Abstract
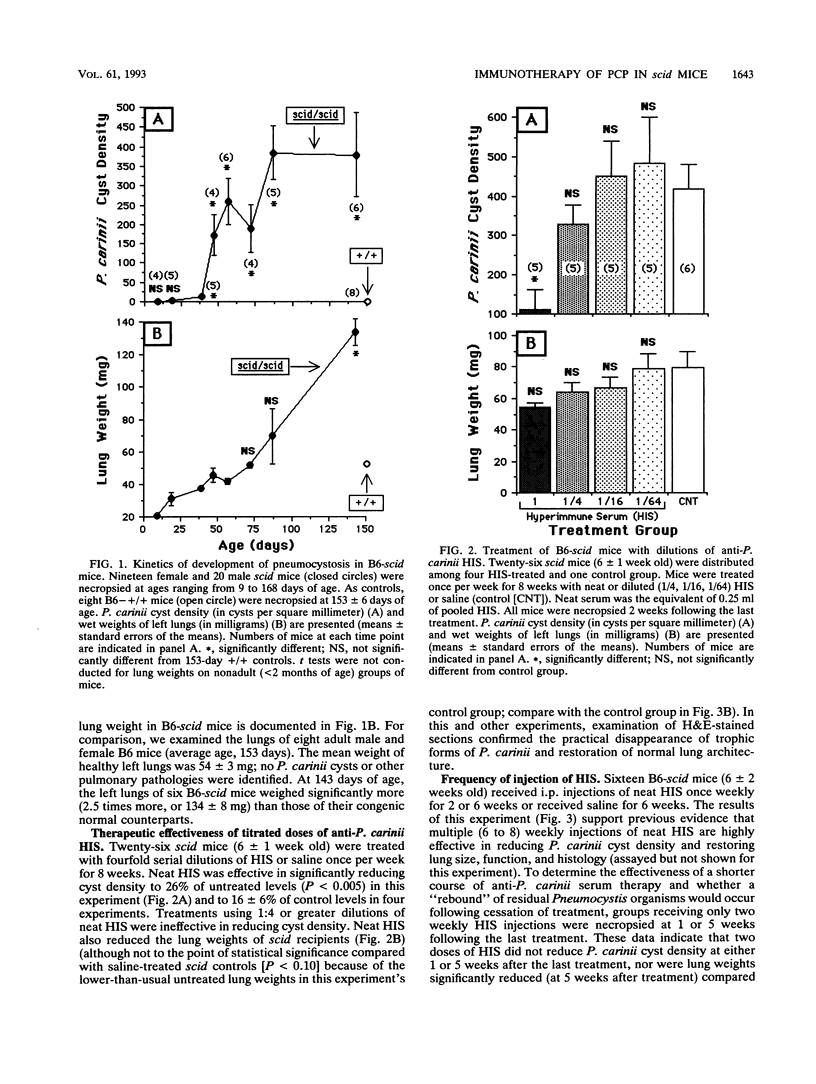
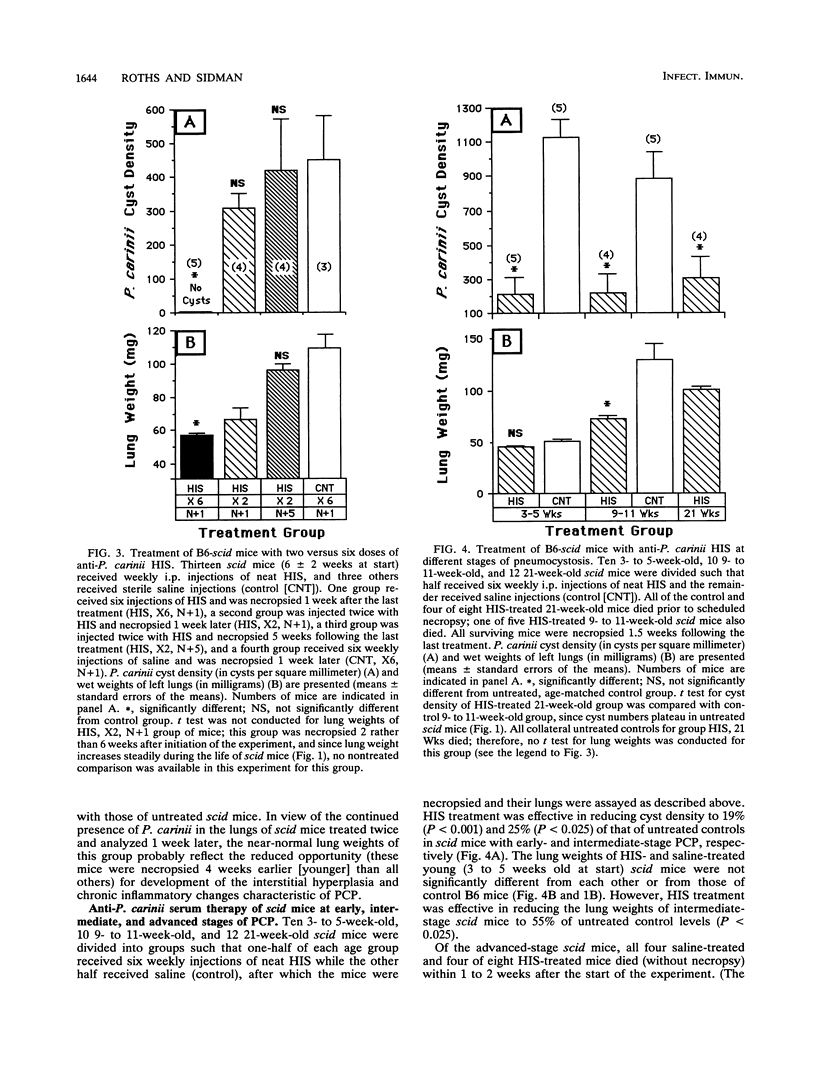
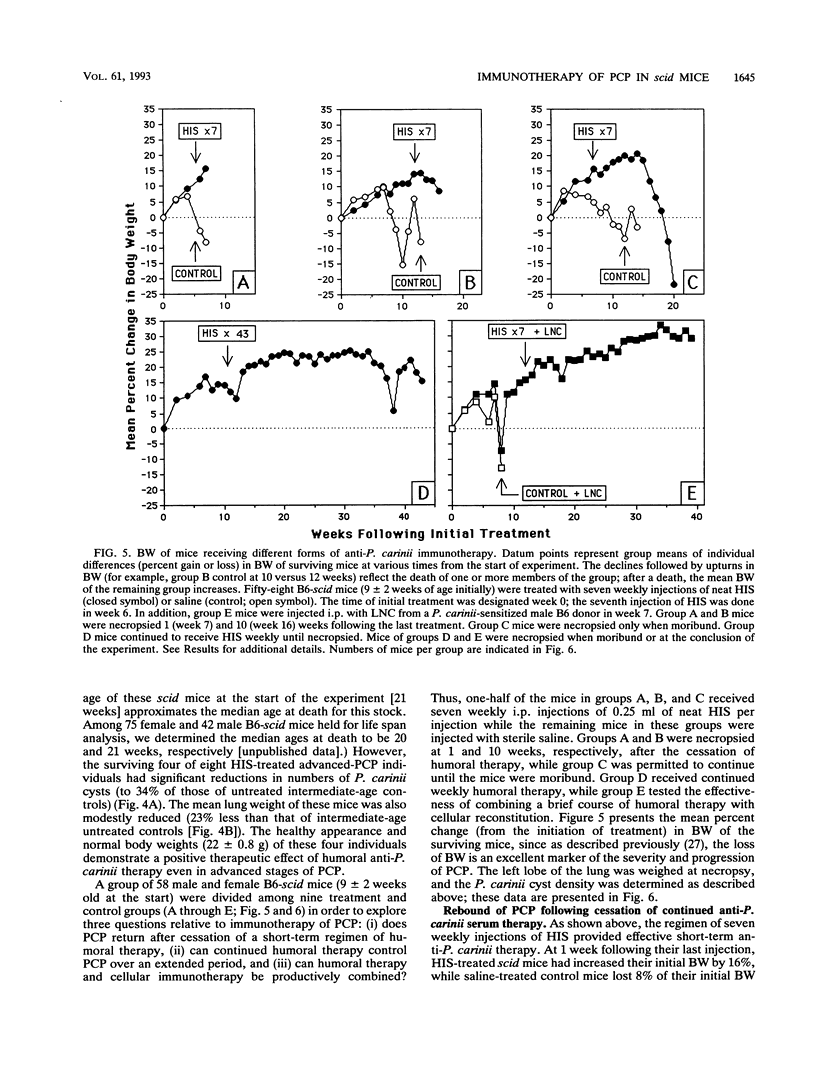
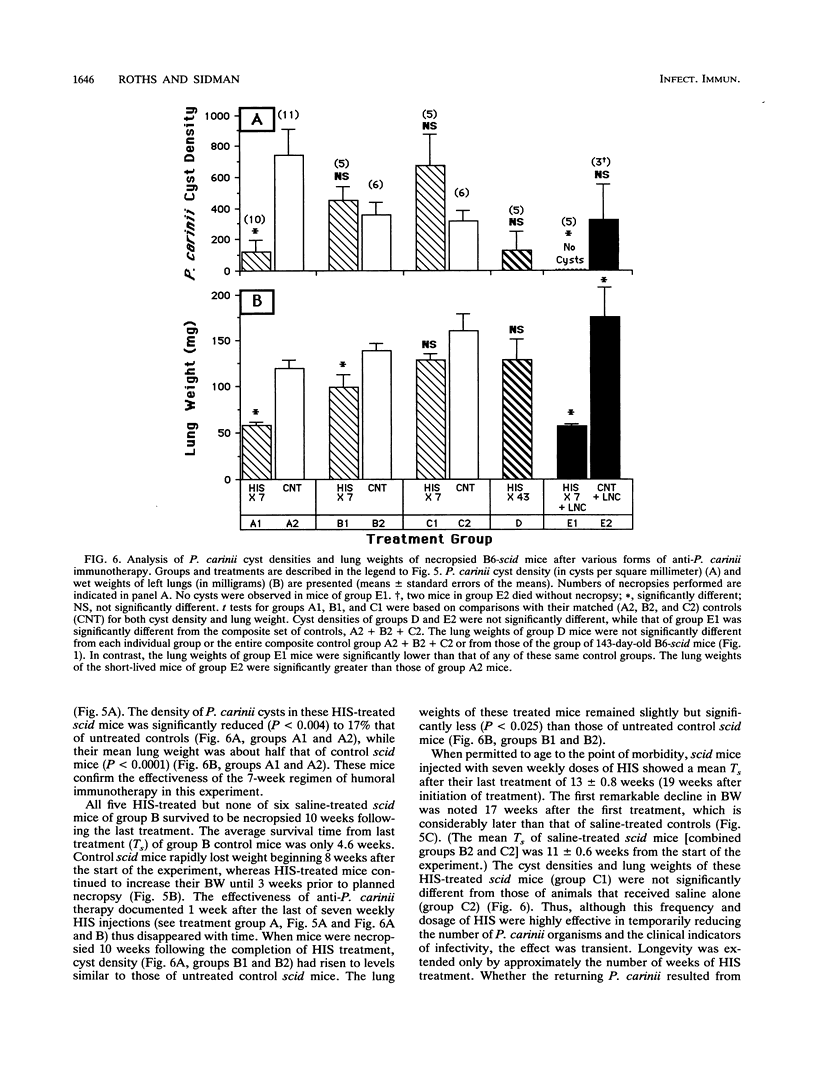
Homozygous mutant scid/scid (severe combined immunodeficiency) mice (referred to as scid mice) lack both specific humoral and cell-mediated immune functions and are exemplary in vivo models for analysis of host-parasite relationships. In our colony, scid mice routinely and predictably develop spontaneous Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP) with high morbidity. Previous studies have identified both T cells (specifically, CD4+ cells) and antibody as independent mechanisms of effective anti-P. carinii resistance; however, CD4+ T cells also cause an often fatal hyperinflammatory reaction. The current study has explored the optimal application of these immune components for conferring protection against P. carinii. Anti-P. carinii hyperimmune serum was highly effective at reducing the number of P. carinii organisms in early, intermediate, and advanced stages of PCP and was capable of increasing the mean life expectancy of P. carinii-infected scid mice by more than threefold if provided on a continuing basis. When a short course of hyperimmune-serum therapy was provided prior to transfer of P. carinii-sensitized normal lymphocytes, scid mice were rendered permanently free of P. carinii without the pathological sequelae of the hyperinflammatory reaction. These findings are discussed in the contexts of mechanism and clinical relevance.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bancroft G. J., Schreiber R. D., Bosma G. C., Bosma M. J., Unanue E. R. A T cell-independent mechanism of macrophage activation by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1104–1107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma G. C., Custer R. P., Bosma M. J. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):527–530. doi: 10.1038/301527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns S. M., Read J. A., Yap P. L., Brettle R. P. Reduced concentrations of IgG antibodies to Pneumocystis carinii in HIV-infected patients during active Pneumocystis carinii infection and the possibility of passive immunisation. J Infect. 1990 Jan;20(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(90)92280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czitrom A. A., Edwards S., Phillips R. A., Bosma M. J., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. The function of antigen-presenting cells in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2276–2280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorshkind K., Keller G. M., Phillips R. A., Miller R. G., Bosma G. C., O'Toole M., Bosma M. J. Functional status of cells from lymphoid and myeloid tissues in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency disease. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1804–1808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorshkind K., Pollack S. B., Bosma M. J., Phillips R. A. Natural killer (NK) cells are present in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency (scid). J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3798–3801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta T., Ueda K., Fujiwara K. Experimental Pneumocystis carinii infection in nude rats. Jpn J Exp Med. 1984 Apr;54(2):65–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta T., Ueda K., Fujiwara K., Yamanouchi K. Cellular and humoral immune responses of mice subclinically infected with Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):544–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.544-548.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Hughes W. T. Passive immunoprophylaxis with specific monoclonal antibody confers partial protection against Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in animal models. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1666–1668. doi: 10.1172/JCI113503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordin F. M., Simon G. L., Wofsy C. B., Mills J. Adverse reactions to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Apr;100(4):495–499. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-4-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. S., Schroff R., Schanker H. M., Weisman J. D., Fan P. T., Wolf R. A., Saxon A. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and mucosal candidiasis in previously healthy homosexual men: evidence of a new acquired cellular immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1425–1431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradus M. S., Ivey M. H. An improved method of isolating Pneumocystis carinii from infected rat lungs. J Parasitol. 1986 Oct;72(5):690–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith B. P., Kormos R. L., Armitage J. M., Dummer J. S., Hardesty R. L. Comparative trial of immunoprophylaxis with RATG versus OKT3. J Heart Transplant. 1990 May-Jun;9(3 Pt 2):301–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Feldman S., Aur R. J., Verzosa M. S., Hustu H. O., Simone J. V. Intensity of immunosuppressive therapy and the incidence of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Cancer. 1975 Dec;36(6):2004–2009. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820360912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Price R. A., Kim H. K., Coburn T. P., Grigsby D., Feldman S. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in children with malignancies. J Pediatr. 1973 Mar;82(3):404–415. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Price R. A., Sisko F., Havron W. S., Kafatos A. G., Schonland M., Smythe P. M. Protein-calorie malnutrition. A host determinant for Pneumocystis carinii infection. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Jul;128(1):44–52. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110260046008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Masur H. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: therapy and prophylaxis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):254–259. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Michelis M. A., Greene J. B., Onorato I., Stouwe R. A., Holzman R. S., Wormser G., Brettman L., Lange M., Murray H. W. An outbreak of community-acquired Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: initial manifestation of cellular immune dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1431–1438. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H., Tauber I., Leeuwenberg A. D., Beckers P. J., Sieben M. Parasitologic and serologic observations of infection with Pneumocystis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. B., Mojon M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay compared with indirect immunofluorescence test for detection of Pneumocystis carinii specific immunoglobulins G, M, and A. APMIS. 1988 Jul;96(7):649–654. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1988.tb00924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peglow S. L., Smulian A. G., Linke M. J., Pogue C. L., Nurre S., Crisler J., Phair J., Gold J. W., Armstrong D., Walzer P. D. Serologic responses to Pneumocystis carinii antigens in health and disease. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):296–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roths J. B., Marshall J. D., Allen R. D., Carlson G. A., Sidman C. L. Spontaneous Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in immunodeficient mutant scid mice. Natural history and pathobiology. Am J Pathol. 1990 May;136(5):1173–1186. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roths J. B., Sidman C. L. Both immunity and hyperresponsiveness to Pneumocystis carinii result from transfer of CD4+ but not CD8+ T cells into severe combined immunodeficiency mice. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):673–678. doi: 10.1172/JCI115910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelhamer J. H., Ognibene F. P., Macher A. M., Tuazon C., Steiss R., Longo D., Kovacs J. A., Parker M. M., Natanson C., Lane H. C. Persistence of Pneumocystis carinii in lung tissue of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients treated for pneumocystis pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Dec;130(6):1161–1165. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.6.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E. Humoral immunity in experimental Pneumocystis carinii infection. I. Serum and bronchial lavage fluid antibody responses in rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Jun;97(6):820–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E. Serum antibody responses to Pneumocystis carinii among different strains of normal and athymic mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):620–626. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.620-626.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E., Yoneda K. Experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in C3H/HeJ and C3HeB/FeJ mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Jan;33(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Schnelle V., Armstrong D., Rosen P. P. Nude mouse: a new experimental model for Pneumocystis carinii infection. Science. 1977 Jul 8;197(4299):177–179. doi: 10.1126/science.301657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Schultz M. G., Western K. A., Robbins J. B. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and primary immune deficiency diseases of infancy and childhood. J Pediatr. 1973 Mar;82(3):416–422. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J. M., Coleman D. L., Wofsy C. B., Luce J. M., Blumenfeld W., Hadley W. K., Ingram-Drake L., Volberding P. A., Hopewell P. C. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or pentamidine for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A prospective randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Jul;105(1):37–44. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde H., Chomchey P., Punyaratabandhu P., Phanupak P., Chutivongse S. Purified equine rabies immune globulin: a safe and affordable alternative to human rabies immune globulin. Bull World Health Organ. 1989;67(6):731–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


