Abstract
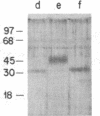
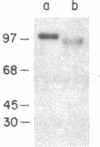
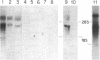
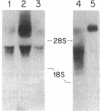
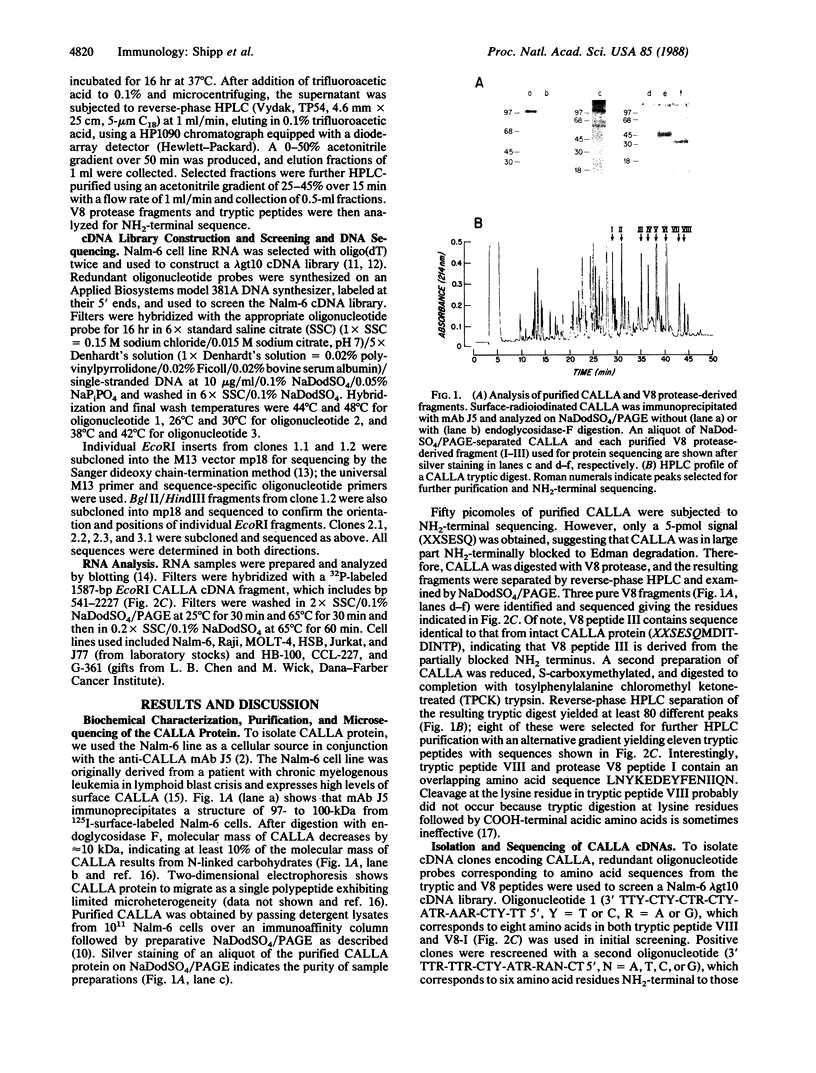
Common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA) is a 100-kDa cell-surface glycoprotein expressed on most acute lymphoblastic leukemias and certain other immature lymphoid malignancies and on normal lymphoid progenitors. The latter are either uncommitted to B- or T-cell lineage or committed to only the earliest stages of B- or T-lymphocyte maturation. To elucidate to homogeneity, obtained the NH2-terminal sequence from both the intact protein and derived tryptic and V8 protease peptides and isolated CALLA cDNAs from a Nalm-6 cell line lambda gt10 library using redundant oligonucleotide probes. The CALLA cDNA sequence predicts a 750-amino acid integral membrane protein with a single 24-amino acid hydrophobic segment that could function as both a transmembrane region and a signal peptide. The COOH-terminal 700 amino acids, including six potential N-linked glycosylation sites compose the extracellular protein segment, whereas the 25 NH2-terminal amino acids remaining after cleavage of the initiation methionine form the cytoplasmic tail. CALLA+ cells contain CALLA transcripts of 2.7 to 5.7 kilobases with the major 5.7- and 3.7-kilobase mRNAs being preferentially expressed in specific cell types.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun M. P., Martin P. J., Ledbetter J. A., Hansen J. A. Granulocytes and cultured human fibroblasts express common acute lymphoblastic leukemia-associated antigens. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):718–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catt K. J., Harwood J. P., Aguilera G., Dufau M. L. Hormonal regulation of peptide receptors and target cell responses. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):109–116. doi: 10.1038/280109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Wang J. L., Berggård I., Peterson P. A. The complete amino acid sequence of beta 2-microglobulin. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4811–4822. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabbi M., Acuto O., Smart J. E., Reinherz E. L. Homology of Ti alpha-subunit of a T-cell antigen-MHC receptor with immunoglobulin. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):269–271. doi: 10.1038/312269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Brown G., Rapson N. T., Lister T. A. Antisera to acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 May;4(1):67–84. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Hariri G., Newman R. A., Sutherland D. R., Ritter M. A., Ritz J. Selective expression of the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia (gp 100) antigen on immature lymphoid cells and their malignant counterparts. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):628–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann-Fezer G., Knapp W., Thierfelder S. Anatomical distribution of call antigen expressing cells in normal lymphatic tissue and in lymphomas. Leuk Res. 1982;6(6):761–767. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(82)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokland P., Nadler L. M., Griffin J. D., Schlossman S. F., Ritz J. Purification of common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen positive cells from normal human bone marrow. Blood. 1984 Sep;64(3):662–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokland P., Rosenthal P., Griffin J. D., Nadler L. M., Daley J., Hokland M., Schlossman S. F., Ritz J. Purification and characterization of fetal hematopoietic cells that express the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA). J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):114–129. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland E. C., Leung J. O., Drickamer K. Rat liver asialoglycoprotein receptor lacks a cleavable NH2-terminal signal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7338–7342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker W., Spiess M., Semenza G., Lodish H. F. The sucrase-isomaltase complex: primary structure, membrane-orientation, and evolution of a stalked, intrinsic brush border protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90739-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz R., Hozier J., LeBien T., Minowada J., Gajl-Peczalska K., Kubonishi I., Kersey J. Characterization of a leukemic cell line of the pre-B phenotype. Int J Cancer. 1979 Feb;23(2):174–180. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hütteroth T. H., Cleve H., Litwin S. D. Modulation of membrane associated immunoglobulins of cultured human lymphoid cells by specific antibody. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1325–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating A., Whalen C. K., Singer J. W. Cultured marrow stromal cells express common acute lymphoblastic leukaemia antigen (CALLA): implications for marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol. 1983 Dec;55(4):623–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack R. T., Nelson R. D., LeBien T. W. Structure/function studies of the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA/CD10) expressed on human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):1075–1082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzgar R. S., Borowitz M. J., Jones N. H., Dowell B. L. Distribution of common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen in nonhematopoietic tissues. J Exp Med. 1981 Oct 1;154(4):1249–1254. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.4.1249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Dobkin C., Spiegelman S. RNA primer used in synthesis of anticomplementary DNA by reverse transcriptase of avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1316–1320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neudorf S. M., LeBien T. W., Kersey J. H. Characterization of thymocytes expressing the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen. Leuk Res. 1984;8(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(84)90140-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman R. A., Sutherland R., Greaves M. F. The biochemical characterization of a cell surface antigen associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphocyte precursors. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):2024–2030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesando J. M., Tomaselli K. J., Lazarus H., Schlossman S. F. Distribution and modulation of a human leukemia-associated antigen (CALLA). J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):2038–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph W. W., Webster T., Smith T. F. A modified Chou and Fasman protein structure algorithm. Comput Appl Biosci. 1987 Sep;3(3):211–216. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/3.3.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Meuer S., Fitzgerald K. A., Hussey R. E., Levine H., Schlossman S. F. Antigen recognition by human T lymphocytes is linked to surface expression of the T3 molecular complex. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):735–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz J., Pesando J. M., Notis-McConarty J., Lazarus H., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody to human acute lymphoblastic leukaemia antigen. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):583–585. doi: 10.1038/283583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz J., Pesando J. M., Notis-McConarty J., Schlossman S. F. Modulation of human acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen induced by monoclonal antibody in vitro. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1506–1514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayre P. H., Chang H. C., Hussey R. E., Brown N. R., Richardson N. E., Spagnoli G., Clayton L. K., Reinherz E. L. Molecular cloning and expression of T11 cDNAs reveal a receptor-like structure on human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2941–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. T., Lodish H. F. Multiple mechanisms of protein insertion into and across membranes. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):400–407. doi: 10.1126/science.4048938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]