Abstract
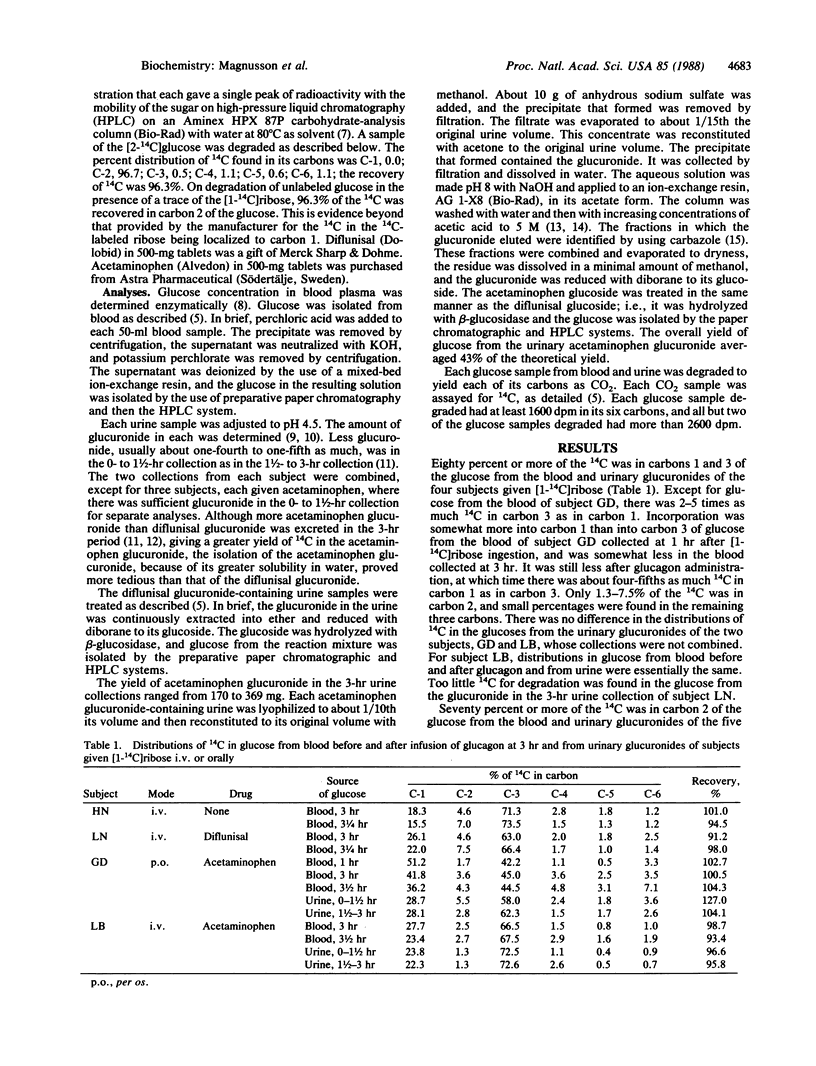
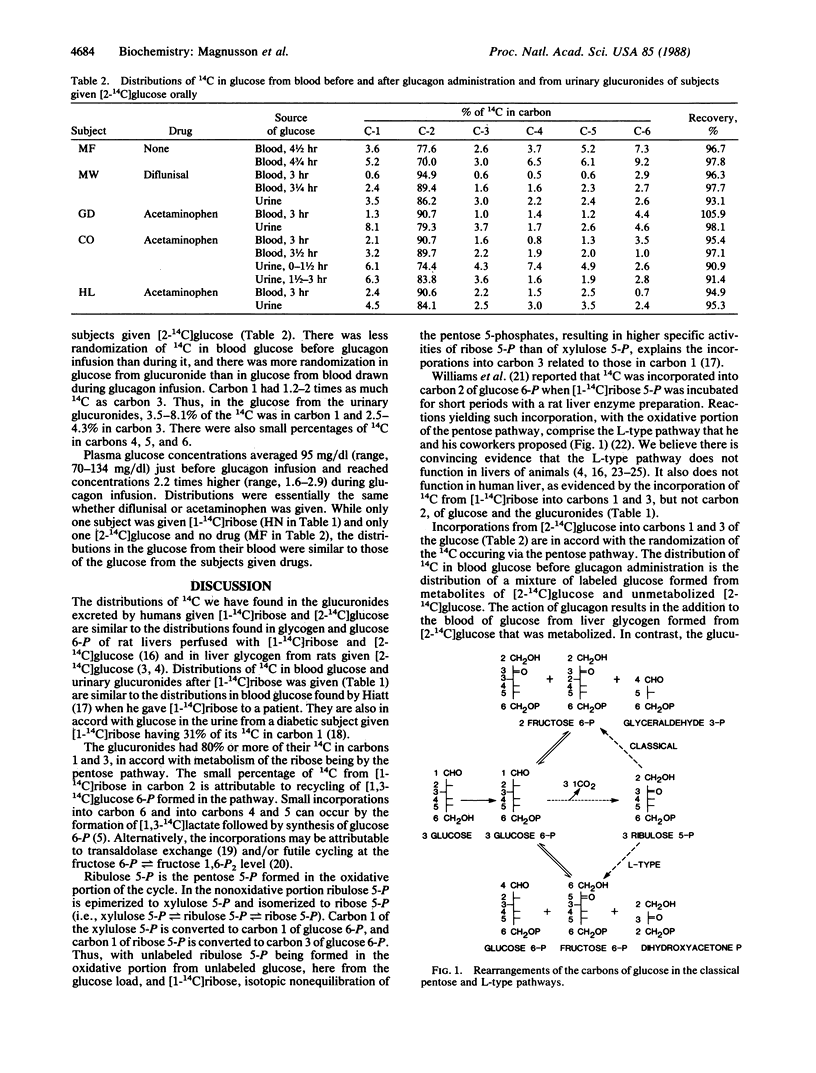
[1-14C]Ribose and [2-14C]glucose were given to normal subjects along with glucose loads (1 g per kg of body weight) after administration of diflunisal and acetaminophen, drugs that are excreted in urine as glucuronides. Distributions of 14C were determined in the carbons of the excreted glucuronides and in the glucose from blood samples drawn from hepatic veins before and after glucagon administration. Eighty percent or more of the 14C from [1-14C]ribose incorporated into the glucuronic acid moiety of the glucuronides was in carbons 1 and 3, with less than 8% in carbon 2. In glucuronic acid from glucuronide excreted when [2-14C]glucose was given, 3.5-8.1% of the 14C was in carbon 1, 2.5-4.3% in carbon 3, and more than 70% in carbon 2. These distributions are in accord with the glucuronides sampling the glucose unit of the glucose 6-phosphate pool that is a component of the pentose pathway and is intermediate in glycogen formation. It is concluded that the glucuronic acid conjugates of the drugs can serve as a noninvasive means of sampling hepatic glucose 6-phosphate. In human liver, as in animal liver, the classical pentose pathway functions, not the L-type pathway, and only a small percentage of the glucose is metabolized via the pathway.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen S. M., Rognstad R., Shulman R. G., Katz J. A comparison of 13C nuclear magnetic resonance and 14C tracer studies of hepatic metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3428–3432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings A. J., King M. L., Martin B. K. A kinetic study of drug elimination: the excretion of paracetamol and its metabolites in man. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Feb;29(2):150–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01948.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIATT H. H. Studies of ribose metabolism. III. The pathway of ribose carbon conversion to glucose in man. J Clin Invest. 1958 May;37(5):651–654. doi: 10.1172/JCI103649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORECKER B. L., MEHLER A. H. Carbohydrate metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1955;24:207–274. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.24.070155.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerstein M. K., Greenblatt D. J., Munro H. N. Glycoconjugates as noninvasive probes of intrahepatic metabolism: I. Kinetics of label incorporation with evidence of a common precursor UDP-glucose pool for secreted glycoconjugates. Metabolism. 1987 Oct;36(10):988–994. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandera P., Churácek J. Ion-exchange chromatography of carboxylic acids. J Chromatogr. 1973 Nov 21;86(2):351–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung D., Zafar N. U. Micro high-performance liquid chromatographic assay of acetaminophen and its major metabolites in plasma and urine. J Chromatogr. 1985 Apr 12;339(1):198–202. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84644-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Rognstad R. Futile cycles in the metabolism of glucose. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;10:237–289. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152810-2.50013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau B. R., Bartsch G. E. Estimations of pathway contributions to glucose metabolism and the transaldolase reactions. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):741–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson I., Chandramouli V., Schumann W. C., Kumaran K., Wahren J., Landau B. R. Quantitation of the pathways of hepatic glycogen formation on ingesting a glucose load. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1748–1754. doi: 10.1172/JCI113267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris M. E., Levy G. Renal clearance and serum protein binding of acetaminophen and its major conjugates in humans. J Pharm Sci. 1984 Aug;73(8):1038–1041. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600730806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musson D. G., Lin J. H., Lyon K. A., Tocco D. J., Yeh K. C. Assay methodology for quantification of the ester and ether glucuronide conjugates of diflunisal in human urine. J Chromatogr. 1985 Feb 8;337(2):363–378. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(85)80049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziuk J. Sources of carbon in hepatic glycogen synthesis during absorption of an oral glucose load in humans. Fed Proc. 1982 Jan;41(1):110–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rognstad R., Wals P., Katz J. Further evidence for the classical pentose phosphate cycle in the liver. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):851–855. doi: 10.1042/bj2080851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEGAL S., FOLEY J. The metabolism of D-ribose in man. J Clin Invest. 1958 May;37(5):719–735. doi: 10.1172/JCI103658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scofield R. F., Kosugi K., Chandramouli V., Kumaran K., Schumann W. C., Landau B. R. The nature of the pentose pathway in liver. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15439–15444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrago E., Glennon J. A., Gordon E. S. Comparative aspects of lipogenesis in mammalian tissues. Metabolism. 1971 Jan;20(1):54–62. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegers C. P., Loeser W., Gieselmann J., Oltmanns D. Biliary and renal excretion of paracetamol in man. Pharmacology. 1984;29(5):301–303. doi: 10.1159/000138026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocco D. J., Breault G. O., Zacchei A. G., Steelman S. L., Perrier C. V. Physiological disposition and metabolism of 5-(2',4'-difluorophenyl)salicyclic acid, a new salicylate. Drug Metab Dispos. 1975 Nov-Dec;3(6):453–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD H. G., KATZ J., LANDAU B. R. ESTIMATION OF PATHWAYS OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM. Biochem Z. 1963;338:809–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. F., Arora K. K., Longenecker J. P. The pentose pathway: a random harvest. Impediments which oppose acceptance of the classical (F-type) pentose cycle for liver, some neoplasms and photosynthetic tissue. The case for the L-type pentose pathway. Int J Biochem. 1987;19(9):749–817. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(87)90239-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. F., Clark M. G., Blackmore P. F. The fate of 14C in glucose 6-phosphate synthesized from [1-14C]Ribose 5-phosphate by enzymes of rat liver. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 15;176(1):241–256. doi: 10.1042/bj1760241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


