Abstract
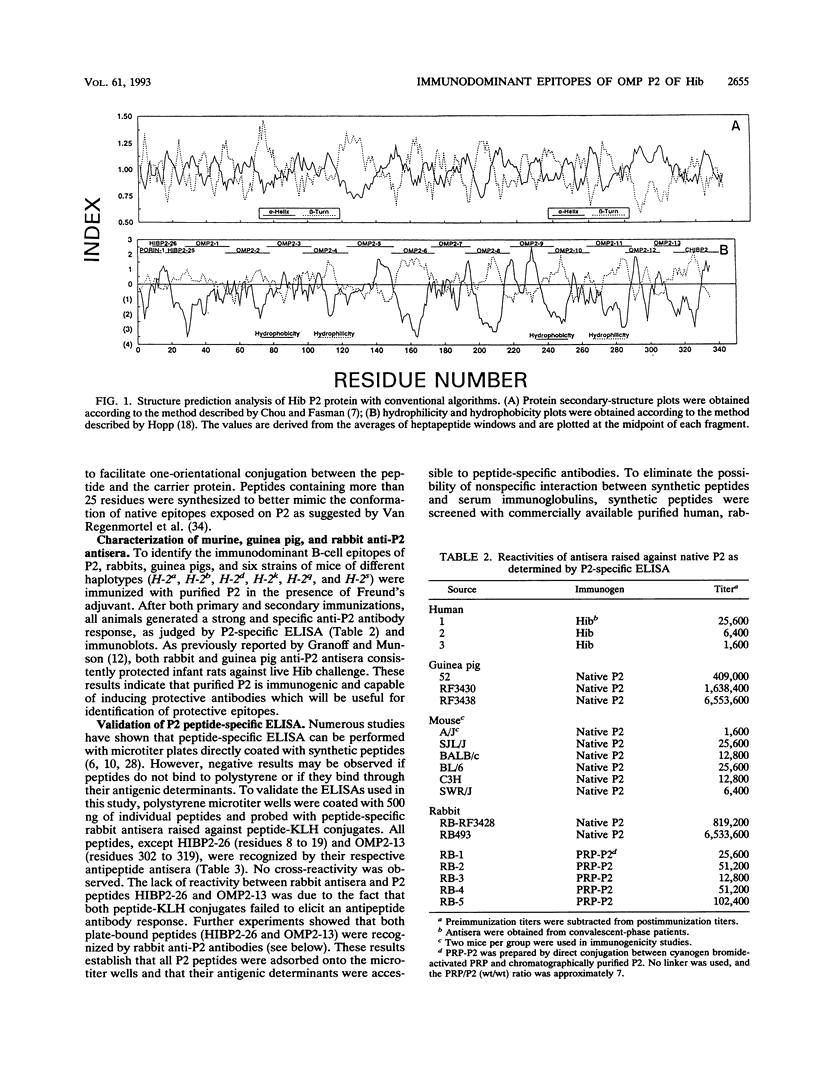
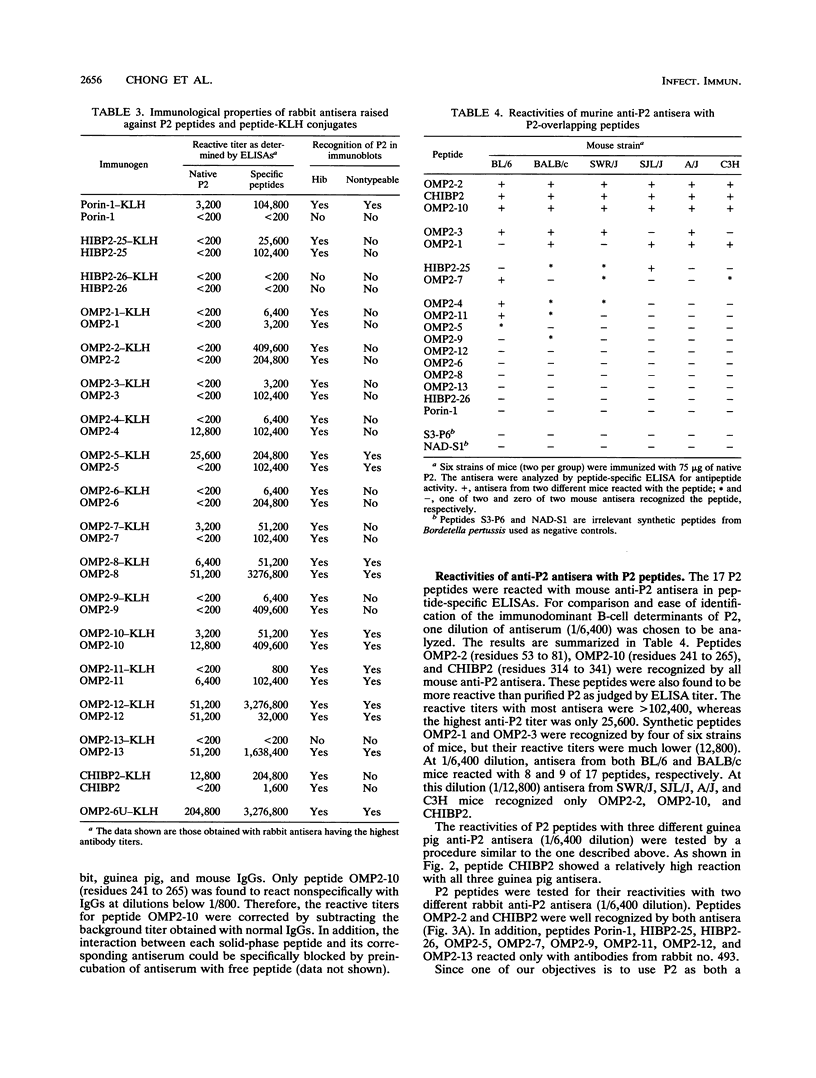
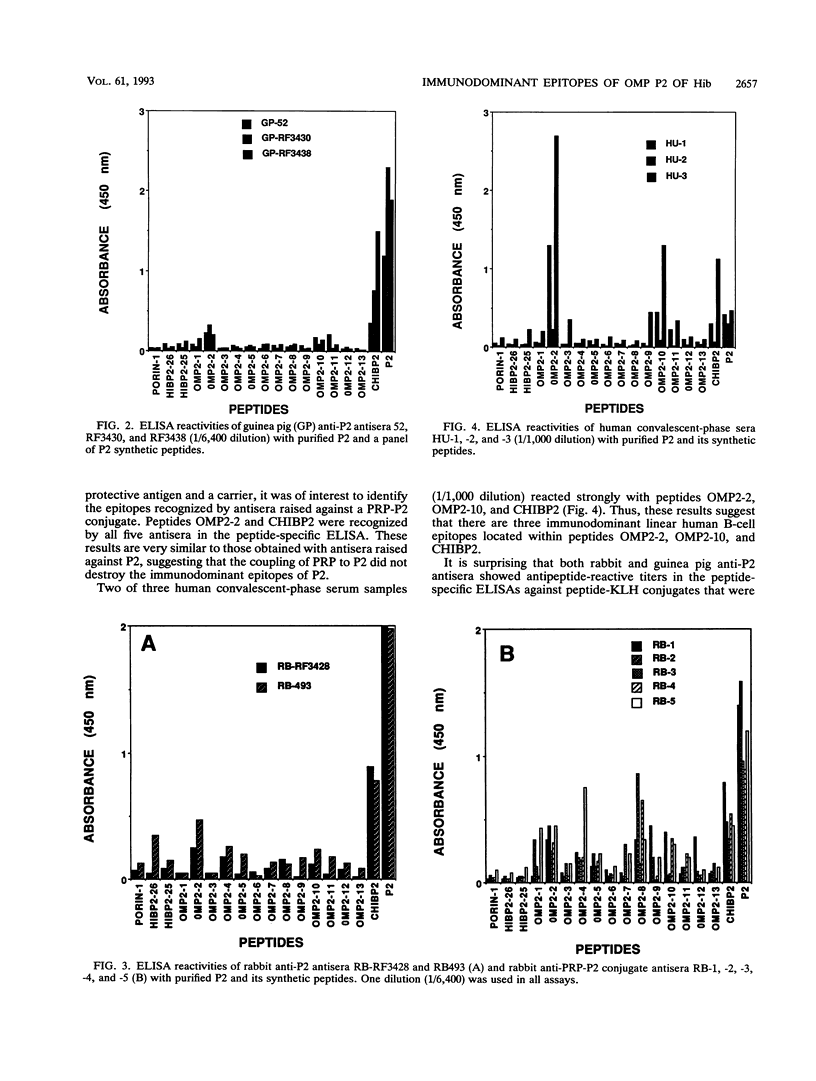
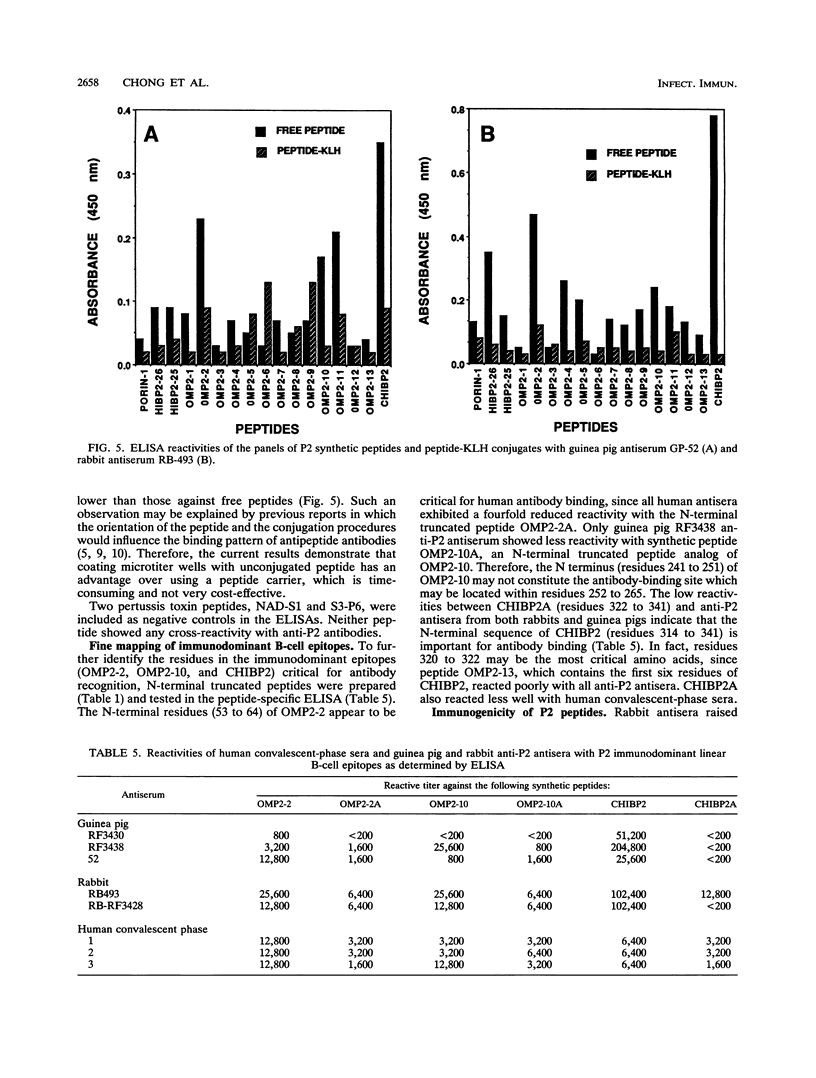
Haemophilus influenzae type b is a major cause of bacterial meningitis in young children. Antibodies against the outer membrane protein P2 are protective in the infant rat model of bacteremia. To identify conserved, surface-exposed, and protective epitopes of P2, 17 overlapping peptides covering the entire sequence of the protein were synthesized. Antisera from mice, guinea pigs, and rabbits raised against chromatographically purified P2 were tested for their reactivities to the peptides by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). Three major linear immunodominant B-cell epitopes were mapped to residues 53 to 81, 241 to 265, and 314 to 341 of mature P2. Human convalescent-phase antisera also reacted strongly with these three epitopes. Rabbit antisera against all peptide-keyhole limpet hemocyanin conjugates except two peptides containing residues 8 to 19 and 302 to 319 recognized the corresponding peptides in ELISA and reacted with P2 on immunoblots. Immunization with all unconjugated peptides, except the 19 N-terminal residues, induced very strong peptide-specific antibody responses, and these antisera reacted with P2 on immunoblots. Rabbit antisera raised against peptides corresponding to residues 1 to 14, 125 to 150, 193 to 219, and 241 to 319 also recognized P2 purified from H. influenzae nontypeable isolates. Identification of these immunodominant B-cell epitopes and conserved regions is a first step toward the rational design of a universal H. influenzae vaccine.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askelöf P., Rodmalm K., Abens J., Undén A., Bartfai T. Use of synthetic peptides to map antigenic sites of Bordetella pertussis toxin subunit S1. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):738–742. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audibert F., Jolivet M., Chedid L., Alouf J. E., Boquet P., Rivaille P., Siffert O. Active antitoxic immunization by a diphtheria toxin synthetic oligopeptide. Nature. 1981 Feb 12;289(5798):593–594. doi: 10.1038/289593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Subtyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b by outer-membrane protein profiles. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):668–676. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzofsky J. A. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors in protein antigenic structure. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):932–940. doi: 10.1126/science.2410982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briand J. P., Muller S., Van Regenmortel M. H. Synthetic peptides as antigens: pitfalls of conjugation methods. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Apr 8;78(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90329-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong P., Sydor M., Wu E., Zobrist G., Boux H., Klein M. Structural and functional analysis of the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin using synthetic peptides. Mol Immunol. 1991 Mar;28(3):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90068-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochi S. L., Broome C. V. Vaccine prevention of Haemophilus influenzae type b disease: past, present and future. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;5(1):12–19. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198601000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyrberg T., Oldstone M. B. Peptides as antigens. Importance of orientation. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1344–1349. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geerligs H. J., Weijer W. J., Bloemhoff W., Welling G. W., Welling-Wester S. The influence of pH and ionic strength on the coating of peptides of herpes simplex virus type 1 in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Feb 10;106(2):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90203-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Munson R. S., Jr Prospects for prevention of Haemophilus influenzae type b disease by immunization. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):448–461. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Weinberg G. A., Shackelford P. G. IgG subclass response to immunization with Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-outer membrane protein conjugate vaccine. Pediatr Res. 1988 Aug;24(2):180–185. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198808000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Gonzales F. R., Chamberlain N. R., Norgard M. V., Miller E. E., Cope L. D., Pelzel S. E., Gaddy B., Clausell A. Cloning of the gene encoding the major outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2709–2716. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2709-2716.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Hasemann C., Clausell A., Capra J. D., Orth K., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C. A., Latimer J. L., Miller E. E. Primary structure of the porin protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b determined by nucleotide sequence analysis. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1100–1107. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1100-1107.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harari I., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G., Arnon R. Synthetic peptides of Shiga toxin B subunit induce antibodies which neutralize its biological activity. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1618–1624. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1618-1624.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetherington S. V., Rutkowski A. F. Antibody affinity in infants after immunization with conjugated capsular polysaccharide from Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1185–1188. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P. Protein surface analysis. Methods for identifying antigenic determinants and other interaction sites. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Apr 3;88(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., Sela M., Arnon R. Antibodies against synthetic peptides of the B subunit of cholera toxin: crossreaction and neutralization of the toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7611–7615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käyhty H., Peltola H., Eskola J., Rönnberg P. R., Kela E., Karanko V., Mäkelä P. H. Immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae oligosaccharide-protein and polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccination of children at 4, 6, and 14 months of age. Pediatrics. 1989 Dec;84(6):995–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Outer membrane protein composition in disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenic and epidemiological implications. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):709–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.709-717.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D., Munson R., Jr, Grass S., Chong P., Hamel J., Zobrist G., Klein M., Brodeur B. R. Mapping of B-cell epitopes on the outer membrane P2 porin protein of Haemophilus influenzae by using recombinant proteins and synthetic peptides. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1457–1464. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1457-1464.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Shenep J. L., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M. Purification and comparison of outer membrane protein P2 from Haemophilus influenzae type b isolates. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):677–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI111017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Bailey C., Grass S. Diversity of the outer membrane protein P2 gene from major clones of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1797–1803. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Tolan R. W., Jr Molecular cloning, expression, and primary sequence of outer membrane protein P2 of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):88–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.88-94.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C. Purification and analysis with monoclonal antibodies of P2, the major outer membrane protein of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1084–1089. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1084-1089.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Kroll J. S., Moxon E. R., Selander R. K. Evolutionary genetics of the encapsulated strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7758–7762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. M., Guo D., Hodges R. S. New hydrophilicity scale derived from high-performance liquid chromatography peptide retention data: correlation of predicted surface residues with antigenicity and X-ray-derived accessible sites. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5425–5432. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes G., Houghten R., Taulane J. P., Carson D., Vaughan J. The immune response to Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen: conformational and structural features of antibody binding to synthetic peptides. Mol Immunol. 1984 Nov;21(11):1047–1054. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr P. I., Peter G. Demographic factors in the epidemiology of hemophilus influenzae meningitis in young children. J Pediatr. 1978 Jun;92(6):884–888. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk D. C. The pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):1–16. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachon V., Laprade R., Coulton J. W. Properties of the porin of Haemophilus influenzae type b in planar lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 25;861(1):74–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90373-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg G. A., Einhorn M. S., Lenoir A. A., Granoff P. D., Granoff D. M. Immunologic priming to capsular polysaccharide in infants immunized with Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-Neisseria meningitidis outer membrane protein conjugate vaccine. J Pediatr. 1987 Jul;111(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80336-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg G. A., Granoff D. M. Polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccines for the prevention of Haemophilus influenzae type b disease. J Pediatr. 1988 Oct;113(4):621–631. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alphen L., Eijk P., Geelen-van den Broek L., Dankert J. Immunochemical characterization of variable epitopes of outer membrane protein P2 of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):247–252. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.247-252.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


