Abstract
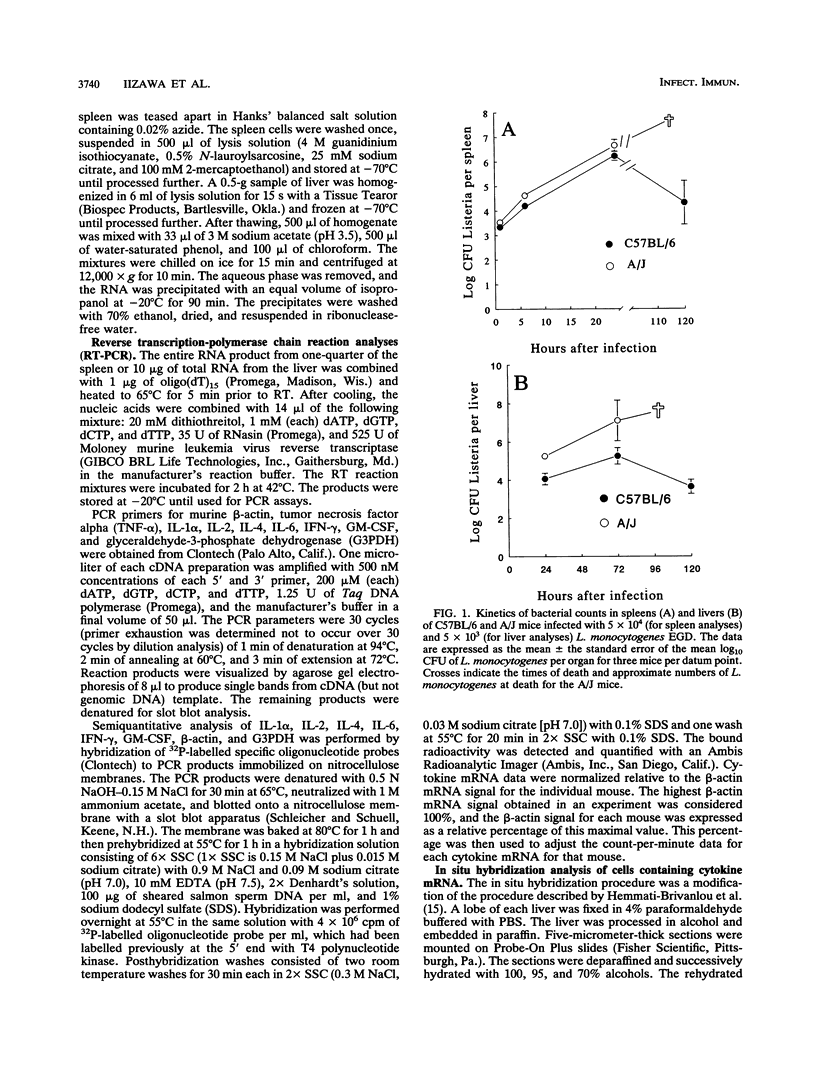
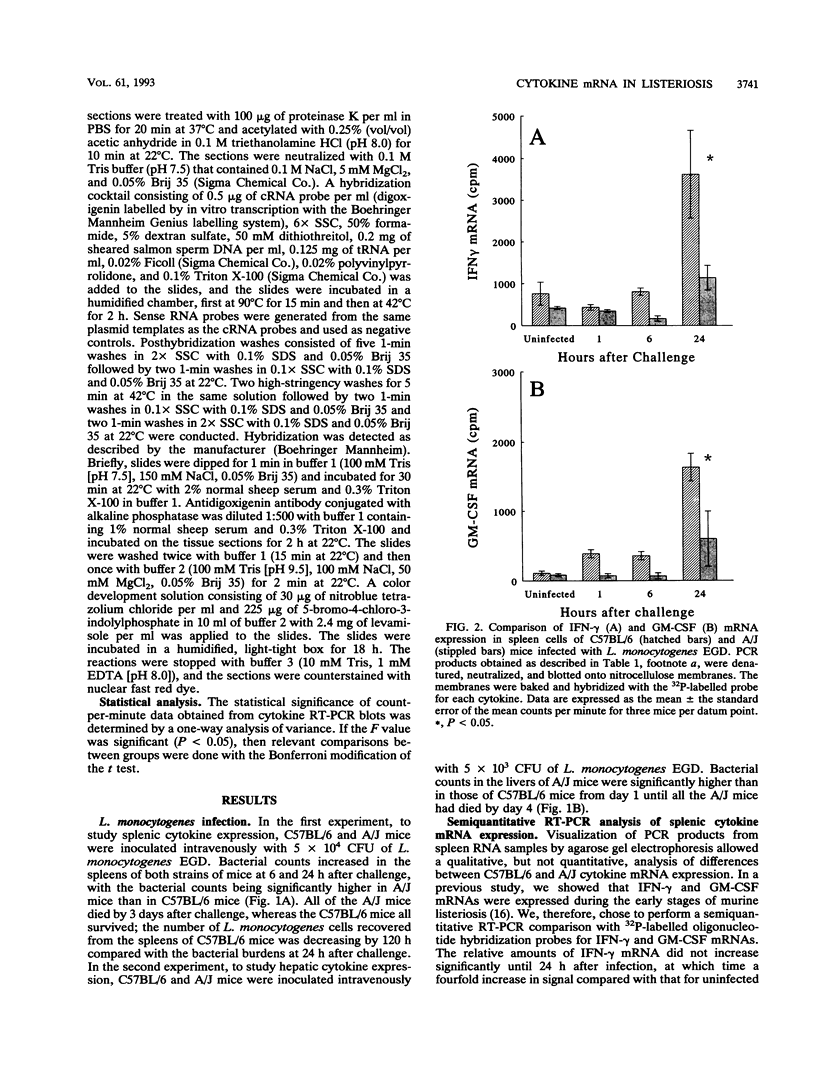
This laboratory previously reported that mRNA expression for many cytokines, as determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis, is induced rapidly in the spleen during murine listeriosis. In the present study, the patterns of cytokine mRNA expression in spleens and livers of Listeria-resistant C57BL/6 and Listeria-susceptible A/J mice were compared. In addition, in situ hybridization was performed to evaluate the distributions of cytokine mRNA-expressing cells in these tissues. Listeria-resistant C57BL/6 mice demonstrated greater expression of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) mRNAs in the spleen than Listeria-susceptible A/J mice. Greater numbers of cells expressing IFN-gamma and GM-CSF mRNAs were observed by in situ hybridization in the spleens of C57BL/6 mice than in those of A/J mice. C57BL/6 and A/J mice did not differ in their expression of IFN-gamma mRNA in the liver. Nor did C57BL/6 and A/J mice differ in their expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1 alpha), IL-2, IL-4, or IL-6 mRNA in the liver or spleen, as determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and in situ hybridization. These results indicate that the greater resistance of C57BL/6 mice to Listeria monocytogenes infection is associated with greater expression of IFN-gamma and GM-CSF mRNAs in the spleen and GM-CSF mRNA in the liver.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandwein S. R., Maenz L. Defective lipopolysaccharide-induced production of both interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta by A/J mouse macrophages is posttranscriptionally regulated. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Jun;51(6):570–578. doi: 10.1002/jlb.51.6.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Requirement of endogenous interferon-gamma production for resolution of Listeria monocytogenes infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7404–7408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Haigh A. M., Kelso A., Metcalf D., Stanley E. R., Young A. M. Production of colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) during infection: separate determinations of macrophage-, granulocyte-, granulocyte-macrophage-, and multi-CSFs. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):247–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.247-251.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., McKenzie I. F., Pavlov H., Waid C., York J. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: course of listeriosis in resistant or susceptible mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):763–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.763-770.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Canono B. P., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Genetically determined resistance to listeriosis is associated with increased accumulation of inflammatory neutrophils and macrophages which have enhanced listericidal activity. Immunology. 1985 Jul;55(3):511–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Killing of Listeria monocytogenes by inflammatory neutrophils and mononuclear phagocytes from immune and nonimmune mice. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Feb;35(2):193–208. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervais F., Morris-Hooke A., Tran T. A., Skamene E. Analysis of macrophage bactericidal function in genetically resistant and susceptible mice by using the temperature-sensitive mutant of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):315–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.315-321.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervais F., Stevenson M., Skamene E. Genetic control of resistance to Listeria monocytogenes: regulation of leukocyte inflammatory responses by the Hc locus. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):2078–2083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haak-Frendscho M., Brown J. F., Iizawa Y., Wagner R. D., Czuprynski C. J. Administration of anti-IL-4 monoclonal antibody 11B11 increases the resistance of mice to Listeria monocytogenes infection. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3978–3985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haak-Frendscho M., Young K. M., Czuprynski C. J. Treatment of mice with human recombinant interleukin-2 augments resistance to the facultative intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3014–3021. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3014-3021.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Moldawer L. L., Helfgott D., Kilian P. L., Sehgal P. B. Type I IL-1 receptor blockade exacerbates murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1486–1492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Sehgal P. B. Tumor necrosis factor-independent IL-6 production during murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):756–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Holaday B. J., Coffman R. L., Locksley R. M. Reciprocal expression of interferon gamma or interleukin 4 during the resolution or progression of murine leishmaniasis. Evidence for expansion of distinct helper T cell subsets. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):59–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Mutha S. S., Locksley R. M. Production of interferon gamma, interleukin 2, interleukin 4, and interleukin 10 by CD4+ lymphocytes in vivo during healing and progressive murine leishmaniasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7011–7015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati-Brivanlou A., Frank D., Bolce M. E., Brown B. D., Sive H. L., Harland R. M. Localization of specific mRNAs in Xenopus embryos by whole-mount in situ hybridization. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):325–330. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizawa Y., Brown J. F., Czuprynski C. J. Early expression of cytokine mRNA in mice infected with Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4068–4073. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4068-4073.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiderlen A. F., Kaufmann S. H., Lohmann-Matthes M. L. Protection of mice against the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes by recombinant immune interferon. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):964–967. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee D. M., Wing E. J. Secretion of colony-stimulating factors by T cell clones. Role in adoptive protection against Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2336–2341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kohanawa M., Chen Y., Sato H., Moriyama M., Tsuruoka N. Interactions between endogenous gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor in host resistance against primary and secondary Listeria monocytogenes infections. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3331–3337. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3331-3337.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Numata A., Minagawa T. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-6, and gamma interferon levels during Listeria monocytogenes infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):523–528. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.523-528.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Schreiber R. D., Connelly P., Tilney L. G. Gamma interferon limits access of Listeria monocytogenes to the macrophage cytoplasm. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2141–2146. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poston R. M., Kurlander R. J. Analysis of the time course of IFN-gamma mRNA and protein production during primary murine listeriosis. The immune phase of bacterial elimination is not temporally linked to IFN production in vivo. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4333–4337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M. M., Kongshavn P. A., Skamene E. Genetic linkage of resistance to Listeria monocytogenes with macrophage inflammatory responses. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):402–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. D., Czuprynski C. J. Cytokine mRNA expression in livers of mice infected with Listeria monocytogenes. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 May;53(5):525–531. doi: 10.1002/jlb.53.5.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. M., Cheers C. Colony-forming cells and colony-stimulating activity during listeriosis in genetically resistant or susceptible mice. Cell Immunol. 1986 Feb;97(2):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90393-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]