Abstract
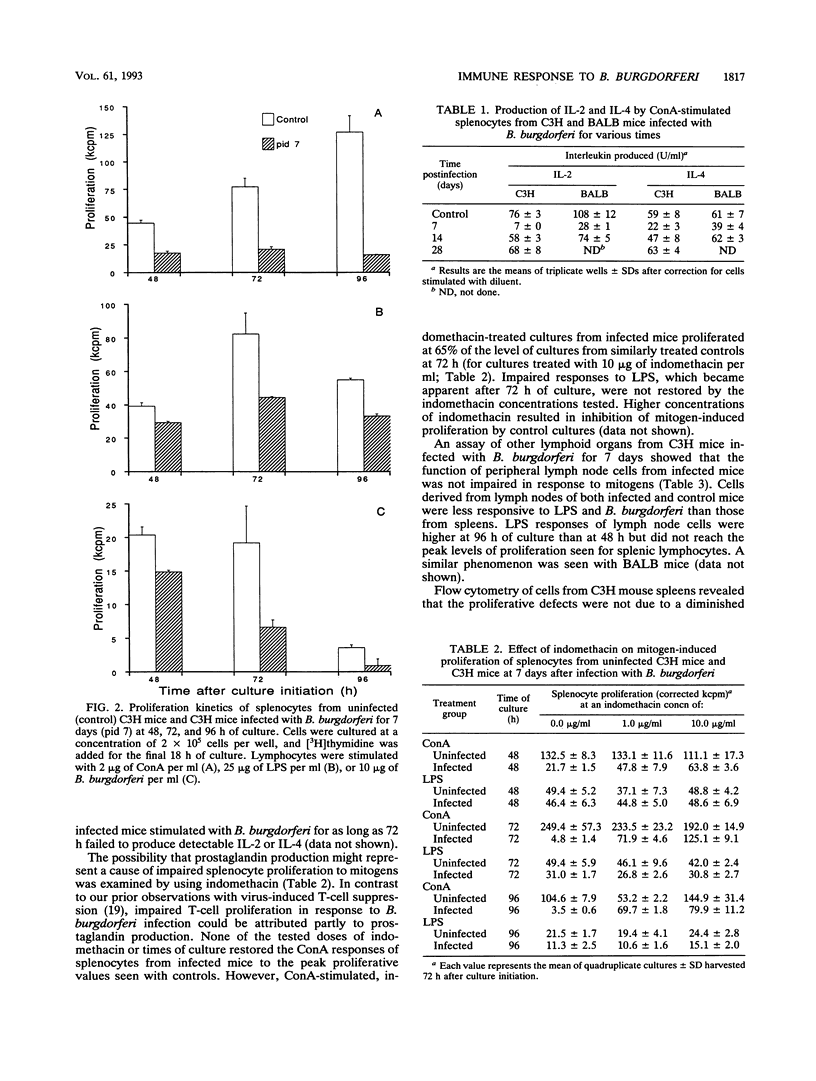
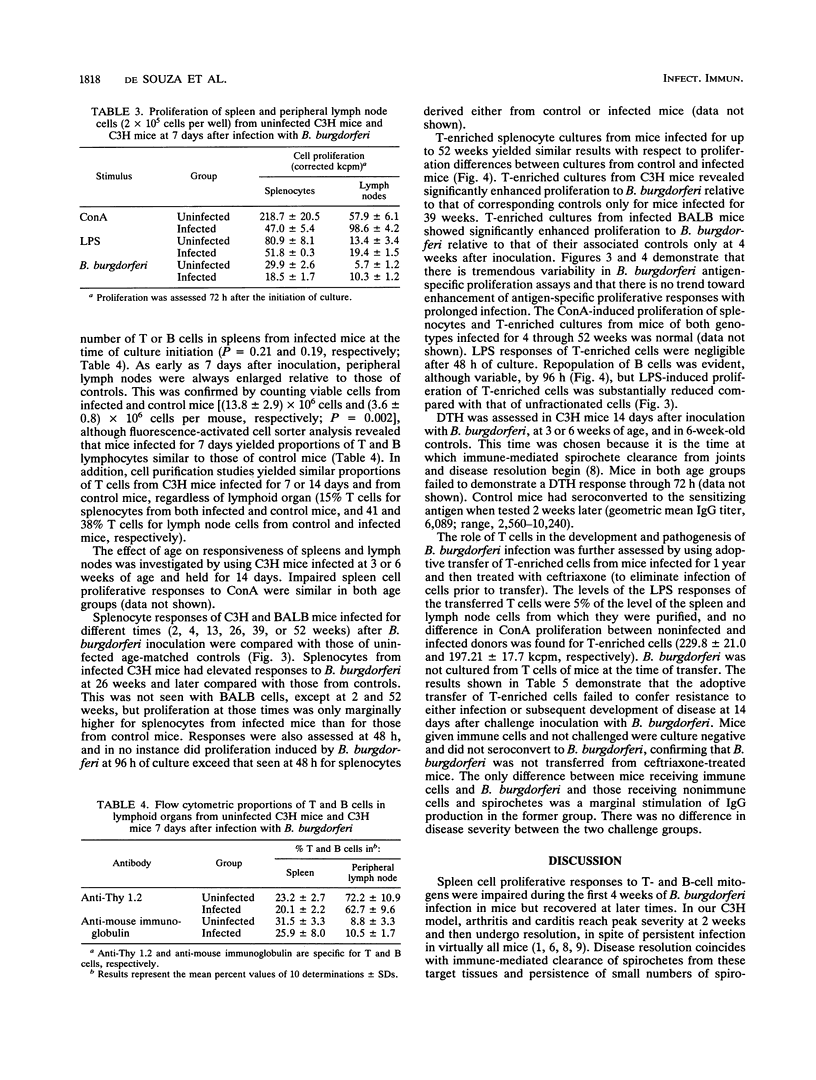
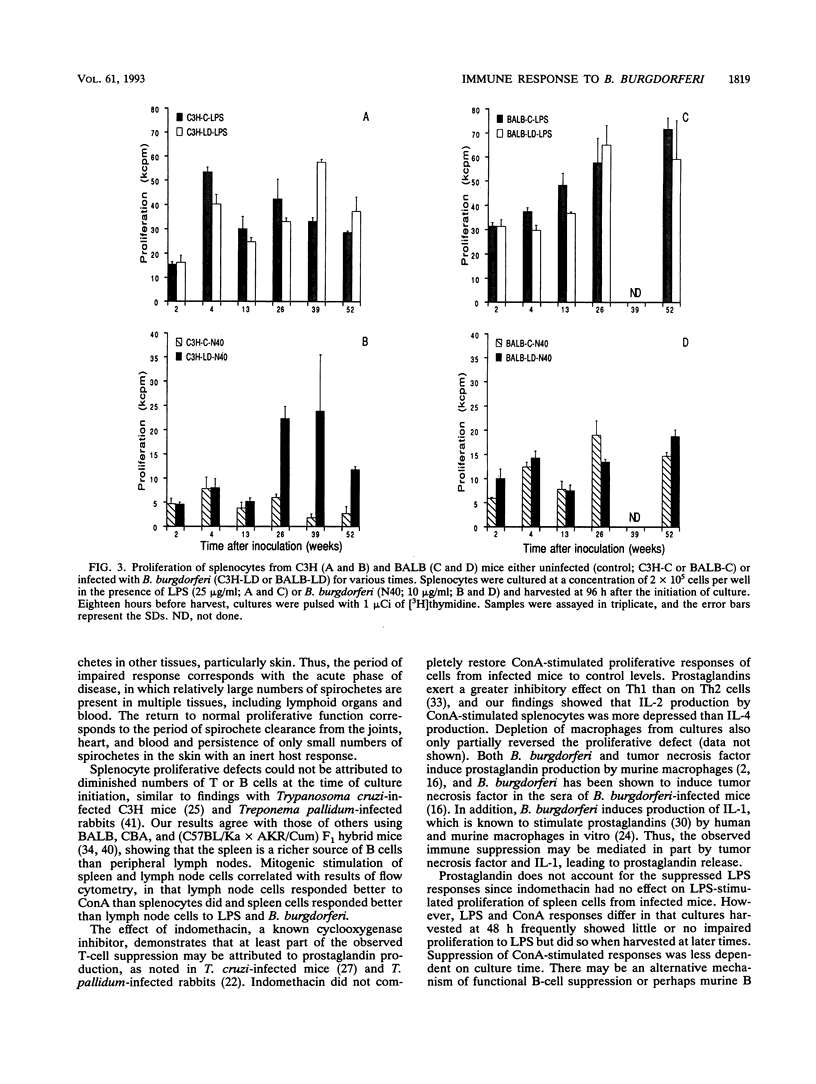
Borrelia burgdorferi infection of disease-susceptible (C3H) and -resistant (BALB) mice resulted in impaired proliferation to both T- and B-cell mitogens up to 30 days after inoculation. Interleukin-2 and -4 production was also impaired, paralleling the T-cell response to concanavalin A. Impaired lymphocyte proliferation could not be attributed to diminished numbers of T or B cells and was found to depend on the lymphoid organ (spleen or lymph node) examined. Prostaglandin production accounted for part of this immune dysfunction. Attempts to assess antigen-specific proliferation to B. burgdorferi were inconsistent, and delayed-type hypersensitivity responses were not detected. Adoptive transfer of T-enriched cells from chronically infected donors failed to prevent infection and disease development in recipient C3H mice. The current study emphasizes caution in the study of B. burgdorferi antigen-specific assays and argues against the role of a vigorous T-cell response in Lyme borreliosis in infected laboratory mice.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong A. L., Barthold S. W., Persing D. H., Beck D. S. Carditis in Lyme disease susceptible and resistant strains of laboratory mice infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Aug;47(2):249–258. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.47.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachwich P. R., Chensue S. W., Larrick J. W., Kunkel S. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates interleukin-1 and prostaglandin E2 production in resting macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):94–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90881-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Beck D. S., Hansen G. M., Terwilliger G. A., Moody K. D. Lyme borreliosis in selected strains and ages of laboratory mice. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):133–138. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W. Infectivity of Borrelia burgdorferi relative to route of inoculation and genotype in laboratory mice. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):419–420. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Moody K. D., Terwilliger G. A., Jacoby R. O., Steere A. C. An animal model for Lyme arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:264–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Persing D. H., Armstrong A. L., Peeples R. A. Kinetics of Borrelia burgdorferi dissemination and evolution of disease after intradermal inoculation of mice. Am J Pathol. 1991 Aug;139(2):263–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Sidman C. L., Smith A. L. Lyme borreliosis in genetically resistant and susceptible mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Nov;47(5):605–613. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.47.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Coleman J. L., Garcia-Monco J. C., Deponte P. C. Biological activity of Borrelia burgdorferi antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:115–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham D. S., Benavides G. R., Kuhn R. E. Suppression of mitogen-induced blastogenesis by the Trypanosoma cruzi-induced suppressor substance. J Parasitol. 1980 Oct;66(5):722–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham D. S., Kuhn R. E. Trypanosoma cruzi-induced suppression of the primary immune response in murine cell cultures to T-cell-dependent and -independent antigens. J Parasitol. 1980 Feb;66(1):16–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattwyler R. J., Thomas J. A., Benach J. L., Golightly M. G. Cellular immune response in Lyme disease: the response to mitogens, live Borrelia burgdorferi, NK cell function and lymphocyte subsets. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):151–159. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattwyler R. J., Volkman D. J., Luft B. J., Halperin J. J., Thomas J., Golightly M. G. Seronegative Lyme disease. Dissociation of specific T- and B-lymphocyte responses to Borrelia burgdorferi. N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 1;319(22):1441–1446. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812013192203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defosse D. L., Johnson R. C. In vitro and in vivo induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha by Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1109–1113. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1109-1113.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler F., Yoshinari N. H., Steere A. C. The T-cell proliferative assay in the diagnosis of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Oct 1;115(7):533–539. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-7-533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Protection of mice against the Lyme disease agent by immunizing with recombinant OspA. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2237407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Tomai M. A., Trachte G. J., Rice T. Prostaglandins in experimental syphilis: treponemes stimulate adherent spleen cells to secrete prostaglandin E2, and indomethacin upregulates immune functions. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):143–149. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.143-149.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habicht G. S., Beck G., Benach J. L., Coleman J. L., Leichtling K. D. Lyme disease spirochetes induce human and murine interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3147–3154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Joskowicz M., Fradelizi D., Eisen H. Modification of T-cell proliferation and interleukin 2 production in mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3466–3469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu-Li J., Ohara J., Watson C., Tsang W., Paul W. E. Derivation of a T cell line that is highly responsive to IL-4 and IL-2 (CT.4R) and of an IL-2 hyporesponsive mutant of that line (CT.4S). J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):800–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum F. Immunologic deficiency during experimental Chagas' disease (Trypanosoma cruzi infection): role of adherent, nonspecific esterase-positive splenic cells. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2202–2205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause A., Brade V., Schoerner C., Solbach W., Kalden J. R., Burmester G. R. T cell proliferation induced by Borrelia burgdorferi in patients with Lyme borreliosis. Autologous serum required for optimum stimulation. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Apr;34(4):393–402. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Dayer J. M., Krane S. M., Mergenhagen S. E. Stimulation of rheumatoid synovial cell collagenase and prostaglandin production by partially purified lymphocyte-activating factor (interleukin 1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2474–2477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody K. D., Barthold S. W., Terwilliger G. A., Beck D. S., Hansen G. M., Jacoby R. O. Experimental chronic Lyme borreliosis in Lewis rats. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Feb;42(2):165–174. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.42.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overton W. R. Modified histogram subtraction technique for analysis of flow cytometry data. Cytometry. 1988 Nov;9(6):619–626. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990090617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phipps R. P., Stein S. H., Roper R. L. A new view of prostaglandin E regulation of the immune response. Immunol Today. 1991 Oct;12(10):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90064-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Owen J. J. Thymus-derived lymphocytes: their distribution and role in the development of peripheral lymphoid tissues of the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Jan;1(1):27–30. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Eichmann K., Modolell M., Museteanu C., Simon M. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the outer surface protein A (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi prevent Lyme borreliosis in severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3768–3772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Justus C. W., Museteanu C., Simon M. M. Demonstration of antigen-specific T cells and histopathological alterations in mice experimentally inoculated with Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):41–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.41-47.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld R., Araneo B., Ma Y., Yang L. M., Weis J. J. Demonstration of a B-lymphocyte mitogen produced by the Lyme disease pathogen, Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):455–464. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.455-464.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal L. H., Steere A. C., Freeman D. H., Dwyer J. M. Proliferative responses of mononuclear cells in Lyme disease. Reactivity to Borrelia burgdorferi antigens is greater in joint fluid than in blood. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Jun;29(6):761–769. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simkin N. J., Jelinek D. F., Lipsky P. E. Inhibition of human B cell responsiveness by prostaglandin E2. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1074–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens S. K., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. Differences in the migration of B and T lymphocytes: organ-selective localization in vivo and the role of lymphocyte-endothelial cell recognition. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):844–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomai M. A., Elmquist B. J., Warmka S. M., Fitzgerald T. J. Macrophage-mediated suppression of con A-induced IL-2 production in spleen cells from syphilitic rabbits. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):309–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yssel H., Shanafelt M. C., Soderberg C., Schneider P. V., Anzola J., Peltz G. Borrelia burgdorferi activates a T helper type 1-like T cell subset in Lyme arthritis. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):593–601. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoschke D. C., Skemp A. A., Defosse D. L. Lymphoproliferative responses to Borrelia burgdorferi in Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Feb 15;114(4):285–289. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-4-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Souza M. S., Fikrig E., Smith A. L., Flavell R. A., Barthold S. W. Nonspecific proliferative responses of murine lymphocytes to Borrelia burgdorferi antigens. J Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;165(3):471–478. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Souza M. S., Smith A. L., Bottomly K. Infection of BALB/cByJ mice with the JHM strain of mouse hepatitis virus alters in vitro splenic T cell proliferation and cytokine production. Lab Anim Sci. 1991 Apr;41(2):99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Souza M. S., Smith A. L. Characterization of accessory cell function during acute infection of BALB/cByJ mice with mouse hepatitis virus (MHV), strain JHM. Lab Anim Sci. 1991 Apr;41(2):112–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


