Abstract
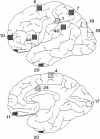
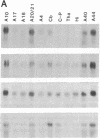
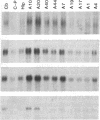
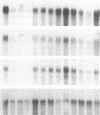
GAP-43 is a neuron-specific phosphoprotein that has been linked with the development and functional modulation of synaptic relationships. cDNAs for the human GAP-43 gene were used to reveal high overall levels of GAP-43 mRNA in a number of integrative areas of the neocortex, but low levels in cortical areas involved in the initial processing of sensory information, in several brainstem structures, and in caudate-putamen. Neurons expressing highest levels of GAP-43 mRNA were found by in situ hybridization to be concentrated in layer 2 of association cortex and in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Control studies showed that several other RNAs had regional distributions that were different from GAP-43, although the mRNA encoding the precursor of the Alzheimer amyloid beta protein followed a similar pattern of expression. These results suggest that a restricted subset of cortical and hippocampal neurons may be specialized for synaptic remodeling and might play a role in information storage in the human brain.
Full text
PDF

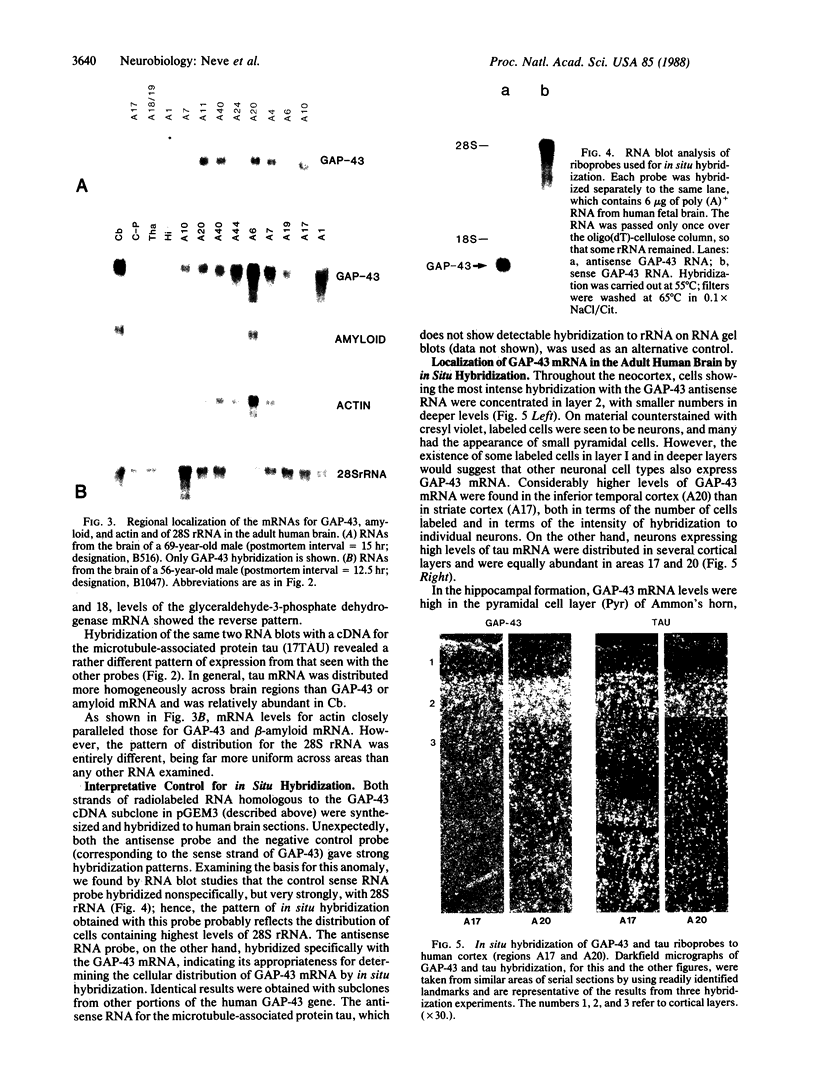


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akers R. F., Routtenberg A. Protein kinase C phosphorylates a 47 Mr protein (F1) directly related to synaptic plasticity. Brain Res. 1985 May 13;334(1):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basi G. S., Jacobson R. D., Virág I., Schilling J., Skene J. H. Primary structure and transcriptional regulation of GAP-43, a protein associated with nerve growth. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):785–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90616-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benowitz L. I., Apostolides P. J., Perrone-Bizzozero N., Finklestein S. P., Zwiers H. Anatomical distribution of the growth-associated protein GAP-43/B-50 in the adult rat brain. J Neurosci. 1988 Jan;8(1):339–352. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-01-00339.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benowitz L. I., Lewis E. R. Increased transport of 44,000- to 49,000-dalton acidic proteins during regeneration of the goldfish optic nerve: a two-dimensional gel analysis. J Neurosci. 1983 Nov;3(11):2153–2163. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-11-02153.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gispen W. H., Leunissen J. L., Oestreicher A. B., Verkleij A. J., Zwiers H. Presynaptic localization of B-50 phosphoprotein: the (ACTH)-sensitive protein kinase substrate involved in rat brain polyphosphoinositide metabolism. Brain Res. 1985 Mar 4;328(2):381–385. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson R. D., Virág I., Skene J. H. A protein associated with axon growth, GAP-43, is widely distributed and developmentally regulated in rat CNS. J Neurosci. 1986 Jun;6(6):1843–1855. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-06-01843.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolles J., Zwiers H., van Dongen C. J., Schotman P., Wirtz K. W., Gispen W. H. Modulation of brain polyphosphoinositide metabolism by ACTH-sensitive protein phosphorylation. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):623–625. doi: 10.1038/286623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karns L. R., Ng S. C., Freeman J. A., Fishman M. C. Cloning of complementary DNA for GAP-43, a neuronal growth-related protein. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):597–600. doi: 10.1126/science.2437653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F., Ellis L., Pfenninger K. H. Nerve growth cones isolated from fetal rat brain. III. Calcium-dependent protein phosphorylation. J Neurosci. 1985 Jun;5(6):1402–1411. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-06-01402.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H. Quantitative analysis of in situ hybridization methods for the detection of actin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1777–1799. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovinger D. M., Akers R. F., Nelson R. B., Barnes C. A., McNaughton B. L., Routtenberg A. A selective increase in phosporylation of protein F1, a protein kinase C substrate, directly related to three day growth of long term synaptic enhancement. Brain Res. 1985 Sep 16;343(1):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91167-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiri K. F., Pfenninger K. H., Willard M. B. Growth-associated protein, GAP-43, a polypeptide that is induced when neurons extend axons, is a component of growth cones and corresponds to pp46, a major polypeptide of a subcellular fraction enriched in growth cones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3537–3541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitani A., Shimokouchi M., Itoh K., Nomura S., Kudo M., Mizuno N. Morphology and laminar organization of electrophysiologically identified neurons in the primary auditory cortex in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 May 22;235(4):430–447. doi: 10.1002/cne.902350403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. B., Friedman D. P., O'Neill J. B., Mishkin M., Routtenberg A. Gradients of protein kinase C substrate phosphorylation in primate visual system peak in visual memory storage areas. Brain Res. 1987 Jul 28;416(2):387–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90924-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neve R. L., Perrone-Bizzozero N. I., Finklestein S., Zwiers H., Bird E., Kurnit D. M., Benowitz L. I. The neuronal growth-associated protein GAP-43 (B-50, F1): neuronal specificity, developmental regulation and regional distribution of the human and rat mRNAs. Brain Res. 1987 Jul;388(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(87)80012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neve R. L., Selkoe D. J., Kurnit D. M., Kosik K. S. A cDNA for a human microtubule associated protein 2 epitope in the Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangle. Brain Res. 1986 Nov;387(2):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(86)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oestreicher A. B., Gispen W. H. Comparison of the immunocytochemical distribution of the phosphoprotein B-50 in the cerebellum and hippocampus of immature and adult rat brain. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 11;375(2):267–279. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90747-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrone-Bizzozero N. I., Finklestein S. P., Benowitz L. I. Synthesis of a growth-associated protein by embryonic rat cerebrocortical neurons in vitro. J Neurosci. 1986 Dec;6(12):3721–3730. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-12-03721.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skene J. H., Willard M. Axonally transported proteins associated with axon growth in rabbit central and peripheral nervous systems. J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;89(1):96–103. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skene J. H., Willard M. Changes in axonally transported proteins during axon regeneration in toad retinal ganglion cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;89(1):86–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]