Abstract
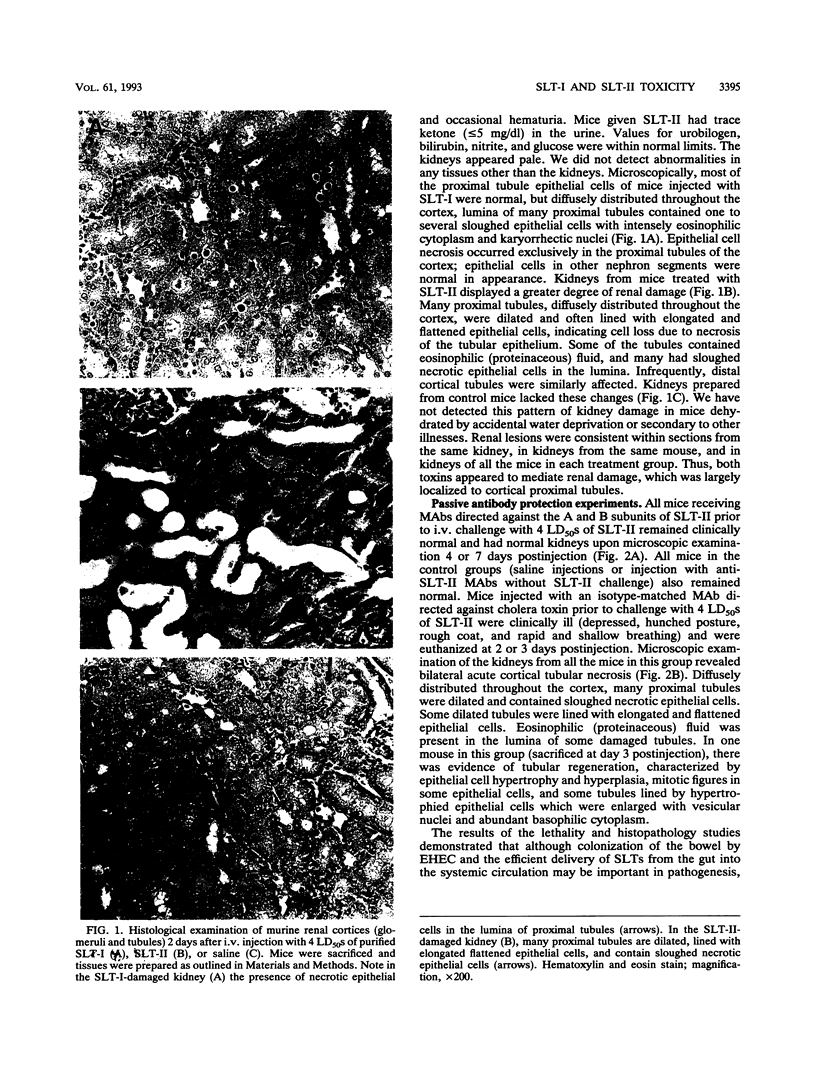
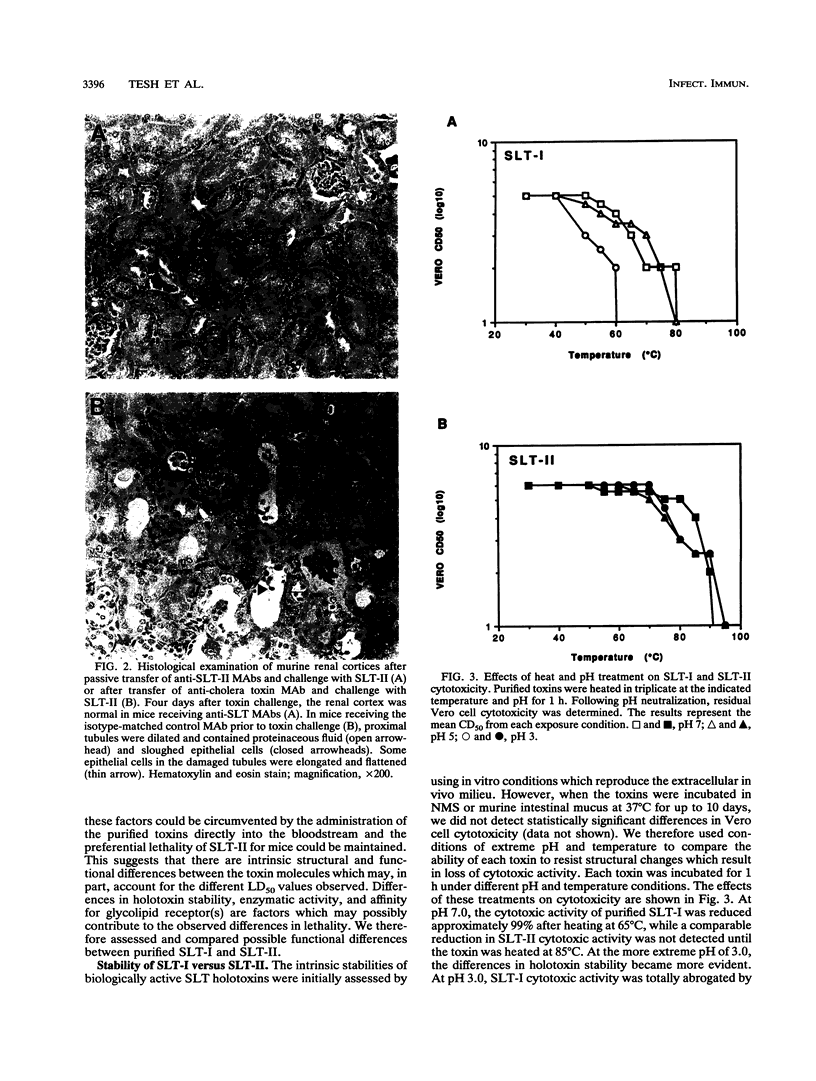
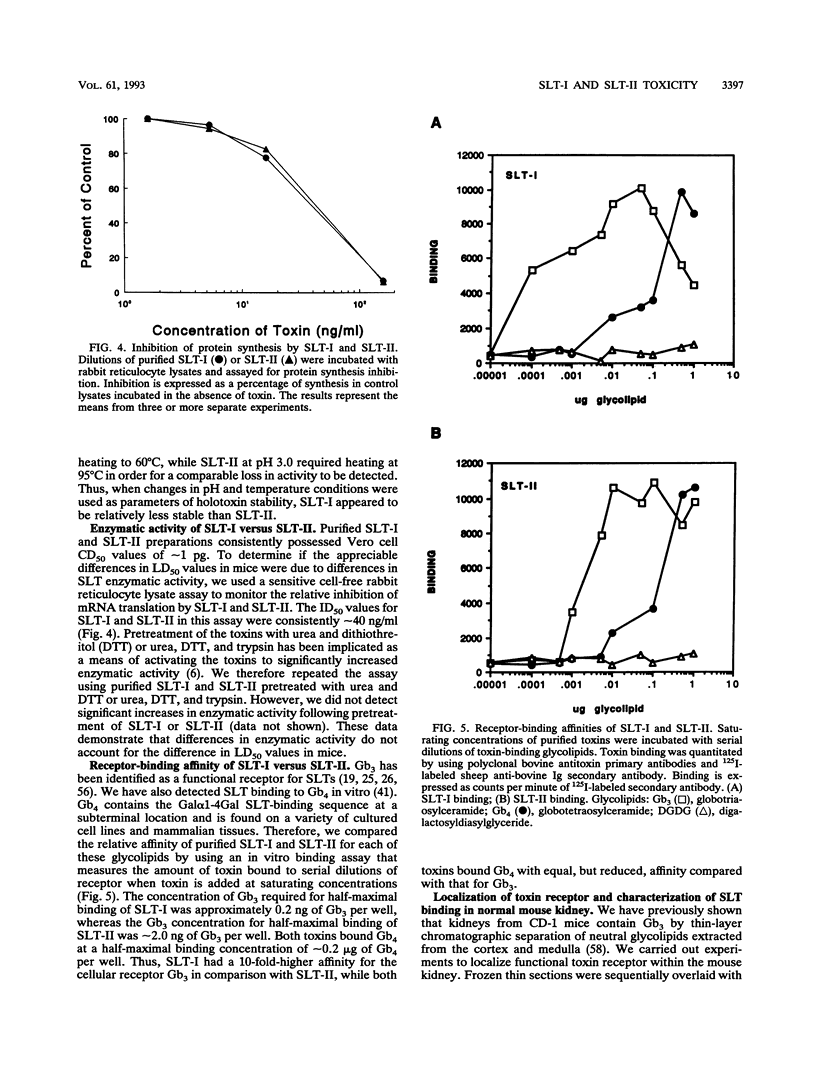
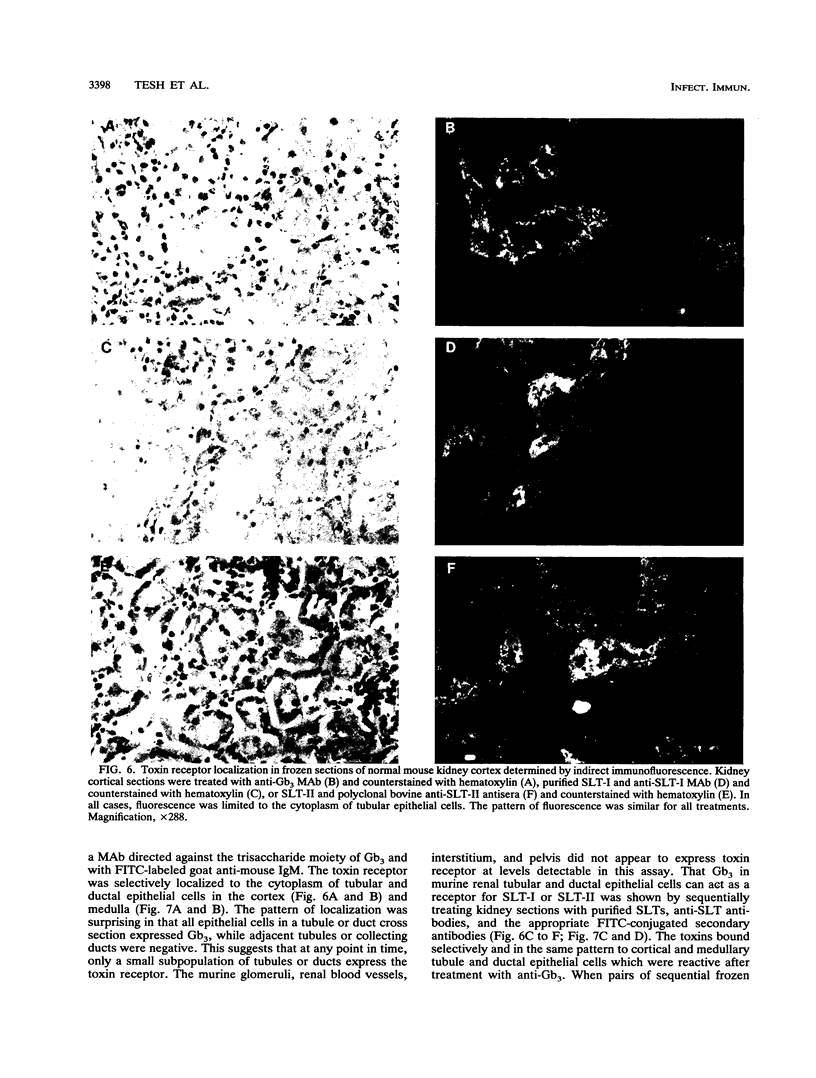
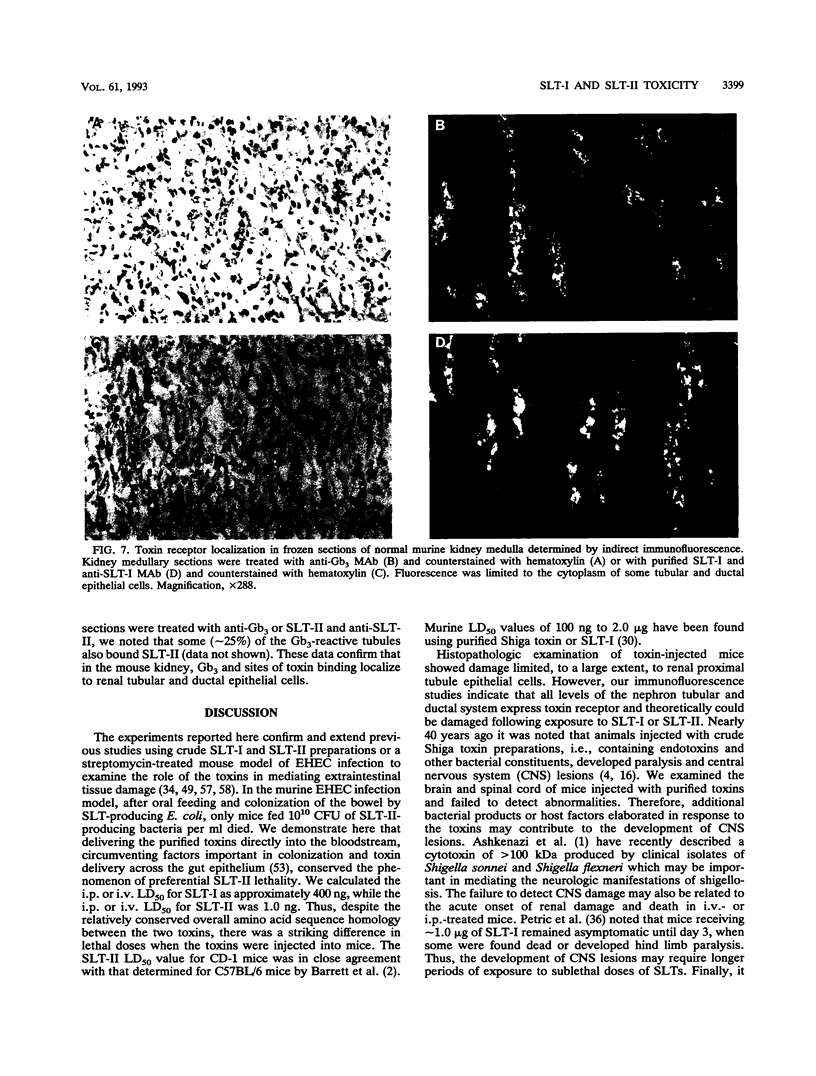
In earlier studies using a streptomycin-treated mouse model of infection caused by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC), animals fed Shiga-like toxin type II (SLT-II)-producing strains developed acute renal cortical necrosis and died, while mice fed Shiga-like toxin type I (SLT-I)-producing clones did not die (E. A. Wadolkowski, L. M. Sung, J. A. Burris, J. E. Samuel, and A. D. O'Brien, Infect. Immun. 58:3959-3965, 1990). To examine the bases for the differences we noted between the two toxins in the murine infection model, we injected mice with purified toxins and carried out histopathological examinations. Despite the genetic and structural similarities between the two toxins, SLT-II had a 50% lethal dose (LD50) which was approximately 400 times lower than that of SLT-I when injected intravenously or intraperitoneally into mice. Histopathologic examination of toxin-injected mice revealed that detectable damage was limited to renal cortical tubule epithelial cells. Passive administration of anti-SLT-II antibodies protected mice from SLT-II-mediated kidney damage and death. Immunofluorescence staining of normal murine kidney sections incubated with purified SLT-I or SLT-II demonstrated that both toxins bound to cortical tubule and medullary duct epithelial cells. Compared with SLT-I, SLT-II was more heat and pH stable, suggesting that SLT-II is a relatively more stable macromolecule. Although both toxins bound to globotriaosylceramide, SLT-I bound with a higher affinity in a solid-phase binding assay. Differences in enzymatic activity between the two toxins were not detected. These data suggest that structural/functional differences between the two toxins, possibly involving holotoxin stability and/or receptor affinity, may contribute to the differential LD50s in mice.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi S., Cleary K. R., Pickering L. K., Murray B. E., Cleary T. G. The association of Shiga toxin and other cytotoxins with the neurologic manifestations of shigellosis. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):961–965. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIDGWATER F. A., MORGAN R. S., ROWSON K. E., WRIGHT G. P. The neurotoxin of Shigella shigae: morphological and functional lesions produced in the central nervous system of rabbits. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Oct;36(5):447–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. J., Potter M. E., Strockbine N. A. Evidence for participation of the macrophage in Shiga-like toxin II-induced lethality in mice. Microb Pathog. 1990 Aug;9(2):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd B., Lingwood C. Verotoxin receptor glycolipid in human renal tissue. Nephron. 1989;51(2):207–210. doi: 10.1159/000185286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodin N. T., Dahmén J., Nilsson B., Messeter L., Mårtensson S., Heldrup J., Sjögren H. O., Lundblad A. Monoclonal antibodies produced by immunization with neoglycoproteins containing Gal alpha 1-4Gal beta 1-4Glc beta-O and Gal alpha 1-4Gal beta 1-4GlcNAc beta-O residues: useful immunochemical and cytochemical reagents for blood group P antigens and a differentiation marker in Burkitt lymphoma and other B-cell malignancies. Int J Cancer. 1988 Aug 15;42(2):185–194. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Ussery M. A., Leppla S. H., Rothman S. W. Inhibition of protein synthesis by Shiga toxin: activation of the toxin and inhibition of peptide elongation. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):84–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80918-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Madrid-Marina V., Estrov Z., Freedman M. H., Lingwood C. A., Dosch H. M. Expression of glycolipid receptors to Shiga-like toxin on human B lymphocytes: a mechanism for the failure of long-lived antibody response to dysenteric disease. Int Immunol. 1990;2(1):1–8. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Edson C., Thorley-Lawson D., Jacewicz M. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. IX. Simplified high yield purification of Shigella toxin and characterization of subunit composition and function by the use of subunit-specific monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1767–1781. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes F. P., Barrett T. J., Green J. H., Aloisio C. H., Spika J. S., Strockbine N. A., Wachsmuth I. K. Affinity purification and characterization of Shiga-like toxin II and production of toxin-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1926–1933. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1926-1933.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K., Yutsudo T., Takeda Y., Ogasawara T., Igarashi K. Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes. RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon V. P., Teerling C., Masri S. A., Gyles C. L. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of another variant of the Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxin II family. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1125–1135. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-6-1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. K., Dalrymple J. M. Quantitative microtiter cytotoxicity assay for Shigella toxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):361–366. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.361-366.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon V. M., Whipp S. C., Moon H. W., O'Brien A. D., Samuel J. E. An enzymatic mutant of Shiga-like toxin II variant is a vaccine candidate for edema disease of swine. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):485–490. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.485-490.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD J. G. Observations on the intoxication produced in mice and rabbits by the neurotoxin of Shigella shigae. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Oct;36(5):439–446. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head S. C., Karmali M. A., Lingwood C. A. Preparation of VT1 and VT2 hybrid toxins from their purified dissociated subunits. Evidence for B subunit modulation of a subunit function. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3617–3621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Twiddy E. M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies that react with unique and cross-reacting determinants of cholera enterotoxin and its subunits. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):914–923. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.914-923.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Terai A., Kurazono H., Takeda Y., Nishibuchi M. Cloning and nucleotide sequencing of Vero toxin 2 variant genes from Escherichia coli O91:H21 isolated from a patient with the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jan;8(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90007-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacewicz M., Clausen H., Nudelman E., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea. XI. Isolation of a shigella toxin-binding glycolipid from rabbit jejunum and HeLa cells and its identification as globotriaosylceramide. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1391–1404. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jevnikar A. M., Brennan D. C., Singer G. G., Heng J. E., Maslinski W., Wuthrich R. P., Glimcher L. H., Kelley V. E. Stimulated kidney tubular epithelial cells express membrane associated and secreted TNF alpha. Kidney Int. 1991 Aug;40(2):203–211. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleanthous H., Smith H. R., Scotland S. M., Gross R. J., Rowe B., Taylor C. M., Milford D. V. Haemolytic uraemic syndromes in the British Isles, 1985-8: association with verocytotoxin producing Escherichia coli. Part 2: Microbiological aspects. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Jul;65(7):722–727. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.7.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A., Law H., Richardson S., Petric M., Brunton J. L., De Grandis S., Karmali M. Glycolipid binding of purified and recombinant Escherichia coli produced verotoxin in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8834–8839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louise C. B., Obrig T. G. Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: combined cytotoxic effects of shiga toxin and lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin) on human vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1536–1543. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1536-1543.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Strockbine N. A., Neill R. J. Cloning of genes for production of Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxin type II. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2675–2680. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2675-2680.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Shiga and Shiga-like toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):206–220. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.206-220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara T., Ito K., Igarashi K., Yutsudo T., Nakabayashi N., Takeda Y. Inhibition of protein synthesis by a Vero toxin (VT2 or Shiga-like toxin II) produced by Escherichia coli O157:H7 at the level of elongation factor 1-dependent aminoacyl-tRNA binding to ribosomes. Microb Pathog. 1988 Feb;4(2):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Reisbig R., Eiklid K. Subunit structure of Shigella cytotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8732–8738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff S. M., Tarr P. I., Neill M. A., Lewis J. H., Hargrett-Bean N., Kobayashi J. M. Toxin genotypes and plasmid profiles as determinants of systemic sequelae in Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):994–998. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padhye V. V., Beery J. T., Kittell F. B., Doyle M. P. Colonic hemorrhage produced in mice by a unique vero cell cytotoxin from an Escherichia coli strain that causes hemorrhagic colitis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1249–1253. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Marques L. R., O'Brien A. D. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Shiga-like toxin II of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli and use of the monoclonal antibodies in a colony enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2127–2131. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2127-2131.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remuzzi G. HUS and TTP: variable expression of a single entity. Kidney Int. 1987 Aug;32(2):292–308. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson S. E., Karmali M. A., Becker L. E., Smith C. R. The histopathology of the hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Hum Pathol. 1988 Sep;19(9):1102–1108. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel J. E., Perera L. P., Ward S., O'Brien A. D., Ginsburg V., Krivan H. C. Comparison of the glycolipid receptor specificities of Shiga-like toxin type II and Shiga-like toxin type II variants. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):611–618. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.611-618.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena S. K., O'Brien A. D., Ackerman E. J. Shiga toxin, Shiga-like toxin II variant, and ricin are all single-site RNA N-glycosidases of 28 S RNA when microinjected into Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):596–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt C. K., McKee M. L., O'Brien A. D. Two copies of Shiga-like toxin II-related genes common in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli strains are responsible for the antigenic heterogeneity of the O157:H- strain E32511. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1065–1073. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1065-1073.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotland S. M., Willshaw G. A., Smith H. R., Rowe B. Properties of strains of Escherichia coli belonging to serogroup O157 with special reference to production of Vero cytotoxins VT1 and VT2. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Dec;99(3):613–624. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800066462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Green P., Parsell Z. Vero cell toxins in Escherichia coli and related bacteria: transfer by phage and conjugation and toxic action in laboratory animals, chickens and pigs. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3121–3137. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. E., Boodhoo A., Tyrrell G. J., Brunton J. L., Read R. J. Crystal structure of the cell-binding B oligomer of verotoxin-1 from E. coli. Nature. 1992 Feb 20;355(6362):748–750. doi: 10.1038/355748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Jackson M. P., Sung L. M., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Cloning and sequencing of the genes for Shiga toxin from Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1116–1122. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1116-1122.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Shiga-like toxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):695–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.695-700.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Newland J. W., Smith H. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Two toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 933 encode antigenically distinct toxins with similar biologic activities. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.135-140.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung L. M., Jackson M. P., O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Transcription of the Shiga-like toxin type II and Shiga-like toxin type II variant operons of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6386–6395. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6386-6395.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., O'Brien A. D. Adherence and colonization mechanisms of enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1992 Apr;12(4):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90043-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., O'Brien A. D. The pathogenic mechanisms of Shiga toxin and the Shiga-like toxins. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1817–1822. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., Samuel J. E., Perera L. P., Sharefkin J. B., O'Brien A. D. Evaluation of the role of Shiga and Shiga-like toxins in mediating direct damage to human vascular endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):344–352. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell T., Head S., Petric M., Cohen A., Lingwood C. Globotriosyl ceramide is specifically recognized by the Escherichia coli verocytotoxin 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 29;152(2):674–679. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadolkowski E. A., Burris J. A., O'Brien A. D. Mouse model for colonization and disease caused by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2438–2445. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2438-2445.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadolkowski E. A., Sung L. M., Burris J. A., Samuel J. E., O'Brien A. D. Acute renal tubular necrosis and death of mice orally infected with Escherichia coli strains that produce Shiga-like toxin type II. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3959–3965. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3959-3965.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Jackson M. P., Perera L. P., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. In vivo formation of hybrid toxins comprising Shiga toxin and the Shiga-like toxins and role of the B subunit in localization and cytotoxic activity. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3743–3750. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3743-3750.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]