Abstract
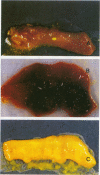
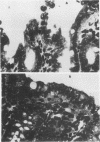
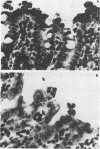
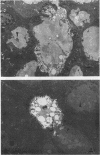
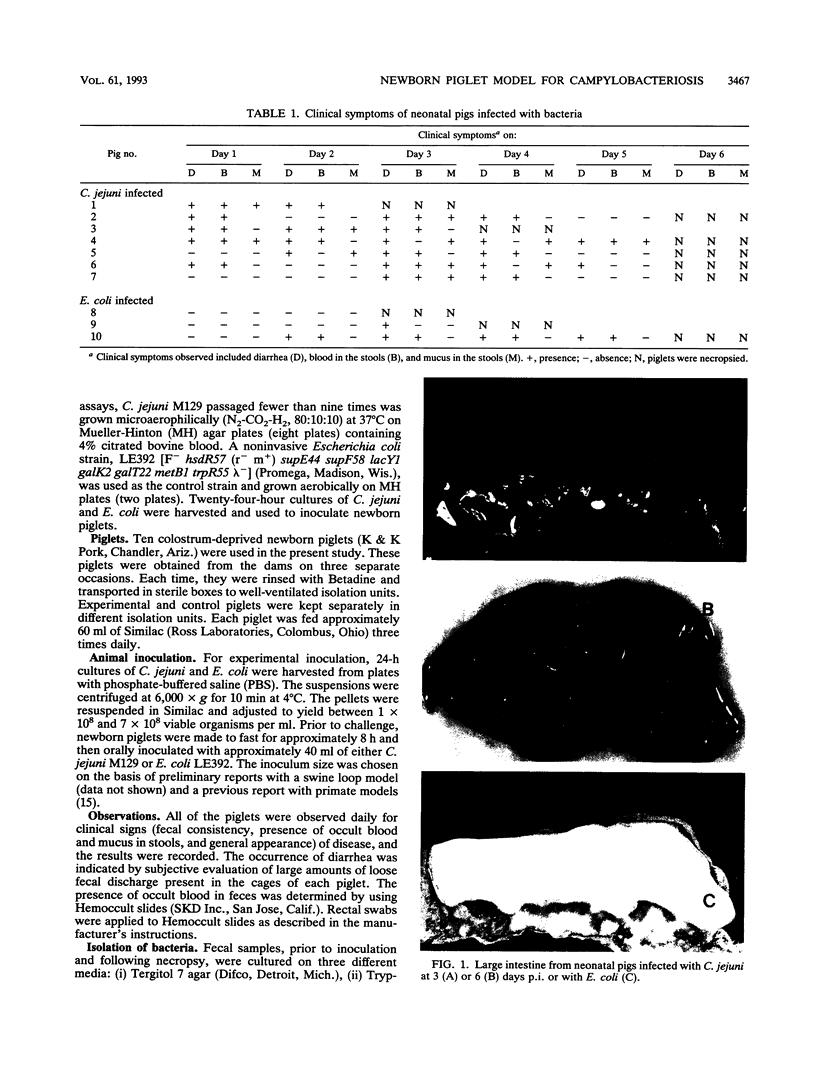
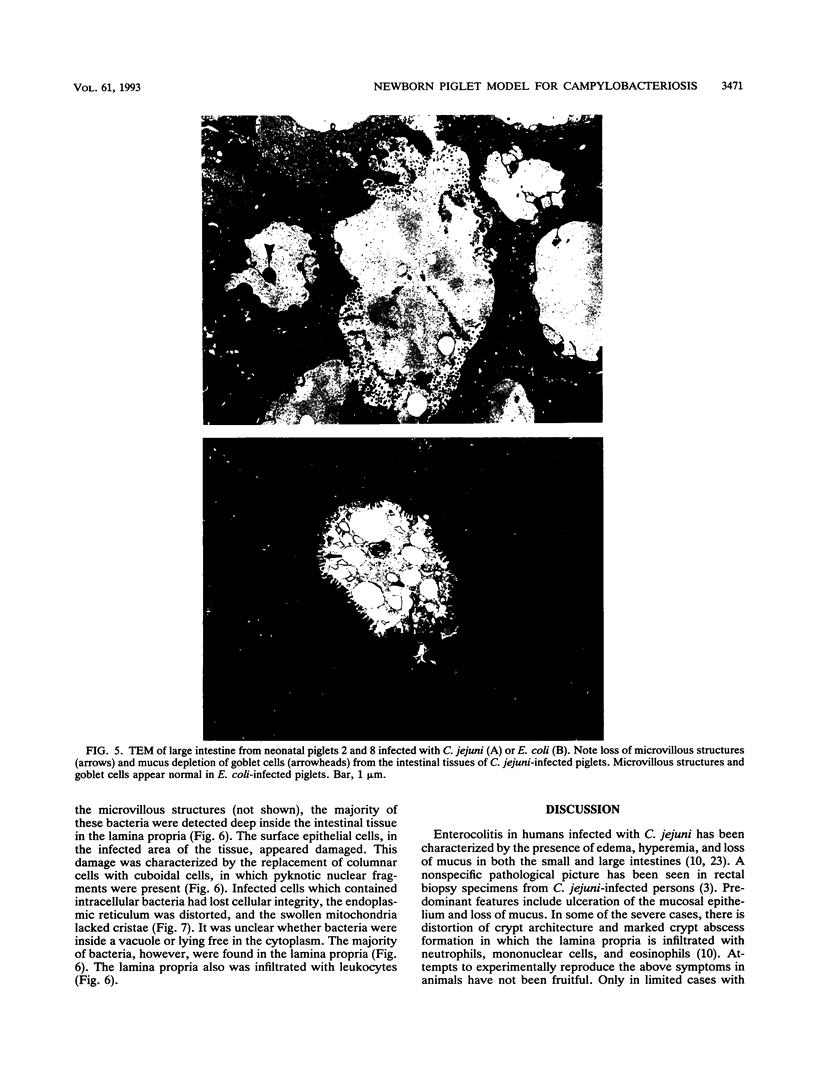
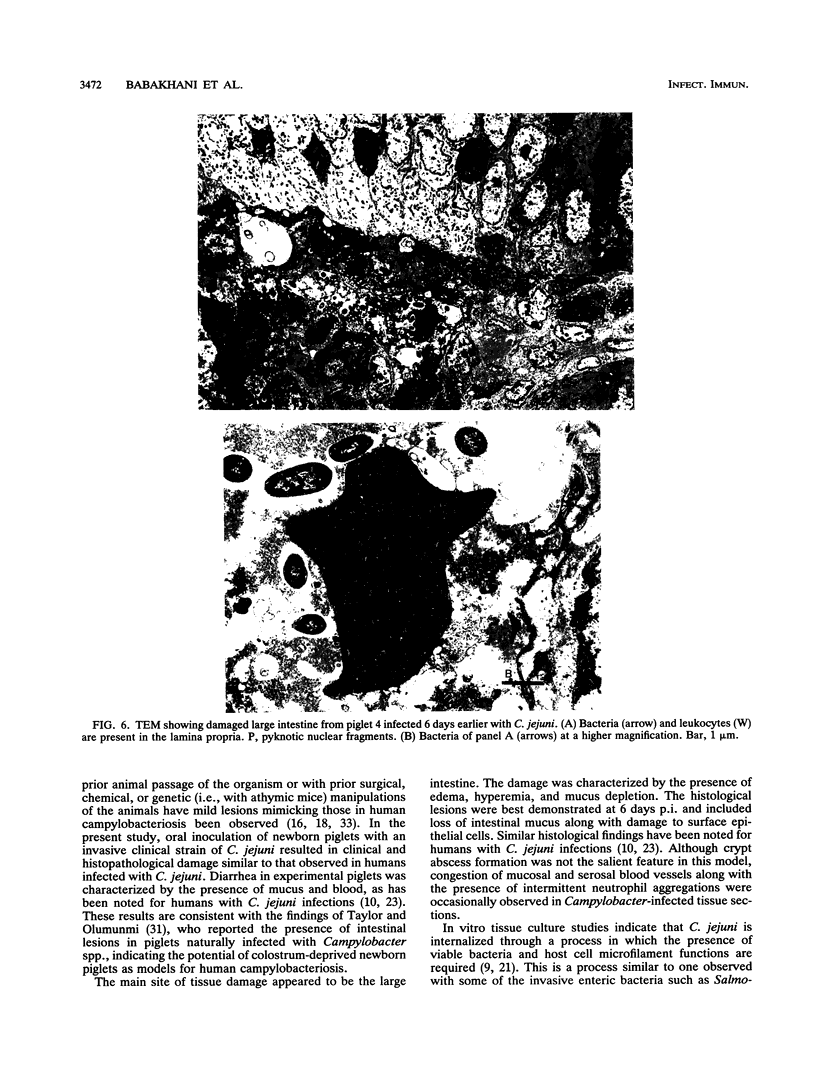
An in vivo model system for human campylobacteriosis has been developed in which colostrum-deprived newborn piglets are orally challenged with an invasive strain of Campylobacter jejuni. Piglets developed clinical symptoms and histopathological lesions similar to those observed in humans infected with C. jejuni. Gross lesion examination at autopsy revealed the presence of edema, hyperemia, and mucus. Histopathologic examinations by light and transmission electron microscopy demonstrated damage to surface epithelial cells with the presence of intracellular bacteria, mainly in the large intestine. Similar lesions were not demonstrated in control piglets.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J. A., Manning D. D. A domestic ferret model of immunity to Campylobacter jejuni-induced enteric disease. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1848–1852. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1848-1852.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. A., Manning D. D. Reproductive failure in mink and ferrets after intravenous or oral inoculation of Campylobacter jejuni. Can J Vet Res. 1990 Oct;54(4):432–437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Dekeyser P., Detrain M., Dehaen F. Related vibrio in stools. J Pediatr. 1973 Mar;82(3):493–495. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell M. B., Walker R. I., Stewart S. D., Rogers J. E. Simple adult rabbit model for Campylobacter jejuni enteritis. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1176–1182. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1176-1182.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Sansonetti P. J. Entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells: evidence for directed phagocytosis involving actin polymerization and myosin accumulation. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2681–2688. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2681-2688.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coker A. O., Obi C. L. Effect of iron-dextran on lethality of Nigerian isolates of Campylobacter jejuni in mice. Cent Afr J Med. 1991 Jan;37(1):20–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Melo M. A., Gabbiani G., Pechère J. C. Cellular events and intracellular survival of Campylobacter jejuni during infection of HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2214–2222. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2214-2222.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy M. C., Benson J. B., Rubin S. J. Mucosal invasion in campylobacter enteritis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 May;73(5):706–708. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/73.5.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. H., Underwood J. L., Payne S. M., Berry L. J. Virulence of Campylobacter jejuni for chicken embryos is associated with decreased bloodstream clearance and resistance to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1448–1456. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1448-1456.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. H., Underwood J. L., Pope L. M., Berry L. J. Intestinal colonization of neonatal animals by Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):884–892. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.884-892.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Comparison of the invasion strategies used by Salmonella cholerae-suis, Shigella flexneri and Yersinia enterocolitica to enter cultured animal cells: endosome acidification is not required for bacterial invasion or intracellular replication. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):1089–1099. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Salmonella as an intracellular parasite. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1833–1841. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgeorge R. B., Baskerville A., Lander K. P. Experimental infection of Rhesus monkeys with a human strain of Campylobacter jejuni. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Jun;86(3):343–351. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Ackerman J. I., Taylor N., Claps M., Murphy J. C. Campylobacter jejuni infection in the ferret: an animal model of human campylobacteriosis. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Jan;48(1):85–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Lahita R. G., Winn W. C., Jr, Roberts R. B. Campylobacteriosis in man: pathogenic mechanisms and review of 91 bloodstream infections. Am J Med. 1978 Oct;65(4):584–592. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90845-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey C. D., Montag D. M., Pittman F. E. Experimental infection of hamsters with Campylobacter jejuni. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):485–493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita E., Oku D., Hamuro A., Nishikawa F., Emoto M., Yagyu Y., Katsui N., Kashiba S. Hepatotoxic activity of Campylobacter jejuni. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Nov;33(3):171–182. doi: 10.1099/00222615-33-3-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel M. E., Babakhani F., Joens L. A. Invasion-related antigens of Campylobacter jejuni. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):888–895. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel M. E., Joens L. A. Adhesion to and invasion of HEp-2 cells by Campylobacter spp. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):2984–2990. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.2984-2990.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel M. E., Mead D. J., Hayes S. F., Cieplak W., Jr Translocation of Campylobacter jejuni across human polarized epithelial cell monolayer cultures. J Infect Dis. 1992 Aug;166(2):308–315. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.2.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manninen K. I., Prescott J. F., Dohoo I. R. Pathogenicity of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from animals and humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):46–52. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.46-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamed A., Zakuth V., Schwartz D., Spirer Z. The immune system response to Campylobacter infection. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(1):75–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Barker I. K., Manninen K. I., Miniats O. P. Campylobacter jejuni colitis in gnotobiotic dogs. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Oct;45(4):377–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Palacios G. M., Escamilla E., Torres N. Experimental Campylobacter diarrhea in chickens. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):250–255. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.250-255.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield J. T., McCardell B. A., Madden J. M. Campylobacter diarrhea in an adult mouse model. Microb Pathog. 1987 Sep;3(3):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. J., Olubunmi P. A. A re-examination of the role of Campylobacter fetus subspecies coli in enteric disease of the pig. Vet Rec. 1981 Aug 8;109(6):112–115. doi: 10.1136/vr.109.6.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vítovec J., Koudela B., Vladík P., Hausner O. Interaction of Cryptosporidium parvum and Campylobacter jejuni in experimentally infected neonatal mice. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1991 Jan;274(4):548–559. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yrios J. W., Balish E. Pathogenesis of Campylobacter spp. in athymic and euthymic germfree mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):384–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.384-392.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]