Abstract
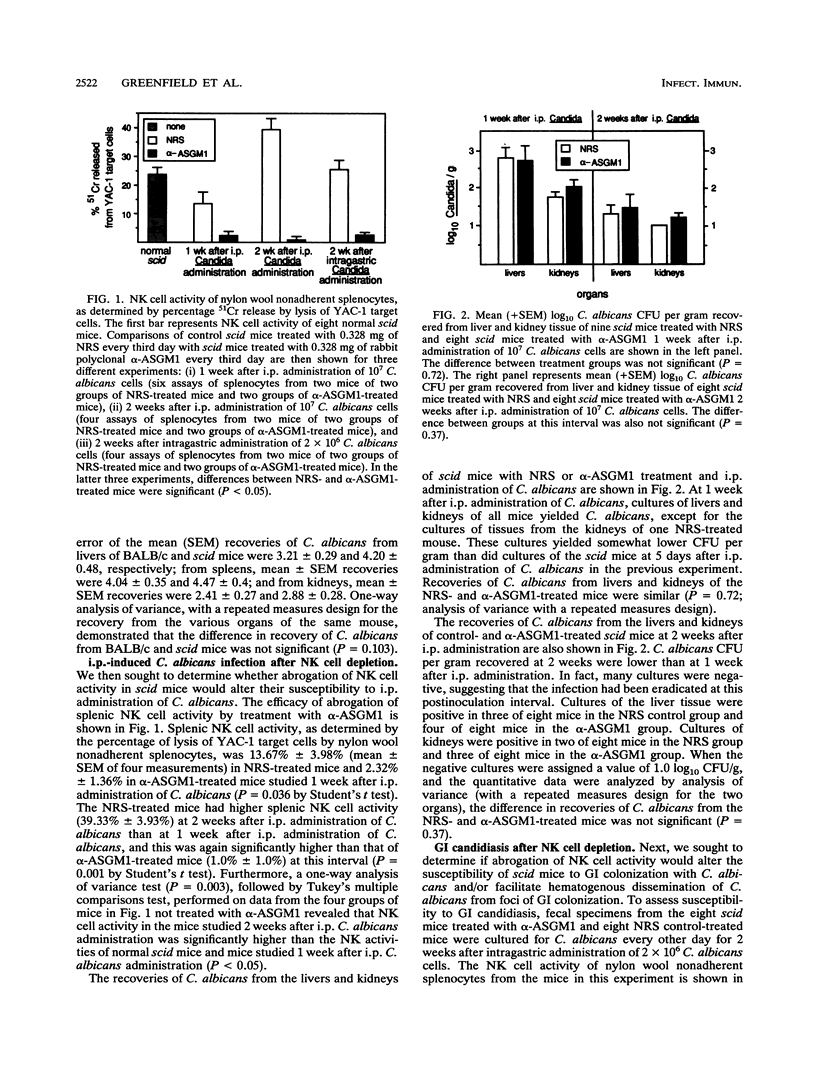
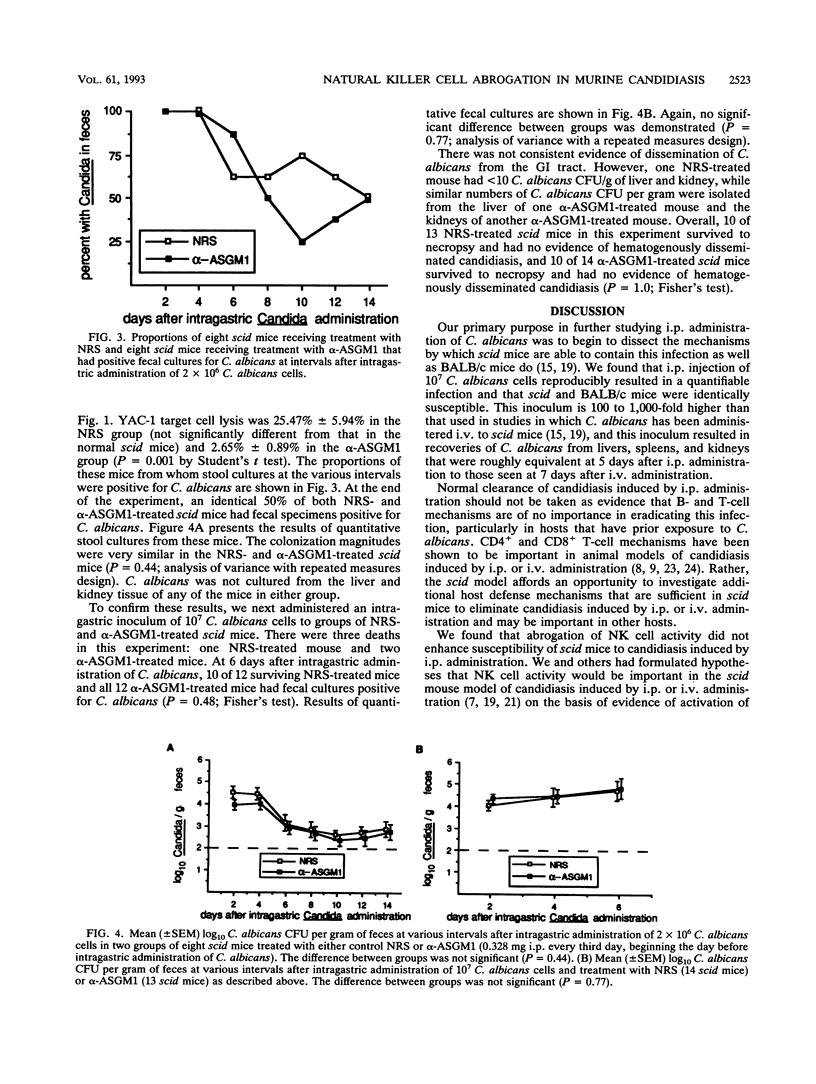
Candida albicans CFU per gram of tissue recovered from livers, spleens, and kidneys of 12 severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) and 12 BALB/c mice 5 days after intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of 10(7) C. albicans cells were not significantly different. Nine scid mice given normal rabbit serum (NRS) as a control and eight scid mice given anti-asialo-GM1 (alpha-ASGM1) had C. albicans CFU per gram recovered from livers and spleens 1 week after i.p. administration of C. albicans that were not significantly different, despite virtual elimination of natural killer (NK) cell activity in mice treated with alpha-ASGM1. At 2 weeks after i.p. administration, despite significantly increased NK cell activity in eight infected NRS-treated scid mice and virtual elimination of NK cell activity by alpha-ASGM1 treatment of eight scid mice, C. albicans CFU per gram recovered from livers and kidneys were not significantly different. At 2 weeks after intragastric administration of 2 x 10(6) C. albicans cells, eight NRS- and eight alpha-ASGM1-treated scid mice had identical proportions colonized with C. albicans and similar C. albicans CFU per gram recovered from feces. There was no evidence of hematogenous dissemination in either group. Similar results were seen 1 week after intragastric administration of 10(7) C. albicans cells. We conclude that NK cell activity is increased by i.p. administration of C. albicans in scid mice, but nontheless, abrogation of NK cell activity is not associated with enhanced susceptibility to candidiasis induced by i.p. administration and also is not associated with enhanced susceptibility to gastrointestinal colonization or hematogenous dissemination after intragastric administration of C. albicans.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashman R. B., Papadimitriou J. M. Susceptibility of beige mutant mice to candidiasis may be linked to a defect in granulocyte production by bone marrow stem cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2140–2146. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2140-2146.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft G. J., Schreiber R. D., Bosma G. C., Bosma M. J., Unanue E. R. A T cell-independent mechanism of macrophage activation by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1104–1107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beno D. W., Mathews H. L. Growth inhibition of Candida albicans by interleukin-2-activated splenocytes. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):853–863. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.853-863.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beno D. W., Mathews H. L. Growth inhibition of Candida albicans by interleukin-2-induced lymph node cells. Cell Immunol. 1990 Jun;128(1):89–100. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90009-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D. K., Michelini-Norris M. B., Djeu J. Y. Production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor by large granular lymphocytes stimulated with Candida albicans: role in activation of human neutrophil function. Blood. 1991 May 15;77(10):2259–2265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma M. J. The scid mutation: occurrence and effect. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;152:3–9. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74974-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantorna M. T., Balish E. Mucosal and systemic candidiasis in congenitally immunodeficient mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1093–1100. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1093-1100.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cenci E., Romani L., Vecchiarelli A., Puccetti P., Bistoni F. Role of L3T4+ lymphocytes in protective immunity to systemic Candida albicans infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3581–3587. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3581-3587.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cenci E., Romani L., Vecchiarelli A., Puccetti P., Bistoni F. T cell subsets and IFN-gamma production in resistance to systemic candidosis in immunized mice. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4333–4339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Blanchard D. K. Regulation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) activity against Candida albicans by large granular lymphocytes via release of a PMN-activating factor. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2761–2767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Blanchard D. K., Richards A. L., Friedman H. Tumor necrosis factor induction by Candida albicans from human natural killer cells and monocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):4047–4052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield R. A. Host defense system interactions with Candida. J Med Vet Mycol. 1992;30(2):89–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habu S., Fukui H., Shimamura K., Kasai M., Nagai Y., Okumura K., Tamaoki N. In vivo effects of anti-asialo GM1. I. Reduction of NK activity and enhancement of transplanted tumor growth in nude mice. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):34–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidore M. R., Murphy J. W. Correlation of natural killer cell activity and clearance of Cryptococcus neoformans from mice after adoptive transfer of splenic nylon wool-nonadherent cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):547–555. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.547-555.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J., Vazquez-Torres A., Balish E. Poly(I.C)-induced interferons enhance susceptibility of SCID mice to systemic candidiasis. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4549–4557. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4549-4557.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M., Iwamori M., Nagai Y., Okumura K., Tada T. A glycolipid on the surface of mouse natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Mar;10(3):175–180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Hackett J., Jr, Tutt M. M., Garni-Wagner B. A., Kuziel W. A., Tucker P. W., Bennett M. Natural killer cells and their precursors in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;152:47–52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74974-2_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai W. C., Bennett M., Pakes S. P., Kumar V., Steutermann D., Owusu I., Mikhael A. Resistance to Mycoplasma pulmonis mediated by activated natural killer cells. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1269–1275. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahanty S., Greenfield R. A., Joyce W. A., Kincade P. W. Inoculation candidiasis in a murine model of severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3162–3166. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3162-3166.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi P., Scaringi L., Tissi L., Boccanera M., Bistoni F., Bonmassar E., Cassone A. Induction of natural killer cell activity by inactivated Candida albicans in mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):297–303. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.297-303.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W. Immunity to fungi. Curr Opin Immunol. 1989;2(3):360–367. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(89)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan R., Joyce W. A., Greenfield R. A. Gastrointestinal candidiasis in a murine model of severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2116–2119. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2116-2119.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani L., Mencacci A., Cenci E., Mosci P., Vitellozzi G., Grohmann U., Puccetti P., Bistoni F. Course of primary candidiasis in T cell-depleted mice infected with attenuated variant cells. J Infect Dis. 1992 Dec;166(6):1384–1392. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.6.1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani L., Mocci S., Bietta C., Lanfaloni L., Puccetti P., Bistoni F. Th1 and Th2 cytokine secretion patterns in murine candidiasis: association of Th1 responses with acquired resistance. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4647–4654. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4647-4654.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaringi L., Cornacchione P., Rosati E., Boccanera M., Cassone A., Bistoni F., Marconi P. Induction of LAK-like cells in the peritoneal cavity of mice by inactivated Candida albicans. Cell Immunol. 1990 Sep;129(2):271–287. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaringi L., Marconi P., Boccanera M., Tissi L., Bistoni F., Cassone A. Cell wall components of Candida albicans as immunomodulators: induction of natural killer and macrophage-mediated peritoneal cell cytotoxicity in mice by mannoprotein and glucan fractions. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 May;134(5):1265–1274. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-5-1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecchiarelli A., Bistoni F., Cenci E., Perito S., Cassone A. In-vitro killing of Candida species by murine immunoeffectors and its relationship to the experimental pathogenicity. Sabouraudia. 1985 Oct;23(5):377–387. doi: 10.1080/00362178585380541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei S., Blanchard D. K., McMillen S., Djeu J. Y. Lymphokine-activated killer cell regulation of T-cell-mediated immunity to Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3586–3595. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3586-3595.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wherry J. C., Schreiber R. D., Unanue E. R. Regulation of gamma interferon production by natural killer cells in scid mice: roles of tumor necrosis factor and bacterial stimuli. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1709–1715. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1709-1715.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zunino S. J., Hudig D. Interactions between human natural killer (NK) lymphocytes and yeast cells: human NK cells do not kill Candida albicans, although C. albicans blocks NK lysis of K562 cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):564–569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.564-569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


