Abstract
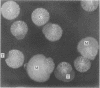
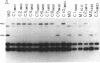
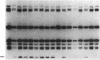
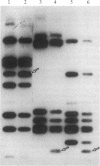
Production of extracellular polysaccharide by the marine bacterium Pseudomonas atlantica is a variable trait. Strains that produce extracellular polysaccharide (EPS+) have a mucoid colony phenotype, but during cultivation in the laboratory nonmucoid, EPS- variants arise that have a crenated colony morphology. This change is reversible since crenated variants rapidly switch to the original mucoid phenotype. We have cloned the locus (eps) controlling variable expression of EPS production by screening a recombinant cosmid library for clones that restore EPS production in the crenated variant. By using eps as a probe of genomic structure in variant strains, expression of EPS production was found to be controlled by a specific DNA rearrangement. Insertion of a 1.2-kilobase-pair DNA sequence in the eps locus results in EPS-, whereas excision of the sequence restores the EPS+ phenotype. Properties of the rearrangement suggest the involvement of a mobile genetic element. The possible significance of this DNA rearrangement to the survival of P. atlantica in the ocean is discussed.
Keywords: recombinant DNA, mobile genetic element
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. M., Freitag C. S., Clements J. R., Eisenstein B. I. An invertible element of DNA controls phase variation of type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5724–5727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed A., Bidwell K., Musso R. Internal rearrangements of IS2 in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):141–151. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas Robert, Bartlett Douglas, Silverman Michael. Cloning and Gene Replacement Mutagenesis of a Pseudomonas atlantica Agarase Gene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.30-37.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A., Krikos A., Simon M. Sensory transducers of E. coli are encoded by homologous genes. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:299–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Bagdasarian M., Feiss D., Franklin F. C., Deshusses J. Stable cosmid vectors that enable the introduction of cloned fragments into a wide range of gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R. Mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the influence of culture medium on the stability of mucus production. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):513–522. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Reed R. R. Transpositional recombination in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:863–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaer R., Pfeifer D., Starlinger P. IS4 is still found at its chromosomal site after transposition to galT. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;178(2):281–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00270473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson C. A., Jeanes A. A new modification of the carbazole analysis: application to heteropolysaccharides. Anal Biochem. 1968 Sep;24(3):470–481. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarter L. L., Silverman M. Phosphate regulation of gene expression in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3441–3449. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3441-3449.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., West M. A., Flynn J. L., Goldberg J. B. Method for gene replacement in Pseudomonas aeruginosa used in construction of recA mutants: recA-independent instability of alginate production. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1068–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1068-1074.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Bergström S., Robbins K., Barrera O., Corwin D., Koomey J. M. Gene conversion involving the pilin structural gene correlates with pilus+ in equilibrium with pilus- changes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90449-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlinger D. J., White D. C. Relationship Between Physiological Status and Formation of Extracellular Polysaccharide Glycocalyx in Pseudomonas atlantica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):64–70. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.64-70.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesper S. J. Production of Pili (Fimbriae) by Pseudomonas fluorescens and Correlation with Attachment to Corn Roots. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1397–1405. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1397-1405.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAPHE W. The use of agarase from Pseudomonas atlantica in the identification of agar in marine algae (Rhodophyceae). Can J Microbiol. 1957 Dec;3(7):987–993. doi: 10.1139/m57-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]