molecular characterization of a corticotropin (ACTH) receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 Jan;44(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bost K. L., Smith E. M., Blalock J. E. Similarity between the corticotropin (ACTH) receptor and a peptide encoded by an RNA that is complementary to ACTH mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1372–1375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentani R. R., Ribeiro S. F., Potocnjak P., Pasqualini R., Lopes J. D., Nakaie C. R. Characterization of the cellular receptor for fibronectin through a hydropathic complementarity approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):364–367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantau B., Guillemette G., Chicot D., Devilliers G. Vasopressin, angiotensin and adrenergic receptors of rat liver Golgi fractions--molecular weight of the angiotensin-receptor irreversible complex after in vitro and in vivo labelling. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 May;51(1-2):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capponi A. M., Catt K. J. Angiotensin II receptors in adrenal cortex and uterus. Binding and activation properties of angiotensin analogues. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5120–5127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capponi A. M., Catt K. J. Solubilization and characterization of adrenal and uterine angiotensin II receptors after photoaffinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12081–12086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D. J., Bost K. L., Blalock J. E. An antibody to a peptide specified by an RNA that is complementary to gamma-endorphin mRNA recognizes an opiate receptor. J Neuroimmunol. 1986 Oct;12(4):329–337. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(86)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. Disulfide bond formation in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:305–329. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Léan A., Ong H., Gutkowska J., Schiller P. W., McNicoll N. Evidence for agonist-induced interaction of angiotensin receptor with a guanine nucleotide-binding protein in bovine adrenal zona glomerulosa. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):498–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J., Aguilera G., Kondo T., Catt K. Angiotensin II receptors and aldosterone production in rat adrenal glomerulosa cells. Endocrinology. 1978 Mar;102(3):685–696. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-3-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gioannini T. L., Howard A. D., Hiller J. M., Simon E. J. Purification of an active opioid-binding protein from bovine striatum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15117–15121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Baukal A. J., Catt K. J. Properties of angiotensin II receptors in the bovine and rat adrenal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):825–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette G., Escher E. Analysis of the adrenal angiotensin II receptor with the photoaffinity labeling method. Biochemistry. 1983 Nov 22;22(24):5591–5596. doi: 10.1021/bi00293a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette G., Guillon G., Marie J., Balestre M. N., Escher E., Jard S. High yield photoaffinity labeling of angiotensin II receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;30(6):544–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette G., Guillon G., Marie J., Pantaloni C., Balestre M. N., Escher E., Jard S. Angiotensin-induced changes in the apparent size of rat liver angiotensin receptors. J Recept Res. 1984;4(1-6):267–281. doi: 10.3109/10799898409042554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görcs T. J., Gottschall P. E., Coy D. H., Arimura A. Possible recognition of the GnRH receptor by an antiserum against a peptide encoded by nucleotide sequence complementary to mRNA of a GnRH precursor peptide. Peptides. 1986 Nov-Dec;7(6):1137–1145. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90144-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Sekura R. D., Aguilera G., Catt K. J. Control of aldosterone production by angiotensin II is mediated by two guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1668–1678. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanij V., Hur K. C. Direct cross-linking of 125I-labeled glucagon to its membrane receptor by UV irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):325–329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubasik N. P., Warren K., Sine H. E. Evaluation of a new commercial radioassay kit for aldosterone using an iodinated tracer. Clin Biochem. 1979 Apr;12(2):59–61. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(79)80008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laribi C., Allard M., Vincent J. D., Simonnet G. Solubilization and characterization of covalently labeled angiotensin II receptors in cultured mouse spinal cord cells. Neuropeptides. 1987 May-Jun;9(4):345–356. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(87)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Krönke M., Robb R. J., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. The human receptor for T-cell growth factor. Evidence for variable post-translational processing, phosphorylation, sulfation, and the ability of precursor forms of the receptor to bind T-cell growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1872–1880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., George S. T., Graziano M. P., Brandwein H. J., Malbon C. C. Mammalian beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Immunological and structural comparisons. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14562–14570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., Malbon C. C. Fat cell beta 1-adrenergic receptor: structural evidence for existence of disulfide bridges essential for ligand binding. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6072–6077. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulchahey J. J., Neill J. D., Dion L. D., Bost K. L., Blalock J. E. Antibodies to the binding site of the receptor for luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH): generation with a synthetic decapeptide encoded by an RNA complementary to LHRH mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9714–9718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo H., Kageyama R., Ujihara M., Hirose T., Inayama S., Nakanishi S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for rat angiotensinogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2196–2200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAGE I. H., BUMPUS F. M. Angiotensin. Physiol Rev. 1961 Apr;41:331–390. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1961.41.2.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pobiner B. F., Hewlett E. L., Garrison J. C. Role of Ni in coupling angiotensin receptors to inhibition of adenylate cyclase in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16200–16209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKEGGS L. T., Jr, KAHN J. R., SHUMWAY N. P. The preparation and function of the hypertensin-converting enzyme. J Exp Med. 1956 Mar 1;103(3):295–299. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.3.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen I., Bull H. G., Soffer R. L. Isolation of an angiotensin II-binding protein from liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1679–1683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen I., Jim K. F., Soffer R. L. Solubilization and characterization of an angiotensin II binding protein from liver. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 17;136(1):41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shai Y., Flashner M., Chaiken I. M. Anti-sense peptide recognition of sense peptides: direct quantitative characterization with the ribonuclease S-peptide system using analytical high-performance affinity chromatography. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 10;26(3):669–675. doi: 10.1021/bi00377a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soffer R. L., Bandyopadhyay S., Rosenberg E., Hoeprich P., Teitelbaum A., Brunck T., Colby C. B., Gloff C. Unexpected binding of an octapeptide to the angiotensin II receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9219–9222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen P., Farber N. M., Krystal G. Identification of the interleukin-3 receptor using an iodinatable, cleavable, photoreactive cross-linking agent. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9094–9097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimalasena J., Abel J. A., Jr, Wiebe J. P., Chen T. T. The porcine ovarian luteinizing hormone/human chorionic gonadotropin receptor II. Is the purified receptor an oligomer of identical subunits? J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9416–9420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]