Abstract
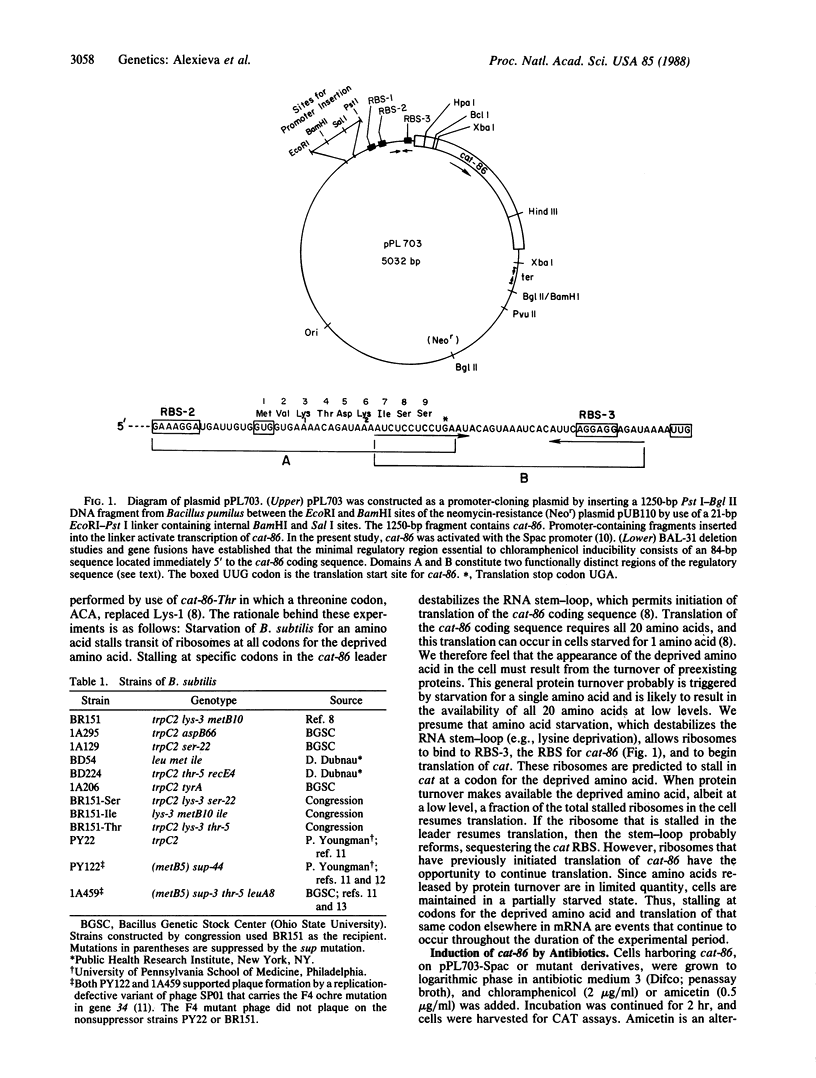
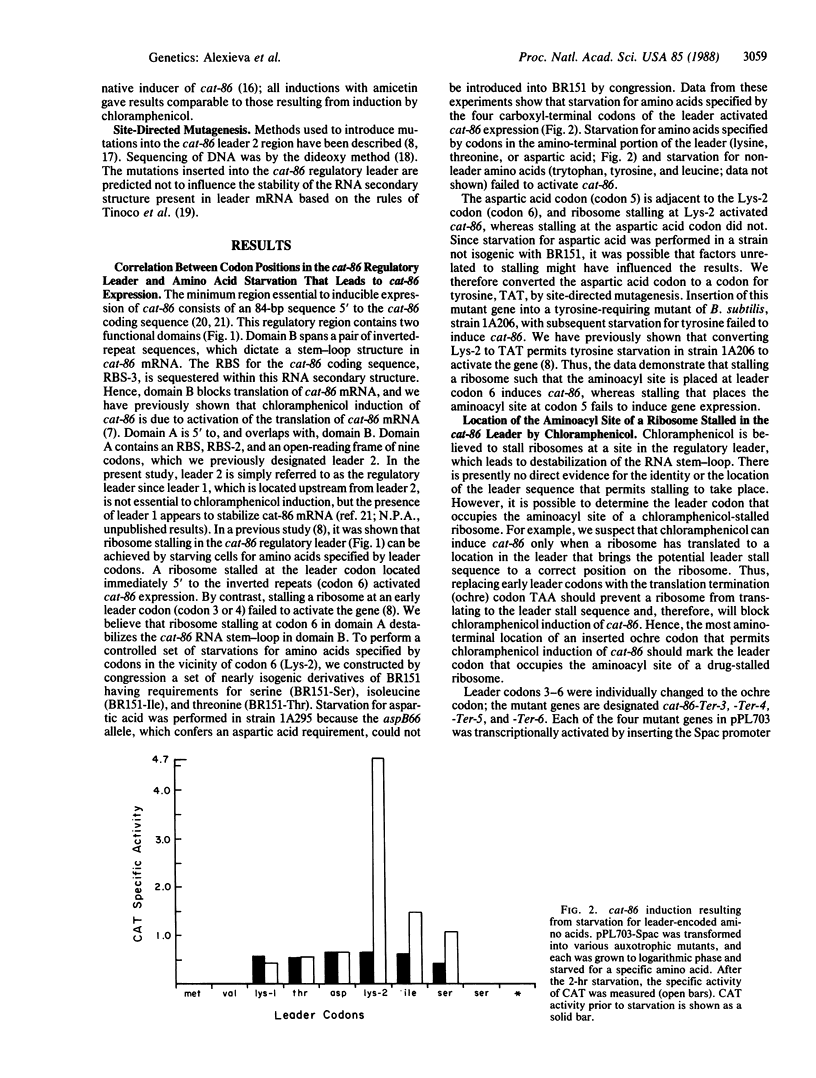
The plasmid gene cat-86 specifies chloramphenicol-inducible chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in Bacillus subtilis. Induction by the antibiotic is primarily due to activation of the translation of cat-86-encoded mRNA. It has been suggested that the inducer stalls ribosomes at a discrete location in the leader region of cat-86 mRNA, which causes the destabilization of a downstream RNA secondary structure that normally sequesters the cat-86 ribosome binding site. It is the destabilization of this RNA secondary structure that permits translation of the cat-86 coding sequence. In the present report, we show that ribosomes that were stalled in the cat-86 leader by starvation of host cells for the amino acid specified by leader codon 6 induced gene expression to a level above that detected when cells were starved for the amino acids specified by leader codons 7 and 8. Starvation for amino acids specified by leader codons 3, 4, or 5 failed to activate cat-86 expression. These results indicate that the stalled ribosome that is most active in cat-86 induction has its aminoacyl site occupied by leader codon 6. To determine if chloramphenicol also stalled ribosomes in the cat-86 regulatory leader such that the aminoacyl site was occupied by codon 6, we separately changed leader codons 3, 4, 5, and 6 to the translation termination (ochre) codon TAA. Each of the mutated genes was tested for its ability to be induced by chloramphenicol. The results show that replacement of leader codons 3, 4, or 5 by the ochre codon blocked induction, whereas replacement of leader codon 6 by the ochre codon permitted induction. Collectively, these observations lead to the conclusion that cat-86 induction requires ribosome stalling in leader mRNA, and they identify leader codon 6 as the codon most likely to be occupied by the aminoacyl site of a stalled ribosome that is active in the induction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambulos N. P., Jr, Duvall E. J., Lovett P. S. Analysis of the regulatory sequences needed for induction of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene cat-86 by chloramphenicol and amicetin. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):842–849. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.842-849.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brückner R., Dick T., Matzura H. Dependence of expression of an inducible Staphylococcus aureus cat gene on the translation of its leader sequence. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):486–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00331619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brückner R., Matzura H. Regulation of the inducible chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene of the Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pUB112. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2295–2300. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camacho A., Moreno F., Carrascosa J. L., Viñuela E., Salas M. A suppressor of nonsense mutations in Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Aug 15;47(1):199–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M., Brzustowicz L., Hannett N., Pero J. Bacteriophage SPO1 genes 33 and 34. Location and primary structure of genes encoding regulatory subunits of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):533–547. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D. Translational attenuation: the regulation of bacterial resistance to the macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B antibiotics. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;16(2):103–132. doi: 10.3109/10409238409102300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvall E. J., Ambulos N. P., Jr, Lovett P. S. Drug-free induction of a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in Bacillus subtilis by stalling ribosomes in a regulatory leader. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4235–4241. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4235-4241.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvall E. J., Lovett P. S. Chloramphenicol induces translation of the mRNA for a chloramphenicol-resistance gene in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3939–3943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvall E. J., Mongkolsuk S., Kim U. J., Lovett P. S., Henkin T. M., Chambliss G. H. Induction of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene cat-86 through the action of the ribosomal antibiotic amicetin: involvement of a Bacillus subtilis ribosomal component in cat induction. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):665–672. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.665-672.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Yanofsky C. Attenuation in amino acid biosynthetic operons. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:113–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellado R. P., Vinuela E., Salas M. Isolation of a strong suppressor of nonsense mutations in Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 17;65(1):213–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongkolsuk S., Ambulos N. P., Jr, Lovett P. S. Chloramphenicol-inducible gene expression in Bacillus subtilis is independent of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase structural gene and its promoter. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.1-8.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongkolsuk S., Chiang Y. W., Reynolds R. B., Lovett P. S. Restriction fragments that exert promoter activity during postexponential growth of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1399–1406. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1399-1406.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan C. S., Dubnau D. Evidence for the translational attenuation model: ribosome-binding studies and structural analysis with an in vitro run-off transcript of ermC. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7307–7326. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Caskey C. T. Peptide chain termination. V. The role of release factors in mRNA terminator codon recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1235–1241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase: enzymology and molecular biology. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983;14(1):1–46. doi: 10.3109/10409238309102789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivakumar A. G., Hahn J., Grandi G., Kozlov Y., Dubnau D. Posttranscriptional regulation of an erythromycin resistance protein specified by plasmic pE194. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yansura D. G., Henner D. J. Use of the Escherichia coli lac repressor and operator to control gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):439–443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


