Abstract
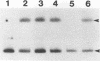
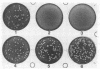
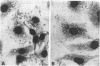
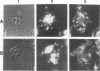
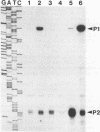
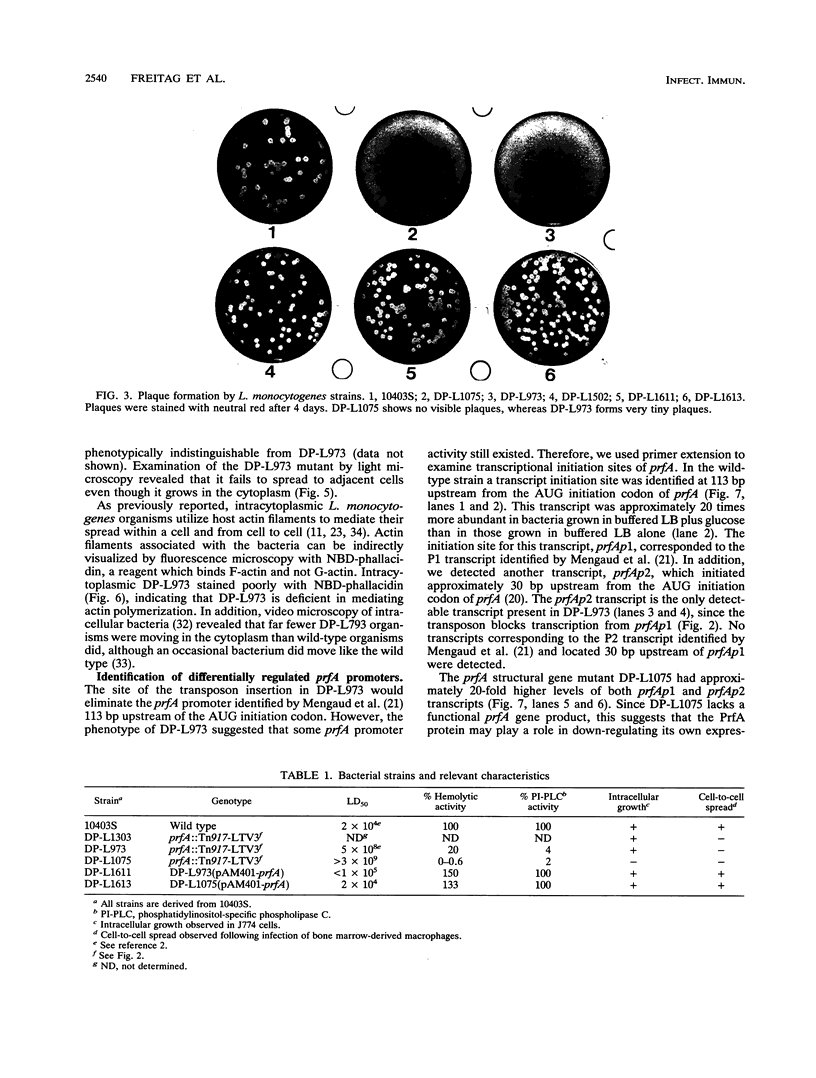
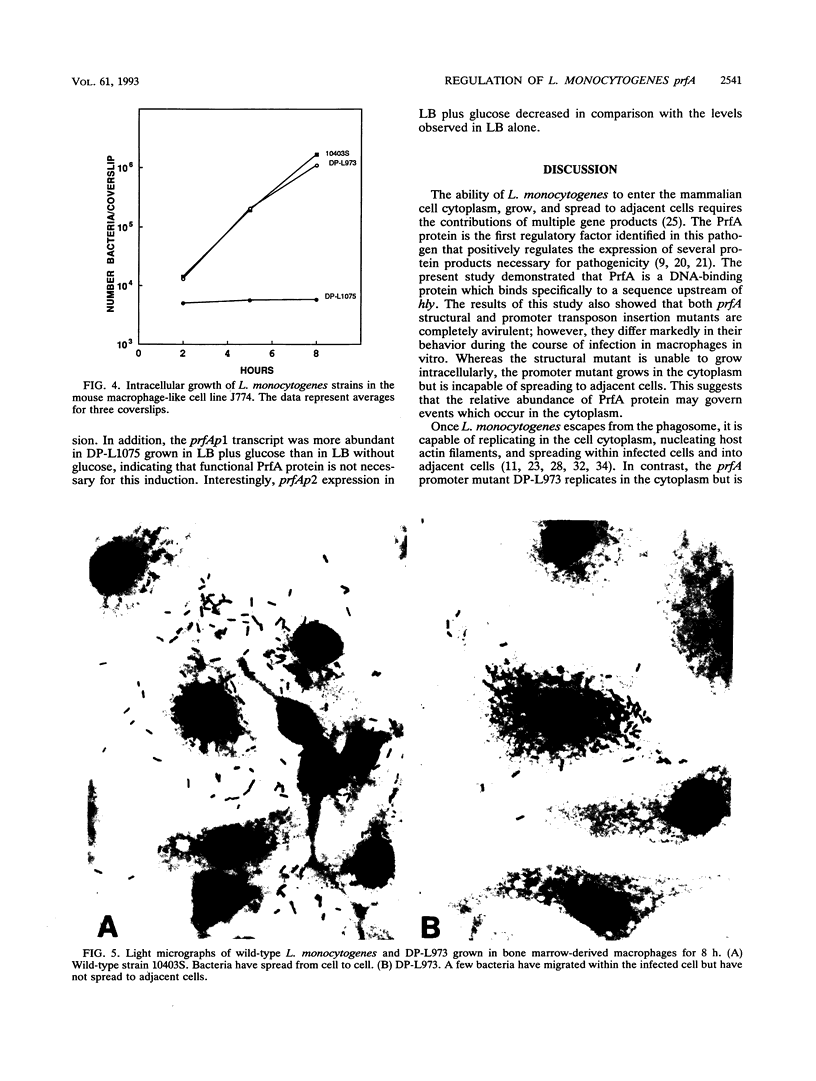
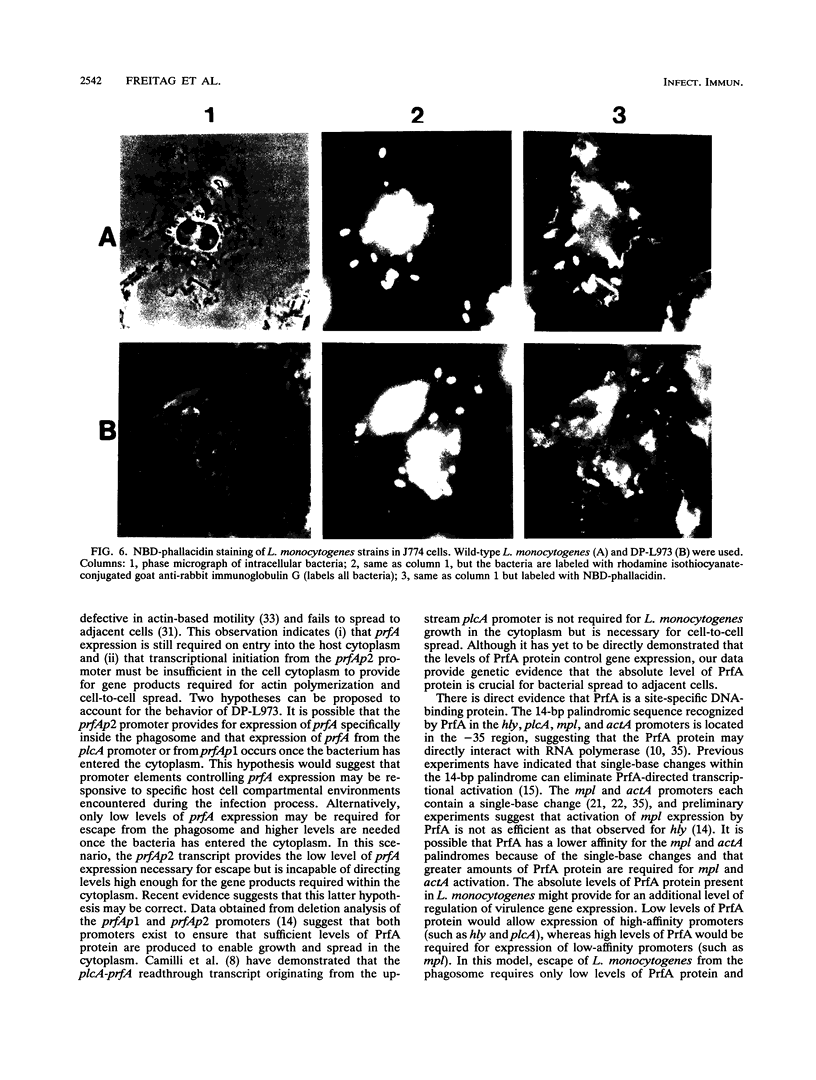
The prfA gene product is a transcriptional activator of Listeria monocytogenes determinants of pathogenicity. In this study, we provide direct evidence that the PrfA protein is a site-specific DNA-binding protein. Additionally, we describe the characterization of two classes of L. monocytogenes mutants which contain transposon insertions either in the prfA structural gene (exemplified by strain DP-L1075) or within the prfA promoter region (exemplified by strain DP-L973). Both mutants are completely avirulent and secrete greatly reduced levels of listeriolysin O and phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, and both are fully complemented by the introduction of prfA on a multicopy plasmid. The behaviors of the two mutants differ markedly within cultured macrophages. Following infection, no cytoplasmic growth was observed for DP-L1075 whereas DP-L973 escaped from the phagosome and grew in the cell cytoplasm. However, DP-L973 was defective in nucleation of actin filaments and spread to adjacent cells. Transcription of prfA in DP-L973 was directed from a single, previously unidentified promoter (prfAp2) located close to the prfA initiation codon. This promoter is therefore capable of providing sufficient prfA expression for escape from the host cell vacuole but is insufficient for wild-type levels of bacterially induced actin polymerization and cell-to-cell spread. Transcription directed from both prfAp1 and prfAp2 promoters was increased in the absence of a functional prfA gene product, suggesting that PrfA protein contributes to down-regulating its own expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry R. A., Bouwer H. G., Portnoy D. A., Hinrichs D. J. Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of Listeria monocytogenes small-plaque mutants defective for intracellular growth and cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1625–1632. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1625-1632.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. K., Hinrichs D. J. Adoptive transfer of immunity to Listeria monocytogenes. The influence of in vitro stimulation on lymphocyte subset requirements. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2005–2009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilli A., Goldfine H., Portnoy D. A. Listeria monocytogenes mutants lacking phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C are avirulent. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):751–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilli A., Paynton C. R., Portnoy D. A. Intracellular methicillin selection of Listeria monocytogenes mutants unable to replicate in a macrophage cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5522–5526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilli A., Portnoy A., Youngman P. Insertional mutagenesis of Listeria monocytogenes with a novel Tn917 derivative that allows direct cloning of DNA flanking transposon insertions. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3738–3744. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3738-3744.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Hartl M., Goebel W., Nichterlein T., Notermans S. Coordinate regulation of virulence genes in Listeria monocytogenes requires the product of the prfA gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):568–574. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.568-574.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collado-Vides J., Magasanik B., Gralla J. D. Control site location and transcriptional regulation in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):371–394. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.371-394.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabiri G. A., Sanger J. M., Portnoy D. A., Southwick F. S. Listeria monocytogenes moves rapidly through the host-cell cytoplasm by inducing directional actin assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6068–6072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M., Peterkin P. I. Listeria monocytogenes, a food-borne pathogen. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):476–511. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.476-511.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitag N. E., Youngman P., Portnoy D. A. Transcriptional activation of the Listeria monocytogenes hemolysin gene in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1293–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1293-1298.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellin B. G., Broome C. V. Listeriosis. JAMA. 1989 Mar 3;261(9):1313–1320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Chakraborty T. The expression of virulence genes in Listeria monocytogenes is thermoregulated. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):947–952. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.947-952.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Haffner C., Domann E., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Identification of a gene that positively regulates expression of listeriolysin, the major virulence factor of listeria monocytogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8336–8340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Dramsi S., Gouin E., Vazquez-Boland J. A., Milon G., Cossart P. Pleiotropic control of Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors by a gene that is autoregulated. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2273–2283. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Vicente M. F., Cossart P. Transcriptional mapping and nucleotide sequence of the Listeria monocytogenes hlyA region reveal structural features that may be involved in regulation. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3695–3701. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3695-3701.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Ryter A., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular and cell-to-cell spread of Listeria monocytogenes involves interaction with F-actin in the enterocytelike cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1048-1058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S. F., Stewart G. S. High-efficiency transformation of Listeria monocytogenes by electroporation of penicillin-treated cells. Gene. 1990 Sep 28;94(1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90479-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Chakraborty T., Goebel W., Cossart P. Molecular determinants of Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1263–1267. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1263-1267.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. M., Sanger J. W., Southwick F. S. Host cell actin assembly is necessary and likely to provide the propulsive force for intracellular movement of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3609–3619. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3609-3619.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun A. N., Camilli A., Portnoy D. A. Isolation of Listeria monocytogenes small-plaque mutants defective for intracellular growth and cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3770–3778. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3770-3778.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J., Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. The rate of actin-based motility of intracellular Listeria monocytogenes equals the rate of actin polymerization. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):257–260. doi: 10.1038/357257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Boland J. A., Kocks C., Dramsi S., Ohayon H., Geoffroy C., Mengaud J., Cossart P. Nucleotide sequence of the lecithinase operon of Listeria monocytogenes and possible role of lecithinase in cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):219–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.219-230.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth R., An F. Y., Clewell D. B. Highly efficient protoplast transformation system for Streptococcus faecalis and a new Escherichia coli-S. faecalis shuttle vector. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):831–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.831-836.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]