Abstract
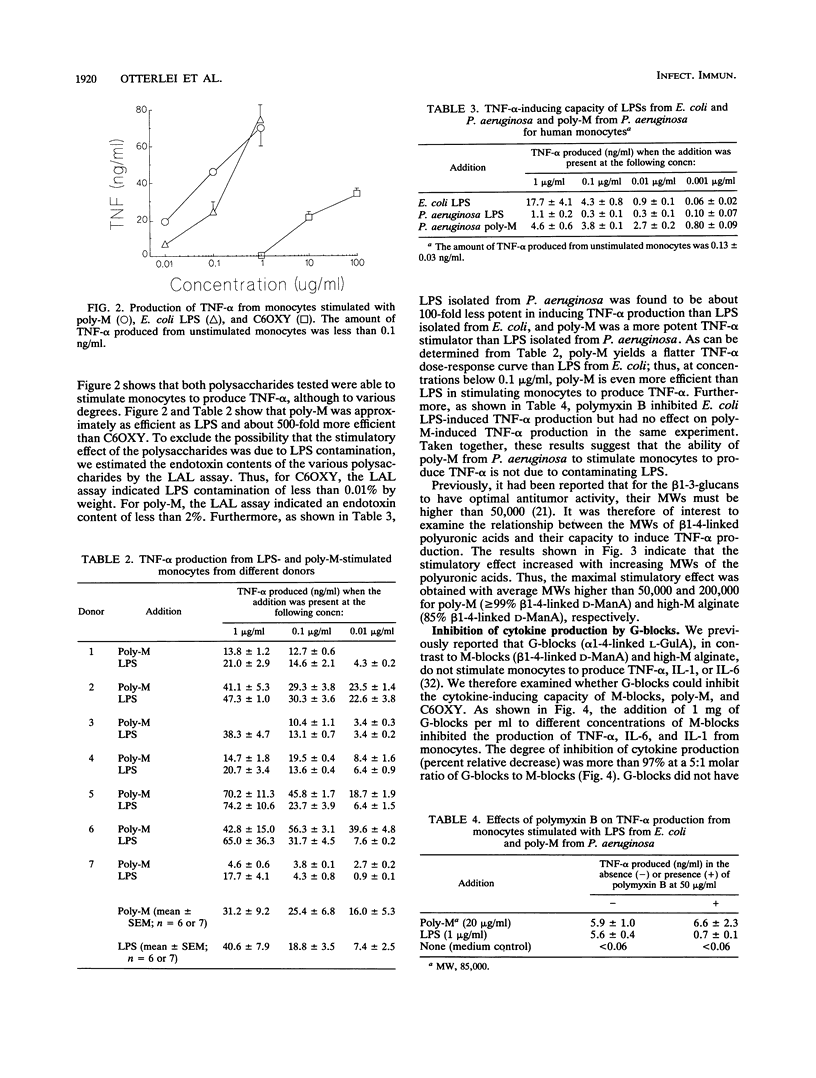
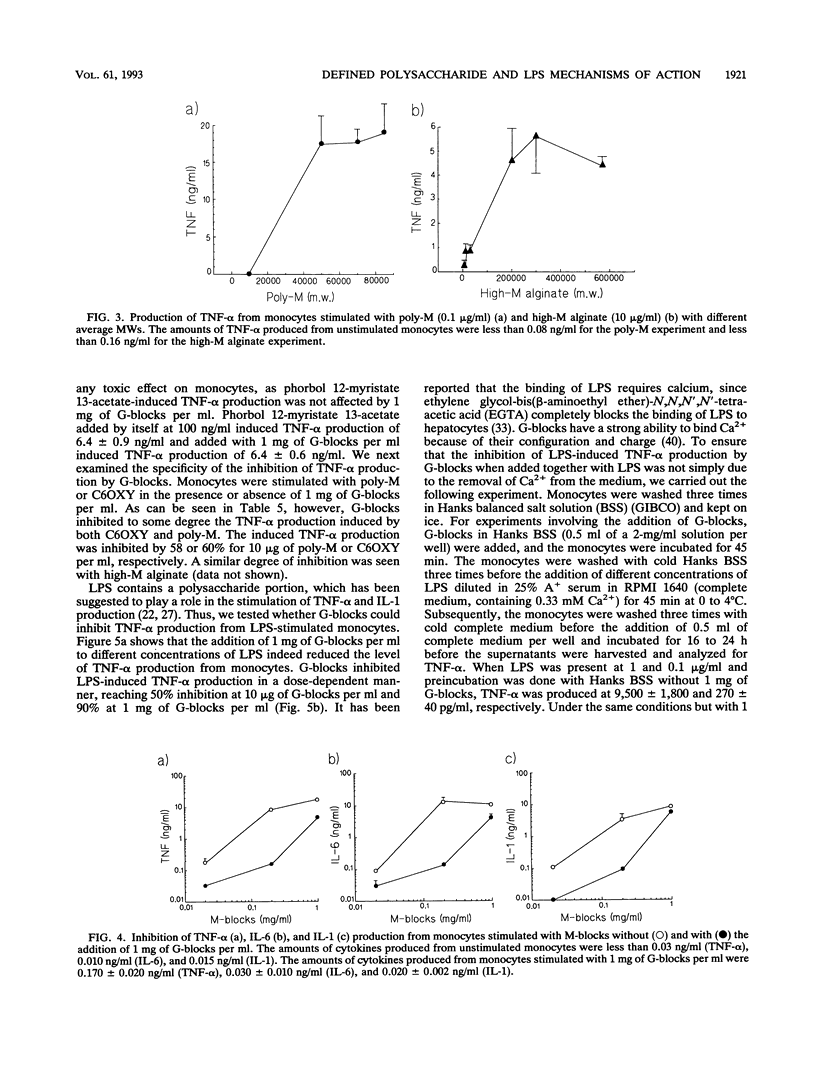
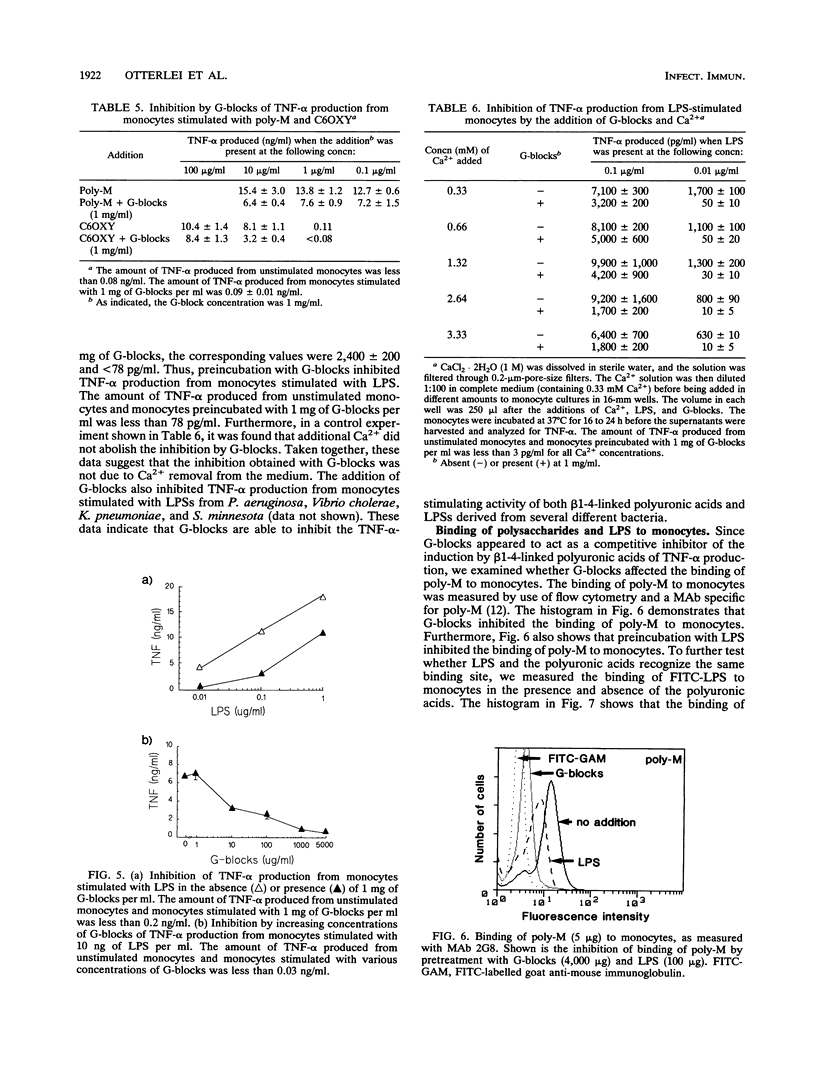
Little has been reported about the effects of different polysaccharides on cytokine production from human monocytes. In this study, we show that several well-defined polysaccharides, including polymers with different sizes of beta 1-4-linked D-mannuronic acid (poly-M, high-M alginate, and M-blocks) and cellulose oxidized in the C-6 position, induced human monocytes to produce tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha). Poly-M was the most efficient polysaccharide tested and, on a weight basis, was approximately as efficient as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from Escherichia coli. TNF-alpha production was shown to depend strongly on the molecular weights of poly-M and high-M alginate, with maximal TNF-alpha production occurring at molecular weights above 50,000 and 200,000, respectively. G-blocks, alpha 1-4-linked L-guluronic acid polymers that did not induce cytokine production from monocytes, reduced the cytokine production induced by the beta 1-4-linked polyuronic acids and LPS. Furthermore, both G-blocks and LPS were found to inhibit the binding of poly-M to monocytes, as measured by flow cytometry. In addition, we found that the binding of LPS to monocytes was inhibited by G-blocks, M-blocks, and poly-M. Our results indicate that beta 1-4-linked polyuronic acids and LPS may stimulate monocytes to produce TNF-alpha by similar mechanisms and may bind to a common receptor.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarden L. A., De Groot E. R., Schaap O. L., Lansdorp P. M. Production of hybridoma growth factor by human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Oct;17(10):1411–1416. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Virelizier J. L. Interferons as macrophage-activating factors. II. Enhanced secretion of interleukin 1 by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Jun;13(6):437–440. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins E. D., Mackie W., Smolko E. E. Crystalline structures of alginic acids. Nature. 1970 Feb 14;225(5233):626–628. doi: 10.1038/225626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brakenhoff J. P., de Groot E. R., Evers R. F., Pannekoek H., Aarden L. A. Molecular cloning and expression of hybridoma growth factor in Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4116–4121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøyum A. Isolation of lymphocytes, granulocytes and macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaillon J. M., Fitting C., Caroff M., Haeffner-Cavaillon N. Dissociation of cell-associated interleukin-1 (IL-1) and IL-1 release induced by lipopolysaccharide and lipid A. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):791–797. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.791-797.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chokri M., Freudenberg M., Galanos C., Poindron P., Bartholeyns J. Antitumoral effects of lipopolysaccharides, tumor necrosis factor, interferon and activated macrophages: synergism and tissue distribution. Anticancer Res. 1989 Jul-Aug;9(4):1185–1190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daley L., Pier G. B., Liporace J. D., Eardley D. D. Polyclonal B cell stimulation and interleukin 1 induction by the mucoid exopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with cystic fibrosis. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3089–3093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Luzio N. R., Williams D. L., McNamee R. B., Edwards B. F., Kitahama A. Comparative tumor-inhibitory and anti-bacterial activity of soluble and particulate glucan. Int J Cancer. 1979 Dec 15;24(6):773–779. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. A highly sensitive cell line, WEHI 164 clone 13, for measuring cytotoxic factor/tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 4;95(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Otterlei M., Skjåk-Braek G., Ryan L., Wright S. D., Sundan A. The involvement of CD14 in stimulation of cytokine production by uronic acid polymers. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jan;23(1):255–261. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feist W., Ulmer A. J., Musehold J., Brade H., Kusumoto S., Flad H. D. Induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha release by lipopolysaccharide and defined lipopolysaccharide partial structures. Immunobiology. 1989 Oct;179(4-5):293–307. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(89)80036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing A. J., Bird C. R., Bristow A., Poole S., Thorpe R. A simple sensitive bioassay for interleukin-1 which is unresponsive to 10(3) U/ml of interleukin-2. J Immunol Methods. 1987 May 4;99(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeffner-Cavaillon N., Chaby R., Cavaillon J. M., Szabó L. Lipopolysaccharide receptor on rabbit peritoneal macrophages. I. Binding characteristics. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):1950–1954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebbar S., Cavaillon J. M., Caroff M., Ledur A., Brade H., Sarfati R., Haeffner-Cavaillon N. Molecular requirement for interleukin 1 induction by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes: involvement of the heptosyl-2-keto-3-deoxyoctulosonate region. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jan;16(1):87–91. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Specific endotoxic lipopolysaccharide-binding proteins on murine splenocytes. II. Membrane localization and binding characteristics. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):1006–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesley J., He Q., Miyake K., Hamann A., Hyman R., Kincade P. W. Requirements for hyaluronic acid binding by CD44: a role for the cytoplasmic domain and activation by antibody. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):257–266. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liabakk N. B., Nustad K., Espevik T. A rapid and sensitive immunoassay for tumor necrosis factor using magnetic monodisperse polymer particles. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Dec 5;134(2):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90387-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loppnow H., Brade H., Dürrbaum I., Dinarello C. A., Kusumoto S., Rietschel E. T., Flad H. D. IL-1 induction-capacity of defined lipopolysaccharide partial structures. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3229–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N. Tumour-necrosis factor from the rabbit. II. Production by monocytes. Br J Cancer. 1978 Aug;38(2):310–315. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1978.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männel D. N., Falk W. Optimal induction of tumor necrosis factor production in human monocytes requires complete S-form lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1953–1958. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1953-1958.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otterlei M., Ostgaard K., Skjåk-Braek G., Smidsrød O., Soon-Shiong P., Espevik T. Induction of cytokine production from human monocytes stimulated with alginate. J Immunother (1991) 1991 Aug;10(4):286–291. doi: 10.1097/00002371-199108000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent J. B. Core-specific receptors for lipopolysaccharide on hepatocytes. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;286:131–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent J. B. Membrane receptors on rat hepatocytes for the inner core region of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3455–3461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Matthews W. J., Jr, Eardley D. D. Immunochemical characterization of the mucoid exopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):494–503. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seljelid R., Figenschau Y., Bøgwald J., Rasmussen L. T., Austgulen R. Evidence that tumor necrosis induced by aminated beta 1-3D polyglucose is mediated by a concerted action of local and systemic cytokines. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Dec;30(6):687–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb02477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J. A., Smith S. E., Dean R. T. Alginate inhibition of the uptake of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by macrophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jan;134(1):29–36. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjåk-Braek G., Grasdalen H., Larsen B. Monomer sequence and acetylation pattern in some bacterial alginates. Carbohydr Res. 1986 Oct 15;154:239–250. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Jong M. T. Adhesion-promoting receptors on human macrophages recognize Escherichia coli by binding to lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1876–1888. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


