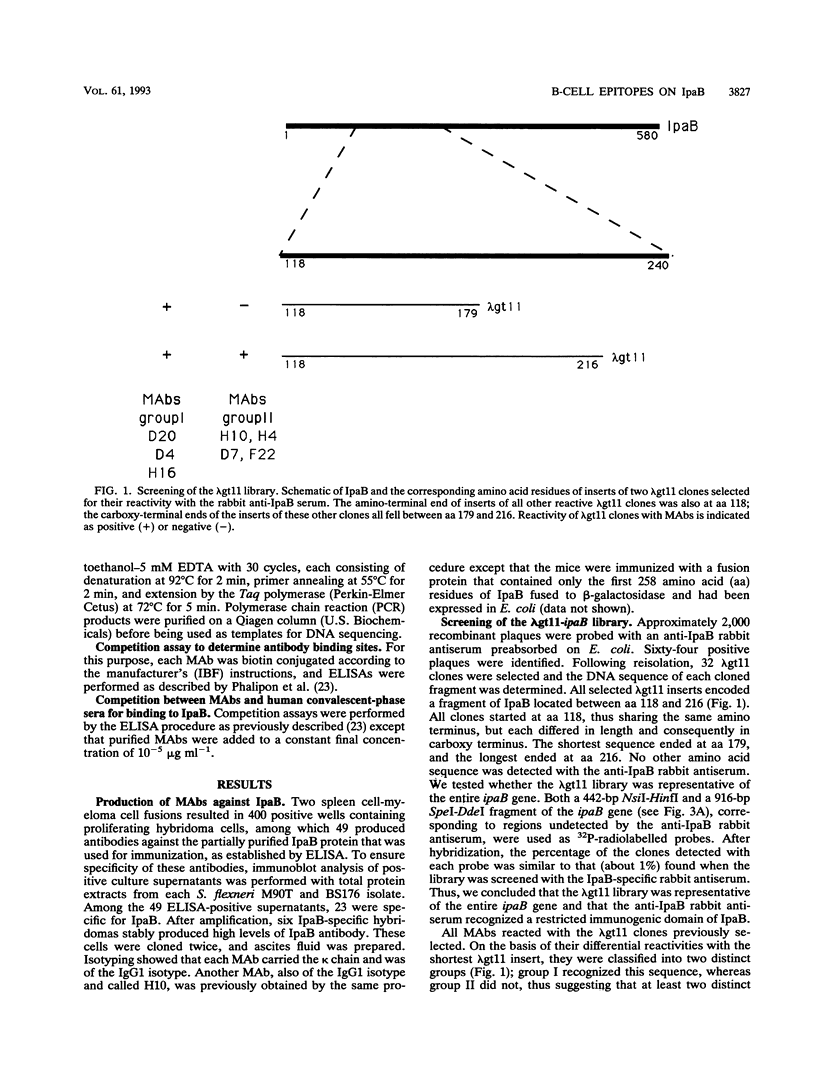
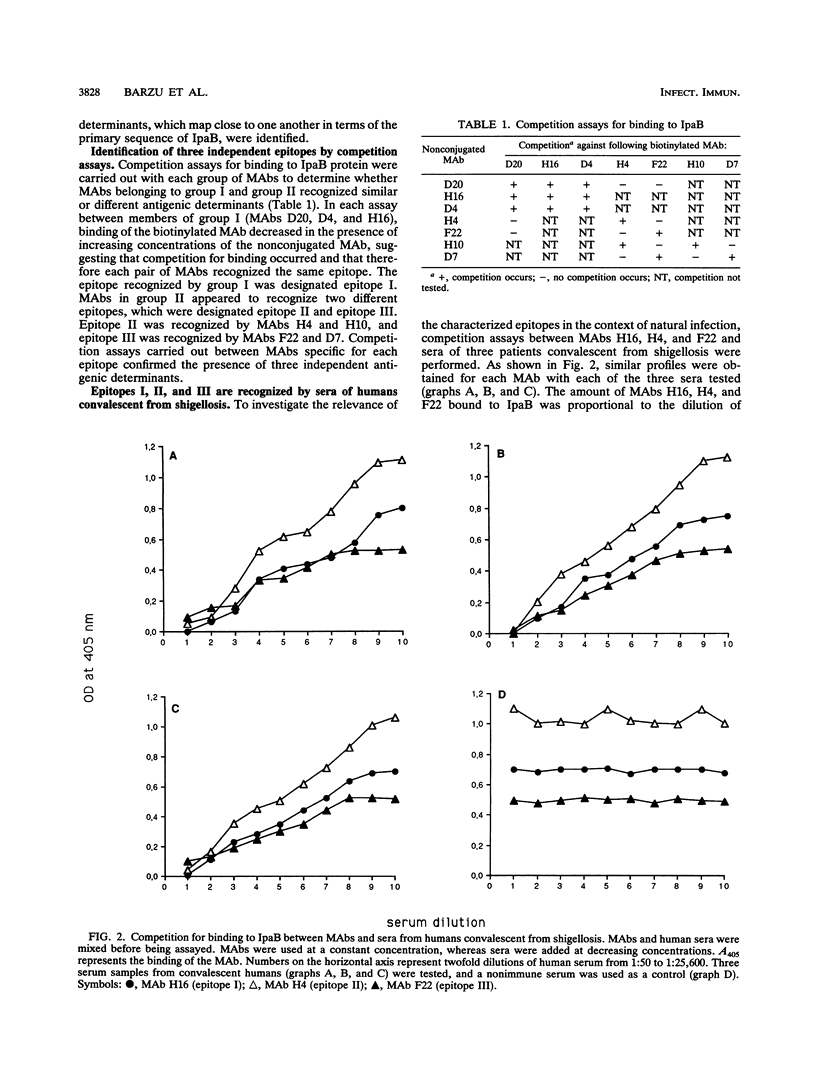
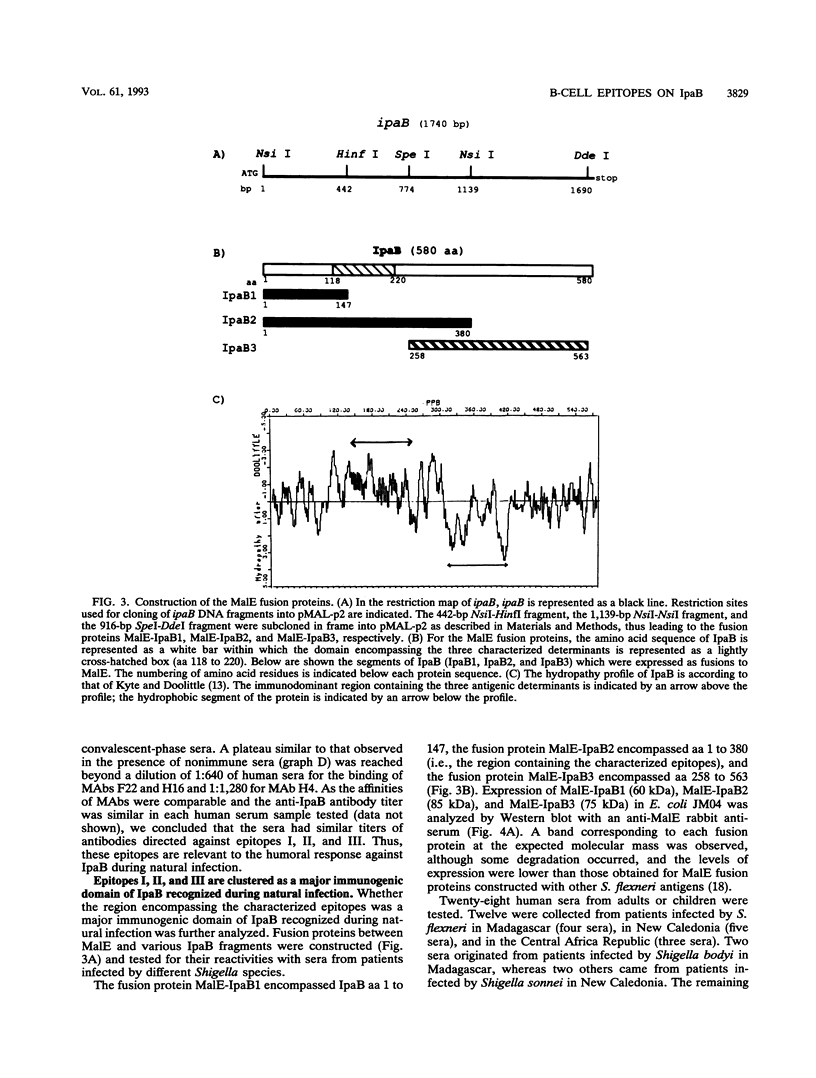
Abstract
The invasion plasmid antigen B (IpaB), a 62-kDa plasmid-encoded protein associated with the ability of shigellae to invade epithelial cells, is the bacterial antigen most strongly and consistently recognized by the host during infection. The strong systemic and mucosal immune responses observed against this invasin prompted us to map its B-cell epitopes. For this purpose, IpaB was first overexpressed in Shigella flexneri and used to raise rabbit polyclonal antiserum and murine monoclonal antibodies, which were subsequently used to screen a lambda gt11 ipaB library. Inserts of recombinant DNA clones that were specifically recognized by the antisera and antibodies were sequenced, and three distinct determinants were identified. Further characterization of these determinants showed that they were recognized by sera from patients convalescent from shigellosis, suggesting that they are relevant to the humoral response during natural infection. Moreover, the IpaB region comprising the three determinants was systematically recognized by all sera from infected patients that we tested, whereas other regions of the protein were not. These data suggest that this region, located between amino acid residues 147 and 258, is the major immunogenic domain of the invasin in the course of natural infection.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allaoui A., Sansonetti P. J., Parsot C. MxiD, an outer membrane protein necessary for the secretion of the Shigella flexneri lpa invasins. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(1):59–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews G. P., Hromockyj A. E., Coker C., Maurelli A. T. Two novel virulence loci, mxiA and mxiB, in Shigella flexneri 2a facilitate excretion of invasion plasmid antigens. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1997–2005. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1997-2005.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry B., Kaczorek M., Sansonetti P. J. Nucleotide sequence of the invasion plasmid antigen B and C genes (ipaB and ipaC) of Shigella flexneri. Microb Pathog. 1988 May;4(5):345–357. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry B., Maurelli A. T., Clerc P., Sadoff J. C., Sansonetti P. J. Localization of plasmid loci necessary for the entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells, and characterization of one locus encoding four immunogenic polypeptides. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Dec;133(12):3403–3413. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-12-3403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinari G., Hale T. L., Austin S. W., Formal S. B. Local and systemic antibody responses to Shigella infection in rhesus monkeys. J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):1065–1069. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Formal S. B., Gangarosa E. J. Immunity in shigellosis. II. Protection induced by oral live vaccine or primary infection. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jan;125(1):12–16. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Kent T. H., May H. C., Palmer A., Falkow S., LaBrec E. H. Protection of monkeys against experimental shigellosis with a living attenuated oral polyvalent dysentery vaccine. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):17–22. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.17-22.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Oaks E. V., Formal S. B. Identification and antigenic characterization of virulence-associated, plasmid-coded proteins of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):620–629. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.620-629.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Van de Verg L., Formal S. B., Hale T. L., Tall B. D., Cryz S. J., Tramont E. C., Levine M. M. Studies in volunteers to evaluate candidate Shigella vaccines: further experience with a bivalent Salmonella typhi-Shigella sonnei vaccine and protection conferred by previous Shigella sonnei disease. Vaccine. 1990 Aug;8(4):353–357. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(90)90094-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- High N., Mounier J., Prévost M. C., Sansonetti P. J. IpaB of Shigella flexneri causes entry into epithelial cells and escape from the phagocytic vacuole. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1991–1999. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05253.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Baudry B., d'Hauteville H., Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J. Cloning of plasmid DNA sequences involved in invasion of HeLa cells by Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.164-171.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mel D. M., Arsić B. L., Nikolić B. D., Radovanić M. L. Studies on vaccination against bacillary dysentery. 4. Oral immunization with live monotypic and combined vaccines. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(3):375–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloen R. H., Briaire J. A study of the cross-reacting antigens on the intact foot-and-mouth disease virus and its 12S Subunits with antisera against the structural proteins. J Gen Virol. 1980 Nov;51(Pt 1):107–116. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-51-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. A., Buysse J. M., Oaks E. V. Shigella flexneri invasion plasmid antigens B and C: epitope location and characterization with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2933–2941. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2933-2941.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Hale T. L., Formal S. B. Serum immune response to Shigella protein antigens in rhesus monkeys and humans infected with Shigella spp. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.57-63.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Turbyfill K. R. Myosin-cross-reactive epitope of Shigella flexneri invasion plasmid antigen B. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):557–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.557-564.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhelman R. A., Kopecko D. J., Salazar-Lindo E., Gotuzzo E., Buysse J. M., Venkatesan M. M., Yi A., Fernandez-Prada C., Guzman M., León-Barúa R. Prospective study of systemic and mucosal immune responses in dysenteric patients to specific Shigella invasion plasmid antigens and lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2341–2350. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2341-2350.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phalipon A., Arondel J., Nato F., Rouyre S., Mazie J. C., Sansonetti P. J. Identification and characterization of B-cell epitopes of IpaC, an invasion-associated protein of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1919–1926. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1919-1926.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J. Genetic and molecular basis of epithelial cell invasion by Shigella species. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Mar-Apr;13 (Suppl 4):S285–S292. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.supplement_4.s285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Adler B., Tobe T., Okada N., Nagai S., Komatsu K., Yoshikawa M. Functional organization and nucleotide sequence of virulence Region-2 on the large virulence plasmid in Shigella flexneri 2a. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1191–1201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M. M., Buysse J. M., Oaks E. V. Surface presentation of Shigella flexneri invasion plasmid antigens requires the products of the spa locus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1990–2001. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1990-2001.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao R., Palchaudhuri S. Nucleotide sequence of the ipaBCD structural genes of Shigella dysenteriae. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2217–2221. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]