Abstract
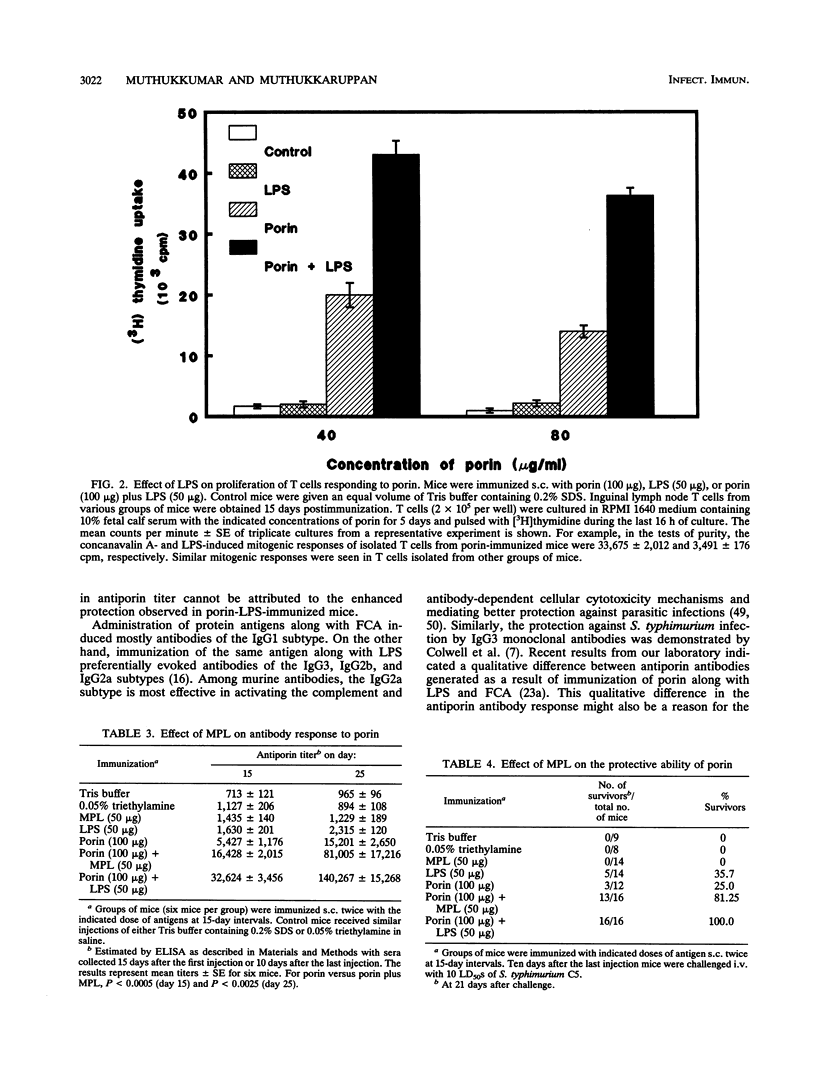
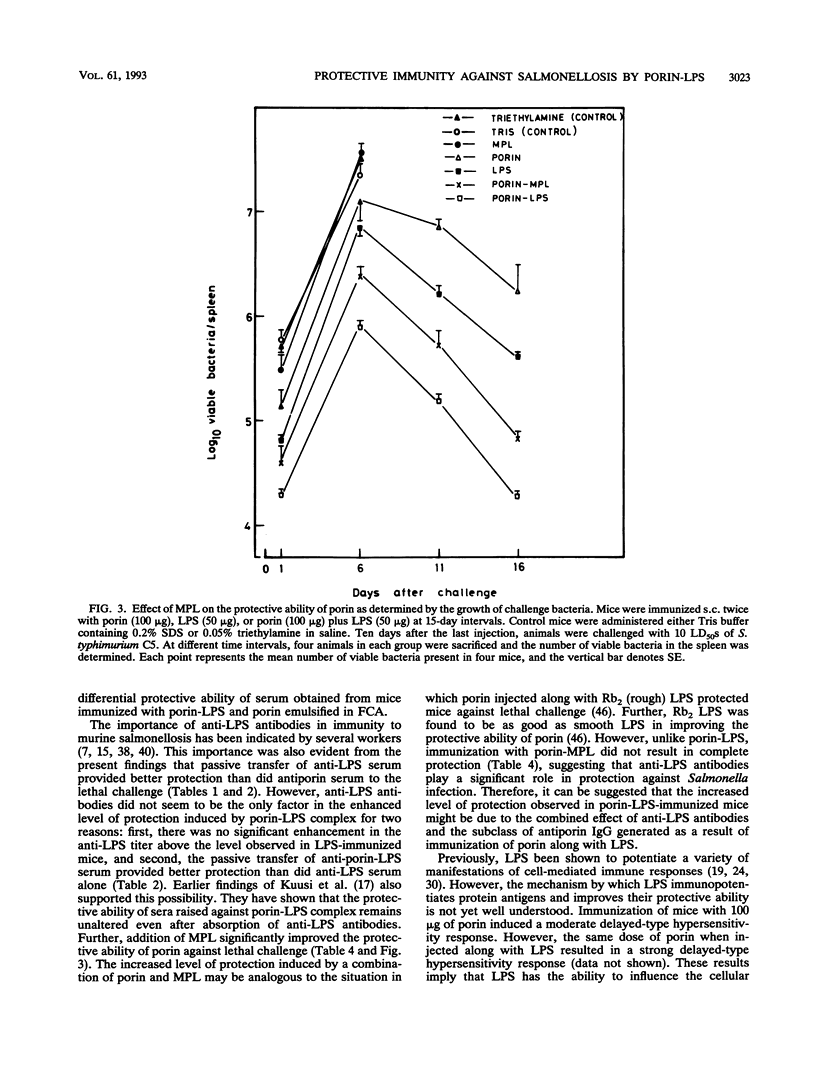
Investigations were undertaken to characterize the protective immunity induced by porin-lipopolysaccharide (LPS) against Salmonella typhimurium infection in mice. Mice immunized with porin-LPS showed higher levels of antiporin immunoglobulin G than mice which received porin alone. Further, T cells from porin-LPS-immunized mice showed an augmented proliferative response to porin in vitro compared with the response of T cells from porin-injected animals. The passive transfer of anti-LPS antibodies conferred significant protection (17%), while antiporin serum failed to protect mice against lethal challenge, indicating the protective ability of anti-LPS antibodies. However, the transfer of serum obtained from porin-LPS-immunized mice resulted in better protection (30%) than did anti-LPS or antiporin antibodies alone. In contrast to LPS, monophosphoryl lipid A completely failed to induce protection against lethal infection. However, comparable to the effect of LPS, injection of porin with monophosphoryl lipid A enhanced antibody response and the protective ability of porin (81.25%). The transfer of T cells from porin-LPS-immunized mice provided higher levels of protection (47%) against lethal challenge than did T cells from porin-immunized mice (23%). The combination of T cells and serum from porin-immunized mice transferred 36% protection. However, a combination of T cells and serum from porin-LPS-immunized mice conferred the highest level of protection (92%), which was reflected by the number of survivors (100%) in the porin-LPS-immunized group. These results demonstrate that besides the protective effect of anti-LPS antibodies, the ability of LPS to augment humoral and cell-mediated immune responses to porin confers effective protection against Salmonella infection.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Davies A. J. Requirement of thymus-dependent lymphocytes for potentiation by adjuvants of antibody formation. Nature. 1971 Oct 1;233(5318):330–332. doi: 10.1038/233330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armerding D., Katz D. H. Activation of T and B lymphocytes in vitro. I. Regulatory influence of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on specific T-cell helper function. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):24–43. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar N., Müller W., Schlecht S. Proteins from Salmonella R-mutants mediating protection against Salmonella typhimurium infection in mice I. Preparation of proteins free from lipopolysaccharide using various chromatographic methods. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1982 Oct;253(1):88–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bismuth G., Duphot M., Theze J. LPS and specific T cell responses: interleukin 1 (IL 1)-independent amplification of antigen-specific T helper (TH) cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1415–1421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Langman R. E. Cell-mediated immunity to bacterial infection in the mouse. Thymus-derived cells as effectors of acquired resistance to Listeria monocytogenes. Scand J Immunol. 1972;1(4):379–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1972.tb03304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiller J. M., Weigle W. O. Termination of tolerance to human gamma globulin in mice by antigen and bacterial lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin). J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):740–750. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell D. E., Michalek S. M., Briles D. E., Jirillo E., McGhee J. R. Monoclonal antibodies to Salmonella lipopolysaccharide: anti-O-polysaccharide antibodies protect C3H mice against challenge with virulent Salmonella typhimurium. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):950–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjipetrou-Kourounakis L., Möller E. Adjuvants influence the immunoglobin subclass distribution of immune responses in vivo. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Mar;19(3):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON A. G., GAINES S., LANDY M. Studies on the O antigen of Salmonella typhosa. V. Enhancement of antibody response to protein antigens by the purified lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1956 Feb 1;103(2):225–246. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörbeck H. J., Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Artificial Salmonella vaccines: Salmonella typhimurium O-antigen-specific oligosaccharide-protein conjugates elicit opsonizing antibodies that enhance phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):497–502. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.497-502.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killion J. W., Morrison D. C. Determinants of immunity to murine salmonellosis: studies involving immunization with lipopolysaccharide-lipid A-associated protein complexes in C3H/HeJ mice. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1988 Jan;1(1):41–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1988.tb02489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killion J. W., Morrison D. C. Protection of C3H/HeJ mice from lethal Salmonella typhimurium LT2 infection by immunization with lipopolysaccharide-lipid A-associated protein complexes. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.1-8.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxen H., Valtonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane proteins in experimental salmonellosis of mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):857–862. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.857-862.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxén H., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane protein (porin) preparations in experimental murine salmonellosis: effect of lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):328–332. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.328-332.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrange P. H., Mackaness G. B. Effects of bacterial lipopolysaccharide on the induction and expression of cell-mediated immunity. II. Stimulation of the efferent arc. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):447–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt M. L., Johnson W. Identification of protective cell surface proteins in ribosomal fractions from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):808–816. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.808-816.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mita A., Ohta H., Mita T. Induction of splenic T cell proliferation by lipid A in mice immunized with sheep red blood cells. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1709–1711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukkumar S., Muthukkaruppan V. R. Detection of porin antigen in serum for early diagnosis of mouse infections with Salmonella typhimurium. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1992 Feb;4(3):147–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb04981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutoh N., Furukawa H., Mizushima S. Role of lipopolysaccharide and outer membrane protein of Escherichia coli K-12 in the receptor activity for bacteriophage T4. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):693–699. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.693-699.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan P. R., Sundharadas G. Differential effects of polyadenylic: polyuridylic acid and lipopolysaccharide on the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1355–1362. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness D. B., Smith S., Talcott J. A., Grumet F. C. T cell requirements for the expression of the lipopolysaccharide adjuvant effect in vivo: evidence for a T cell-dependent and a T cell-independent mode of action. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Sep;6(9):650–654. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newburger P. E., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. Potentiation of helper T cell function in IgE antibody responses by bacterial lipolysaccharide (LPS). J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):824–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Importance of thymus-derived lymphocytes in cell-mediated immunity to infection. Cell Immunol. 1973 Apr;7(1):166–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ortiz L., Jaroslow B. N. Enhancement by the adjuvant, endotoxin, of an immune response induced in vitro. Immunology. 1970 Sep;19(3):387–399. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Wu H. C. Proteins of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:369–422. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Adler W. H., Ebert J. D. Synergism of bacterial lipopolysaccharides and concanavalin A in the activation of thymic lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jun;17(2):532–541. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J. E., Glynn A. A., Valtonen M. V. O-antigenic specificity of the protective supernatant factor from Salmonella typhimurium effective in S. typhimurium-infected mice. Parasite Immunol. 1980 Winter;2(4):293–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1980.tb00060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J. E., Wilson B. M., Glynn A. A. The protein-lipopolysaccharide complex extracted with trichloracetic acid from Salmonella typhimurium effective in protection of mice against S. typhimurium infection. Parasite Immunol. 1982 Jul;4(4):259–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1982.tb00437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A., Wilson B. M. Protective effects of a supernatant factor from Salmonella typhimurium on Salmonella typhimurium infection of inbred mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):125–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.125-131.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribi E., Cantrell J. L., Takayama K., Qureshi N., Peterson J., Ribi H. O. Lipid A and immunotherapy. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):567–572. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocque W. J., Coughlin R. T., McGroarty E. J. Lipopolysaccharide tightly bound to porin monomers and trimers from Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4003–4010. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4003-4010.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saijo N. A spectrophotometric quantitation of cytotoxic action of antiserum and complement by trypan blue. Immunology. 1973 Apr;24(4):683–690. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxen H., Mäkelä O. The protective capacity of immune sera in experimental mouse salmonellosis is mainly due to IgM antibodies. Immunol Lett. 1982 Nov;5(5):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(82)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlecht S., Bhatnagar N. Proteins from Salmonella R-mutants mediating protection against Salmonella typhimurium infection in mice. II. Protection tests performed with proteins free from lipopolysaccharide. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 May;259(3):367–377. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Artificial Salmonella vaccines: Salmonella typhimurium O-antigen-specific oligosaccharide-protein conjugates elicit protective antibodies in rabbits and mice. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.490-496.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga M., Tokunaga H., Okajima Y., Nakae T. Characterization of porins from the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. 2. Physical properties of the functional oligomeric aggregates. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):441–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomai M. A., Solem L. E., Johnson A. G., Ribi E. The adjuvant properties of a nontoxic monophosphoryl lipid A in hyporesponsive and aging mice. J Biol Response Mod. 1987 Apr;6(2):99–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udhayakumar V., Muthukkaruppan V. R. An outer membrane protein (porin) as an eliciting antigen for delayed-type hypersensitivity in murine salmonellosis. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):822–824. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.822-824.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udhayakumar V., Muthukkaruppan V. R. Protective immunity induced by outer membrane proteins of Salmonella typhimurium in mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):816–821. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.816-821.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udhayakumar V., Muthukkaruppan V. Characteristics of live vaccines in relation to delayed-type hypersensitivity and protective immunity in murine experimental salmonellosis. Immunol Lett. 1983 Jun;6(6):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(83)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udhayakumar V., Muthukkaruppan V. Protective immunity induced by porin against Salmonella infection in mice. Indian J Med Res. 1989 May;89:121–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. S. Mediation of macrophage cytolytic and phagocytic activities by antibodies of different classes and class-specific Fc-receptors. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):367–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler D. S., Kongshavn P. A. Heat-labile IgG2a antibodies affect cure of Trypanosoma musculi infection in C57BL/6 mice. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2968–2972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Mizushima S. Interaction between major outer membrane protein (O-8) and lipopolysaccharide in Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(1):209–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Loo W., Gronowicz E. S., Strober S., Herzenberg L. A. Cell differentiation in the presence of cytochalasin B: studies on the "switch" to IgG secretion after polyclonal B cell activation. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1203–1208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


