Abstract
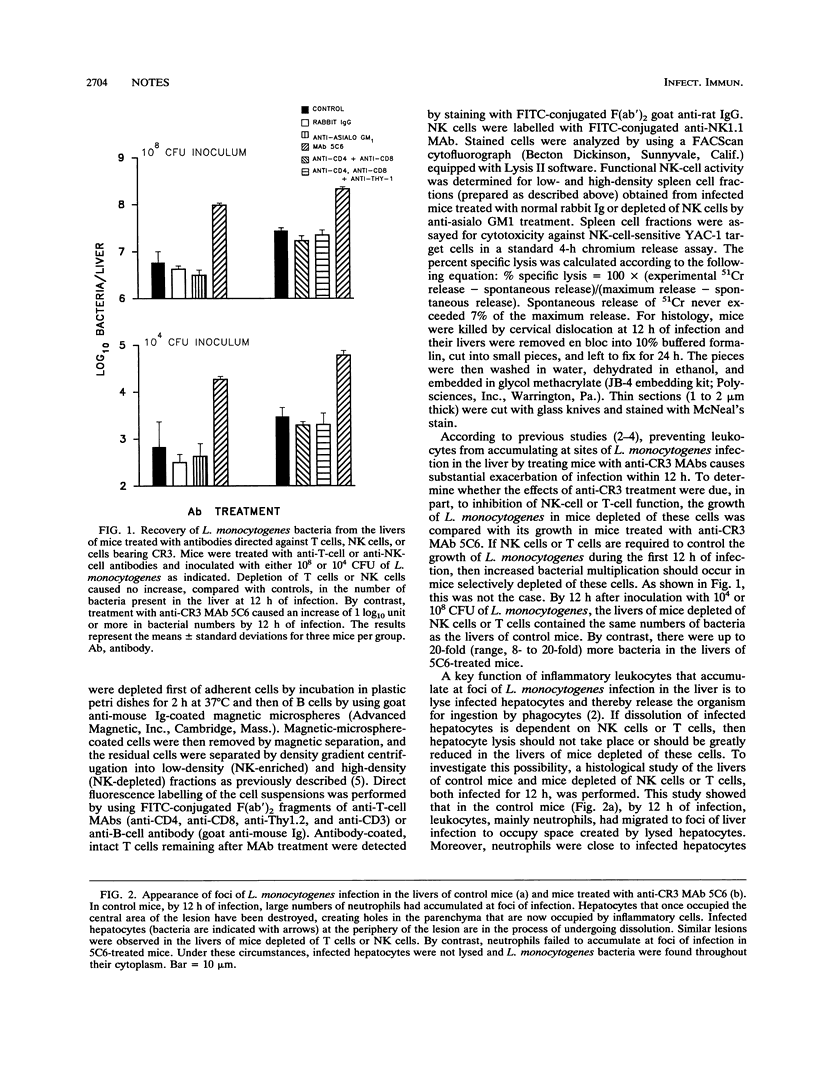
An important early component of defense against listeriosis in mice is the lysis of infected hepatocytes by leukocytes that accumulate at foci of infection in the liver. This serves to release Listeria monocytogenes from permissive parenchymal cells for ingestion and inactivation by phagocytic cells. It is shown here that lysis of infected hepatocytes is as extensive in mice depleted of T cells or NK cells as it is in control mice. This supports the original interpretation that hepatocyte lysis is mediated mainly by neutrophils.
Full text
PDF
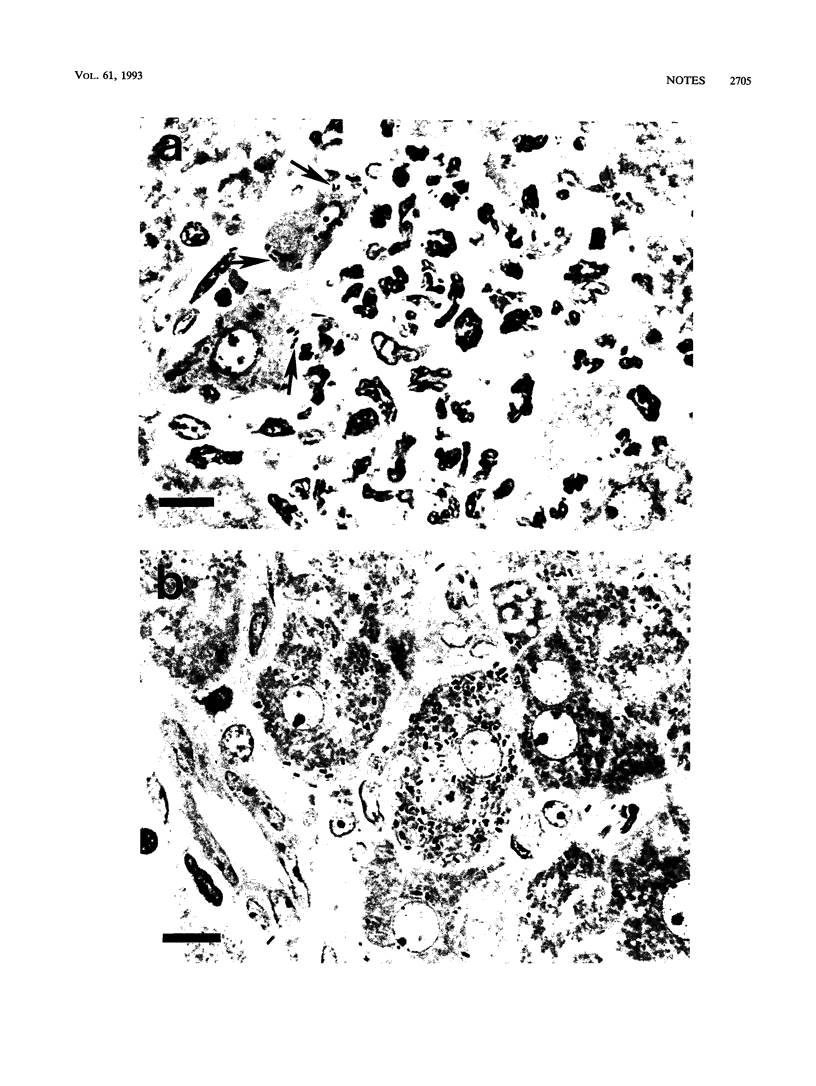

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldridge J. R., Barry R. A., Hinrichs D. J. Expression of systemic protection and delayed-type hypersensitivity to Listeria monocytogenes is mediated by different T-cell subsets. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):654–658. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.654-658.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
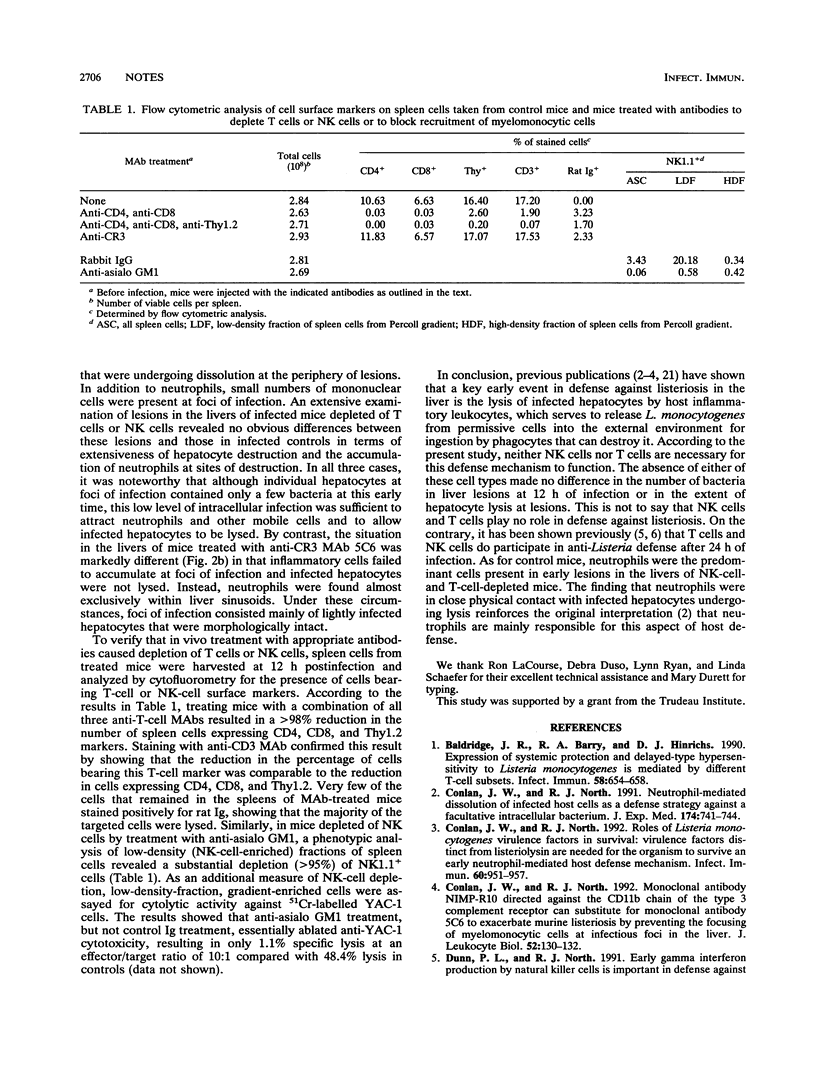
- Conlan J. W., North R. J. Monoclonal antibody NIMP-R10 directed against the CD11b chain of the type 3 complement receptor can substitute for monoclonal antibody 5C6 to exacerbate listeriosis by preventing the focusing of myelomonocytic cells at infectious foci in the liver. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Jul;52(1):130–132. doi: 10.1002/jlb.52.1.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan J. W., North R. J. Neutrophil-mediated dissolution of infected host cells as a defense strategy against a facultative intracellular bacterium. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):741–744. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan J. W., North R. J. Roles of Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors in survival: virulence factors distinct from listeriolysin are needed for the organism to survive an early neutrophil-mediated host defense mechanism. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):951–957. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.951-957.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. L., North R. J. Early gamma interferon production by natural killer cells is important in defense against murine listeriosis. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2892–2900. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2892-2900.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. L., North R. J. Resolution of primary murine listeriosis and acquired resistance to lethal secondary infection can be mediated predominantly by Thy-1+ CD4- CD8- cells. J Infect Dis. 1991 Nov;164(5):869–877. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.5.869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goossens P. L., Jouin H., Milon G. Dynamics of lymphocytes and inflammatory cells recruited in liver during murine listeriosis. A cytofluorimetric study. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 15;147(10):3514–3520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Synthesis and secretion of interferon by murine fibroblasts in response to intracellular Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):787–792. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.787-792.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L. A., Ault K. A. Characterization of natural killer cells induced in the peritoneal exudates of mice infected with Listeria monocytogenes: a study of their tumor target specificity and their expression of murine differentiation antigens and human NK-associated antigens. Cell Immunol. 1984 Nov;89(1):151–168. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Yeager H., Jr, Whalen G., Evans M., Swartz R. P., Roecklein J. Natural killer cell-mediated lysis of Mycobacterium-avium complex-infected monocytes. J Clin Immunol. 1990 Jan;10(1):71–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00917500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Hug E., De Libero G. Listeria monocytogenes-reactive T lymphocyte clones with cytolytic activity against infected target cells. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):363–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel G. R., Niesel D. W., Klimpel K. D. Natural cytotoxic effector cell activity against Shigella flexneri-infected HeLa cells. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1081–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo G. C., Dumont F. J., Tutt M., Hackett J., Jr, Kumar V. The NK-1.1(-) mouse: a model to study differentiation of murine NK cells. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 15;137(12):3742–3747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Hill W. C. The effect of anti-lymphocyte globulin on cell-mediated reistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):993–1012. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland H. I., Nahill S. R., Maciaszek J. W., Welsh R. M. CD11b (Mac-1): a marker for CD8+ cytotoxic T cell activation and memory in virus infection. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1326–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pamer E. G., Harty J. T., Bevan M. J. Precise prediction of a dominant class I MHC-restricted epitope of Listeria monocytogenes. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):852–855. doi: 10.1038/353852a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Gordon S. Monoclonal antibody to the murine type 3 complement receptor inhibits adhesion of myelomonocytic cells in vitro and inflammatory cell recruitment in vivo. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1685–1701. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Gordon S., North R. J. Exacerbation of murine listeriosis by a monoclonal antibody specific for the type 3 complement receptor of myelomonocytic cells. Absence of monocytes at infective foci allows Listeria to multiply in nonphagocytic cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):27–37. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rácz P., Tenner K., Mérö E. Experimental Listeria enteritis. I. An electron microscopic study of the epithelial phase in experimental listeria infection. Lab Invest. 1972 Jun;26(6):694–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun A. N., Camilli A., Portnoy D. A. Isolation of Listeria monocytogenes small-plaque mutants defective for intracellular growth and cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3770–3778. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3770-3778.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Patarroyo M., Gahmberg C. G. CD11a-c/CD18 and GP84 (LB-2) adhesion molecules on human large granular lymphocytes and their participation in natural killing. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):1041–1046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]