Abstract
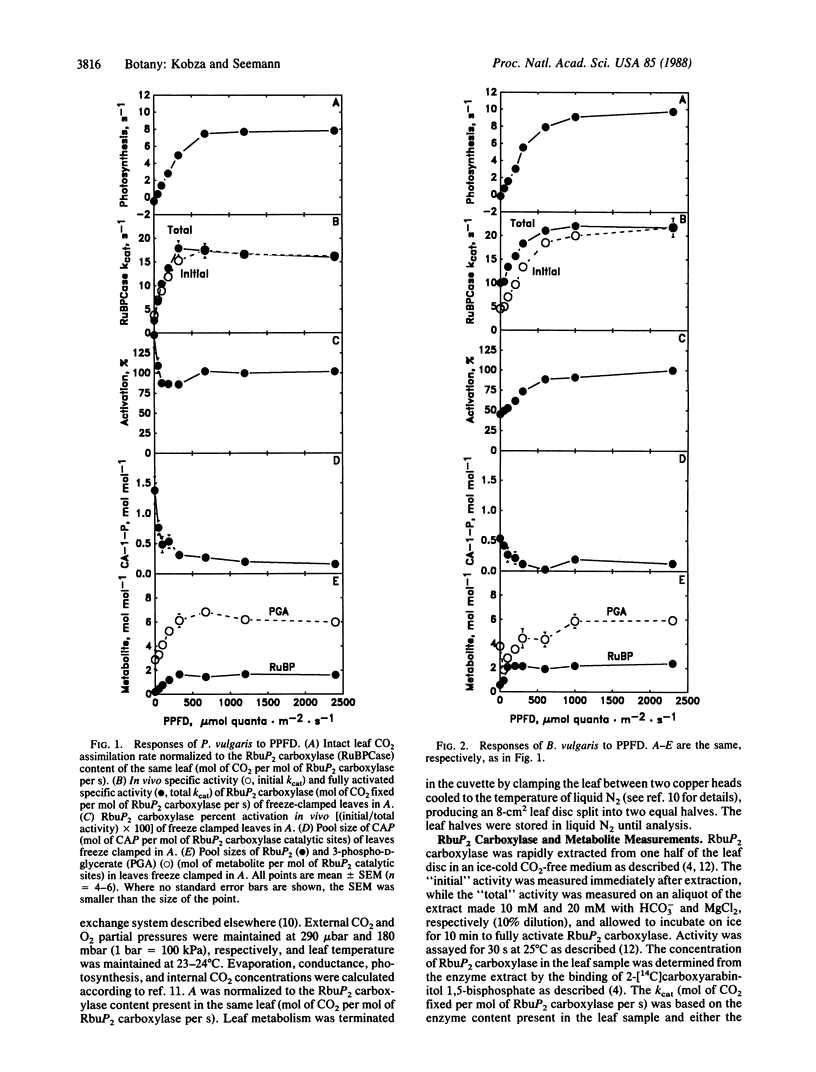
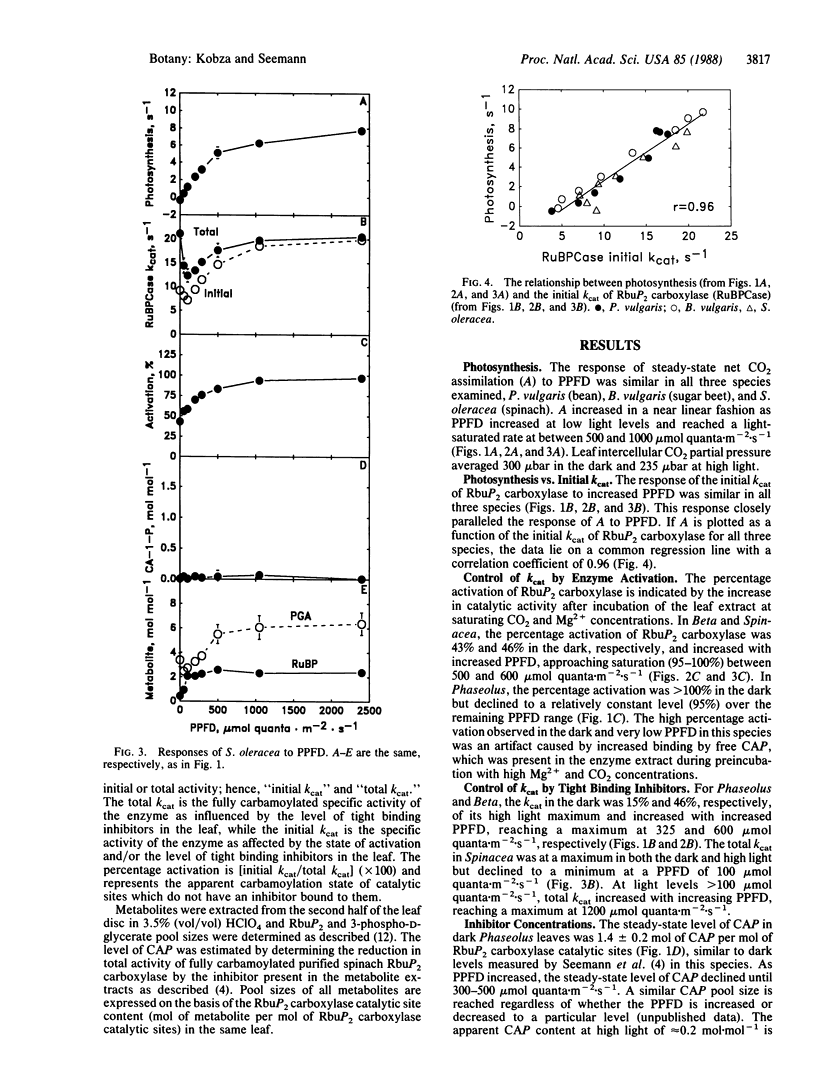
The mechanisms involved in the in vivo light-dependent regulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RbuP2) carboxylase [3-phospho-D-glycerate carboxy-lyase (dimerizing), EC 4.1.1.39] activity in intact leaves were studied. In the three species examined, Phaseolus vulgaris, Beta vulgaris, and Spinacea oleracea, the regulated level of RbuP2 carboxylase activity (assayed in vitro with saturating substrate) was highly correlated (r = 0.96) with the rate of net CO2 uptake of the corresponding leaves measured over a wide range of photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD). However, the mechanisms by which the enzyme was regulated differed between these species. In Phaseolus, the inhibitor 2-carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate (CAP) accounted for all of the PPFD-dependent regulation of RbuP2 carboxylase activity. A similar compound was detected in Beta, and changes in its concentration accounted for about half of the PPFD-dependent regulation of enzyme activity in this species. No CAP was detected in Spinacea, but evidence we obtained suggests that a different inhibitor (possibly RbuP2) accounts for a significant portion of the PPFD-dependent regulation of enzyme activity in this species. Changes in the activation state of the enzyme were observed with Beta and Spinacea, while in Phaseolus the enzyme was apparently fully activated at all PPFD levels. These results indicate that plant species may differ markedly in the mechanisms they use to regulate RbuP2 carboxylase activity as PPFD changes. The results also suggest that tight binding inhibitors are a more widespread mechanism for regulation of this enzyme than previously thought. Furthermore, the results establish the importance of such inhibitors in regulating both the activity of RbuP2 carboxylase and whole leaf photosynthesis over a range of PPFD.
Keywords: CO2 fixation, enzyme inhibitor, enzyme regulation, light
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry J. A., Lorimer G. H., Pierce J., Seemann J. R., Meek J., Freas S. Isolation, identification, and synthesis of 2-carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate, a diurnal regulator of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):734–738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar G. D. Models describing the kinetics of ribulose biphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Apr 1;193(2):456–468. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. B., Chollet R. Inhibition of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase by substrate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13752–13758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. The activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by carbon dioxide and magnesium ions. Equilibria, kinetics, a suggested mechanism, and physiological implications. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):529–536. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott K. A., Jensen R. G., O'leary J. W., Berry J. A. Photosynthesis and Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Concentrations in Intact Leaves of Xanthium strumarium L. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):968–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchorowicz J. T., Raynes D. A., Jensen R. G. Light limitation of photosynthesis and activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in wheat seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis A. R., Salvucci M. E., Ogren W. L. Activation of Ribulosebisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase at Physiological CO(2) and Ribulosebisphosphate Concentrations by Rubisco Activase. Plant Physiol. 1986 Dec;82(4):967–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.4.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvucci M. E., Anderson J. C. Factors affecting the activation state and the level of total activity of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in tobacco protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1987 Sep;85(1):66–71. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvucci M. E., Portis A. R., Ogren W. L. Light and CO(2) Response of Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase Activation in Arabidopsis Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1986 Mar;80(3):655–659. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.3.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvucci M. E., Werneke J. M., Ogren W. L., Portis A. R. Purification and species distribution of rubisco activase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jul;84(3):930–936. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Berry J. A., Freas S. M., Krump M. A. Regulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity in vivo by a light-modulated inhibitor of catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8024–8028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Sharkey T. D. Salinity and Nitrogen Effects on Photosynthesis, Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase and Metabolite Pool Sizes in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1986 Oct;82(2):555–560. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.2.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servaites J. C. Binding of a Phosphorylated Inhibitor to Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase during the Night. Plant Physiol. 1985 Aug;78(4):839–843. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.4.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servaites J. C., Parry M. A., Gutteridge S., Keys A. J. Species variation in the predawn inhibition of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Plant Physiol. 1986 Dec;82(4):1161–1163. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.4.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey T. D., Seemann J. R., Berry J. A. Regulation of Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase Activity in Response to Changing Partial Pressure of O(2) and Light in Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):788–791. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu J. C., Allen L. H., Bowes G. Dark/Light modulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity in plants from different photosynthetic categories. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):843–845. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


