Abstract
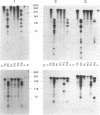
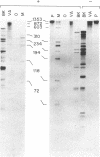
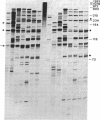
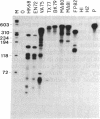
We have applied the RNase A mismatch cleavage method to analyze genetic variability in RNA viruses by using influenza virus as a model system. Uniformly labeled RNA probes synthesized from a cloned hemagglutinin gene of a given viral strain were hybridized to RNA isolated from other strains of characterized or uncharacterized genetic composition. The RNA.RNA heteroduplexes containing a variable number of base mismatches were digested with RNase A, and the resistant products were analyzed by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. We show that many of these single base mismatches are cleaved by RNase A, generating unique and characteristic patterns of resistant RNA fragments specific for each of the different viral strains. Comparative analysis of the cleavage patterns allows a qualitative estimation of the genetic relatedness and evolution of field strains. We also show that cleavage by RNase A at single base mismatches can readily detect and localize point mutations present in monoclonal antibody-resistant variants. This method should have wide applications in the study of RNA viruses, not only for epidemiological analysis but also in some diagnostic problems, such as characterization of phenotypic mutants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almond J. W., Stanway G., Cann A. J., Westrop G. D., Evans D. M., Ferguson M., Minor P. D., Spitz M., Schild G. C. New poliovirus vaccines: a molecular approach. Vaccine. 1984 Sep;2(3):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(84)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Sleigh M. J., Cox N. J., Kendal A. P. Antigenic drift in influenza virus H3 hemagglutinin from 1968 to 1980: multiple evolutionary pathways and sequential amino acid changes at key antigenic sites. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):52–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.52-60.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo E., Martínez-Salas E., Sobrino F., de la Torre J. C., Portela A., Ortín J., López-Galindez C., Pérez-Breña P., Villanueva N., Nájera R. The quasispecies (extremely heterogeneous) nature of viral RNA genome populations: biological relevance--a review. Gene. 1985;40(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester K., Almoguera C., Han K., Grizzle W. E., Perucho M. Detection of high incidence of K-ras oncogenes during human colon tumorigenesis. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):298–303. doi: 10.1038/327298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs R. A., Caskey C. T. Identification and localization of mutations at the Lesch-Nyhan locus by ribonuclease A cleavage. Science. 1987 Apr 17;236(4799):303–305. doi: 10.1126/science.3563511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J., Spindler K., Horodyski F., Grabau E., Nichol S., VandePol S. Rapid evolution of RNA genomes. Science. 1982 Mar 26;215(4540):1577–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.7041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Joklik W. K. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. II. Anomalous electrophoretic migration of certain hybrid RNA molecules composed of mutant plus strands and wild-type minus strands. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90360-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J. M., Naeve C. W., Webster R. G. Host cell-mediated variation in H3N2 influenza viruses. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):386–395. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90418-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. A., Guillen M., Sanchez-Fauquier A., Melero J. A. An antigen-binding assay to determine the specificity of monoclonal antibodies against influenza virus and mapping of epitopes. J Virol Methods. 1986 Jun;13(3):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(86)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Galindez C., Ortín J., Domingo E., del Rio L., Pérez-Breña P., Nájera R. Heterogeneity among influenza H3N2 isolates recovered during an outbreak. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1985;85(1-2):139–144. doi: 10.1007/BF01317013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Larin Z., Maniatis T. Detection of single base substitutions by ribonuclease cleavage at mismatches in RNA:DNA duplexes. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1242–1246. doi: 10.1126/science.4071043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortín J., Nájera R., López C., Dávila M., Domingo E. Genetic variability of Hong Kong (H3N2) influenza viruses: spontaneous mutations and their location in the viral genome. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):319–331. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin J. D., Moscona A., Pan W. T., Leider J. M., Palese P. Measurement of the mutation rates of animal viruses: influenza A virus and poliovirus type 1. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):377–383. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.377-383.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portela A., Melero J. A., Martínez C., Domingo E., Ortín J. Oriented synthesis and cloning of influenza virus nucleoprotein cDNA that leads to its expression in mammalian cells. Virus Res. 1985 Dec;4(1):69–82. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchey M. B., Palese P., Schulman J. L. Mapping of the influenza virus genome. III. Identification of genes coding for nucleoprotein, membrane protein, and nonstructural protein. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):307–313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.307-313.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. I., Parvin J. D., Palese P. Detection of single base substitutions in influenza virus RNA molecules by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of RNA-RNA or DNA-RNA heteroduplexes. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90265-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veres G., Gibbs R. A., Scherer S. E., Caskey C. T. The molecular basis of the sparse fur mouse mutation. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.3603027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Laver W. G., Air G. M., Schild G. C. Molecular mechanisms of variation in influenza viruses. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):115–121. doi: 10.1038/296115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter E., Yamamoto F., Almoguera C., Perucho M. A method to detect and characterize point mutations in transcribed genes: amplification and overexpression of the mutant c-Ki-ras allele in human tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7575–7579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Webster R. G., Gerhard W. U. Antigenic variation in three distinct determinants of an influenza type A haemagglutinin molecule. Nature. 1979 May 17;279(5710):246–248. doi: 10.1038/279246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]