Abstract
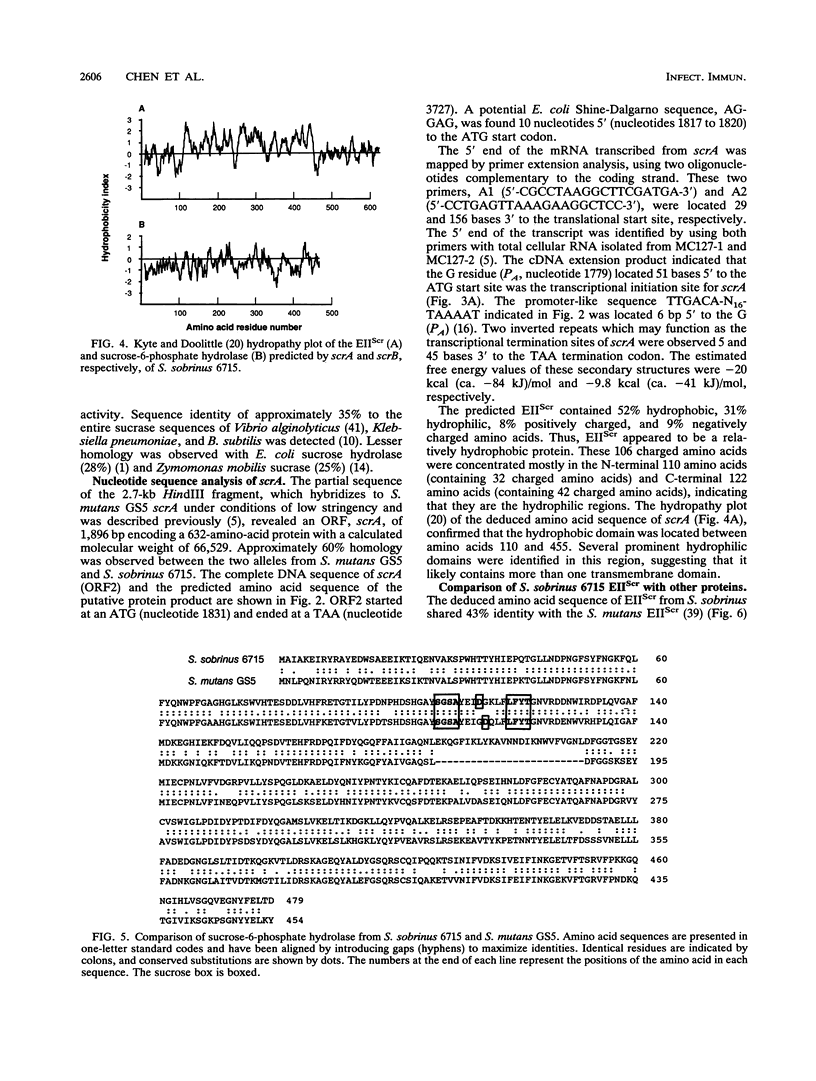
The complete nucleotide sequences of Streptococcus sobrinus 6715 scrA and scrB, which encode sucrose-specific enzyme II of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system and sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase, respectively, have been determined. These two genes were transcribed divergently, and the initiation codons of the two open reading frames were 192 bp apart. The transcriptional initiation sites were determined by primer extension analysis, and the putative promoter regions of these two genes overlapped partially. The gene encoding enzyme IIScr, scrA, contained 1,896 nucleotides, and the molecular mass of the predicted protein was 66,529 Da. The hydropathy plot of the predicted amino acid sequence indicated that enzyme IIScr was a relatively hydrophobic protein. The gene encoding sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase, scrB, contained 1,437 nucleotides. The molecular mass of the predicted protein was 54,501 Da, and the encoded enzyme was hydrophilic. The predicted amino acid sequences of the two open reading frames exhibited approximately 45 and 70% identity with those encoded by scrA and scrB, respectively, from Streptococcus mutans GS5. Homology also was observed between the N-terminal region of the S. sobrinus 6715 enzyme IIScr and other enzyme IIs specific for the glucopyranoside molecule, all of which generate glucopyranoside-6-phosphate during translocation and phosphorylation of the respective substrates. The sequence of the C-terminal domain of the S. sobrinus 6715 enzyme IIScr shared significant homology with enzyme IIIGlc from Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium and with the C-terminal domain of enzyme IIBgl from E. coli, indicating that the two functional domains, enzyme IIScr and enzyme IIIScr, were covalently linked as a single polypeptide in S. sobrinus 6715. The deduced amino acid sequence of the gene product of S. sobrinus scrB shared strong homology with sucrase from Bacillus subtilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Vibrio alginolyticus, suggesting conservation based on the physiological roles of these proteins.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aslanidis C., Schmid K., Schmitt R. Nucleotide sequences and operon structure of plasmid-borne genes mediating uptake and utilization of raffinose in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6753–6763. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6753-6763.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatch G. L., Scholle R. R., Woods D. R. Nucleotide sequence and analysis of the Vibrio alginolyticus sucrose uptake-encoding region. Gene. 1990 Oct 30;95(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90408-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassy B. M., Porter E. V. Sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase from Streptococcus mutans. Methods Enzymol. 1982;90(Pt E):556–559. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. Y., LeBlanc D. J. Genetic analysis of scrA and scrB from Streptococcus sobrinus 6715. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3739–3746. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3739-3746.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Sal G., Manfioletti G., Schneider C. A one-tube plasmid DNA mini-preparation suitable for sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9878–9878. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebner R., Lengeler J. W. DNA sequence of the gene scrA encoding the sucrose transport protein EnzymeII(Scr) of the phosphotransferase system from enteric bacteria: homology of the EnzymeII(Scr) and EnzymeII(Bgl) proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):9–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erni B., Zanolari B. Glucose-permease of the bacterial phosphotransferase system. Gene cloning, overproduction, and amino acid sequence of enzyme IIGlc. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16398–16403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouet A., Arnaud M., Klier A., Rapoport G. Bacillus subtilis sucrose-specific enzyme II of the phosphotransferase system: expression in Escherichia coli and homology to enzymes II from enteric bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8773–8777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouet A., Klier A., Rapoport G. Nucleotide sequence of the sucrase gene of Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1986;45(2):221–225. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli D., Friesenegger A., Wirth R. Transcriptional control of sex-pheromone-inducible genes on plasmid pAD1 of Enterococcus faecalis and sequence analysis of a third structural gene for (pPD1-encoded) aggregation substance. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(10):1297–1308. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Dental caries. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:121–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunasekaran P., Karunakaran T., Cami B., Mukundan A. G., Preziosi L., Baratti J. Cloning and sequencing of the sacA gene: characterization of a sucrase from Zymomonas mobilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6727–6735. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6727-6735.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa M., Aoki H., Kuramitsu H. K. Isolation and characterization of the sucrose 6-phosphate hydrolase gene from Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):582–586. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.582-586.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A. A., Roosendaal B., van Breemen J. F., de Graaf F. K. Role of phenylalanine 150 in the receptor-binding domain of the K88 fibrillar subunit. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4907–4911. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4907-4911.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Mimura C. S., Scott P. J., Thompson P. W. Identification and properties of distinct sucrose and glucose phosphotransferase enzyme II activities in Streptococcus mutans 6715g. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):854–856. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.854-856.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Lee L. N., Abu-Al-Jaibat A. Molecular, genetic, and functional analysis of the basic replicon of pVA380-1, a plasmid of oral streptococcal origin. Plasmid. 1992 Sep;28(2):130–145. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(92)90044-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengeler J. W., Titgemeyer F., Vogler A. P., Wöhrl B. M. Structures and homologies of carbohydrate: phosphotransferase system (PTS) proteins. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Jan 30;326(1236):489–504. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1990.0027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunsford R. D., Macrina F. L. Molecular cloning and characterization of scrB, the structural gene for the Streptococcus mutans phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):426–434. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.426-434.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow N. D., Fox D. K., Roseman S. The bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: glycose phosphotransferase system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:497–542. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S. O., Schuitema A. R., Benne R., van der Ploeg L. H., Plijter J. S., Aan F., Postma P. W. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and expression of the crr gene: the structural gene for IIIGlc of the bacterial PEP:glucose phosphotransferase system. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1587–1593. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pas H. H., Robillard G. T. Enzyme IIMtl of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system: identification of the activity-linked cysteine on the mannitol carrier. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 26;27(15):5515–5519. doi: 10.1021/bi00415a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pas H. H., Robillard G. T. S-phosphocysteine and phosphohistidine are intermediates in the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent mannitol transport catalyzed by Escherichia coli EIIMtl. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):5835–5839. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer A., Pao G. M., Saier M. H., Jr Evolutionary relationships among the permease proteins of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Construction of phylogenetic trees and possible relatedness to proteins of eukaryotic mitochondria. J Mol Evol. 1991 Aug;33(2):179–193. doi: 10.1007/BF02193633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard G. T., Lolkema J. S. Enzymes II of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar transport systems: a review of their structure and mechanism of sugar transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 11;947(3):493–519. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr Evolution of permease diversity and energy-coupling mechanisms: an introduction. Res Microbiol. 1990 Mar-Apr;141(3):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Reizer J. Proposed uniform nomenclature for the proteins and protein domains of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1433–1438. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1433-1438.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Yamada M., Erni B., Suda K., Lengeler J., Ebner R., Argos P., Rak B., Schnetz K., Lee C. A. Sugar permeases of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system: sequence comparisons. FASEB J. 1988 Mar 1;2(3):199–208. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.3.2832233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Kuramitsu H. K. Sequence analysis of the Streptococcus mutans scrB gene. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1956–1960. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1956-1960.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Poy F., Jacobson G. R., Kuramitsu H. K. Characterization and sequence analysis of the scrA gene encoding enzyme IIScr of the Streptococcus mutans phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):263–271. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.263-271.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid K., Ebner R., Altenbuchner J., Schmitt R., Lengeler J. W. Plasmid-mediated sucrose metabolism in Escherichia coli K12: mapping of the scr genes of pUR400. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholle R. R., Robb S. M., Robb F. T., Woods D. R. Nucleotide sequence and analysis of the Vibrio alginolyticus sucrase gene (scrB). Gene. 1989 Aug 1;80(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder V. A., Michalek S. M., Macrina F. L. Biochemical characterization and evaluation of virulence of a fructosyltransferase-deficient mutant of Streptococcus mutans V403. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3560–3569. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3560-3569.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slee A. M., Tanzer J. M. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase activity in Streptococcus mutans NCTC 10449. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):821–828. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.821-828.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slee A. M., Tanzer J. M. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase activity in five serotypes of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):783–786. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.783-786.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Martin E. J., Wittenberger C. L. Characterization of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):865–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.865-868.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogler A. P., Lengeler J. W. Comparison of the sequences of the nagE operons from Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli K12: enhanced variability of the enzyme IIN-acetylglucosamine in regions connecting functional domains. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Nov;230(1-2):270–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00290677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wootton J. C., Drummond M. H. The Q-linker: a class of interdomain sequences found in bacterial multidomain regulatory proteins. Protein Eng. 1989 May;2(7):535–543. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.7.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung M. K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Actinomyces viscosus T14V sialidase gene: presence of a conserved repeating sequence among strains of Actinomyces spp. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):109–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.109-116.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]