Abstract
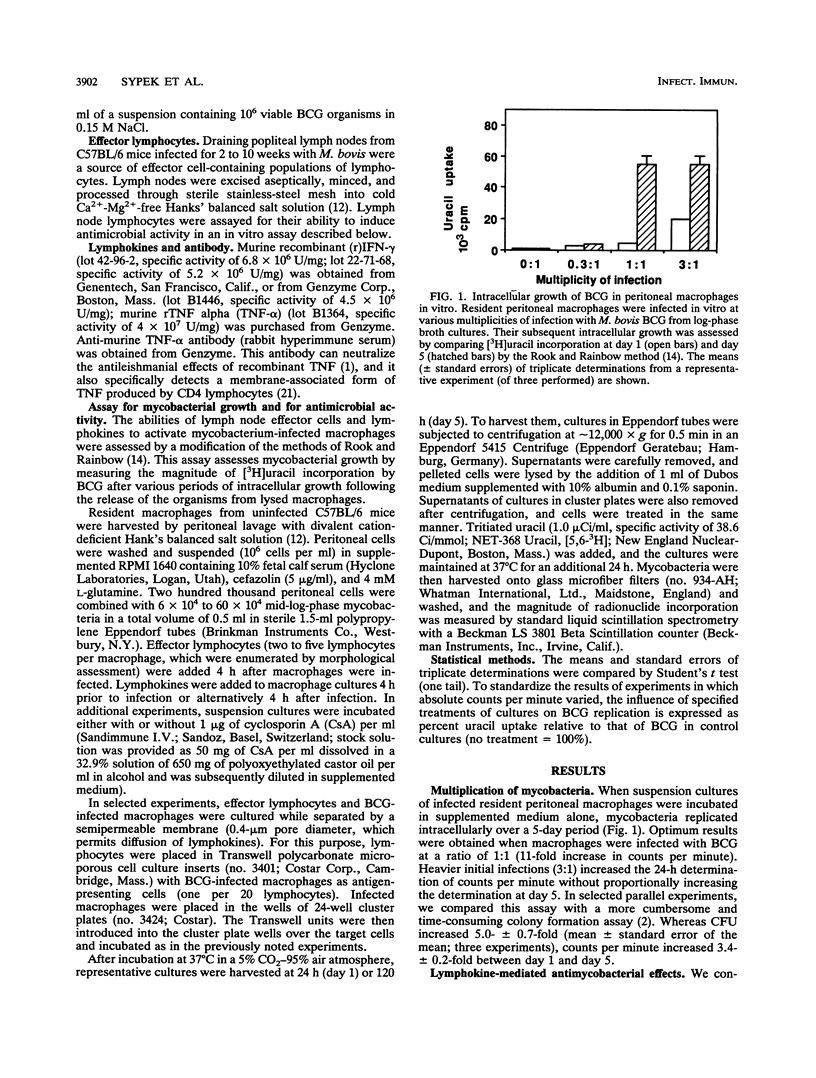
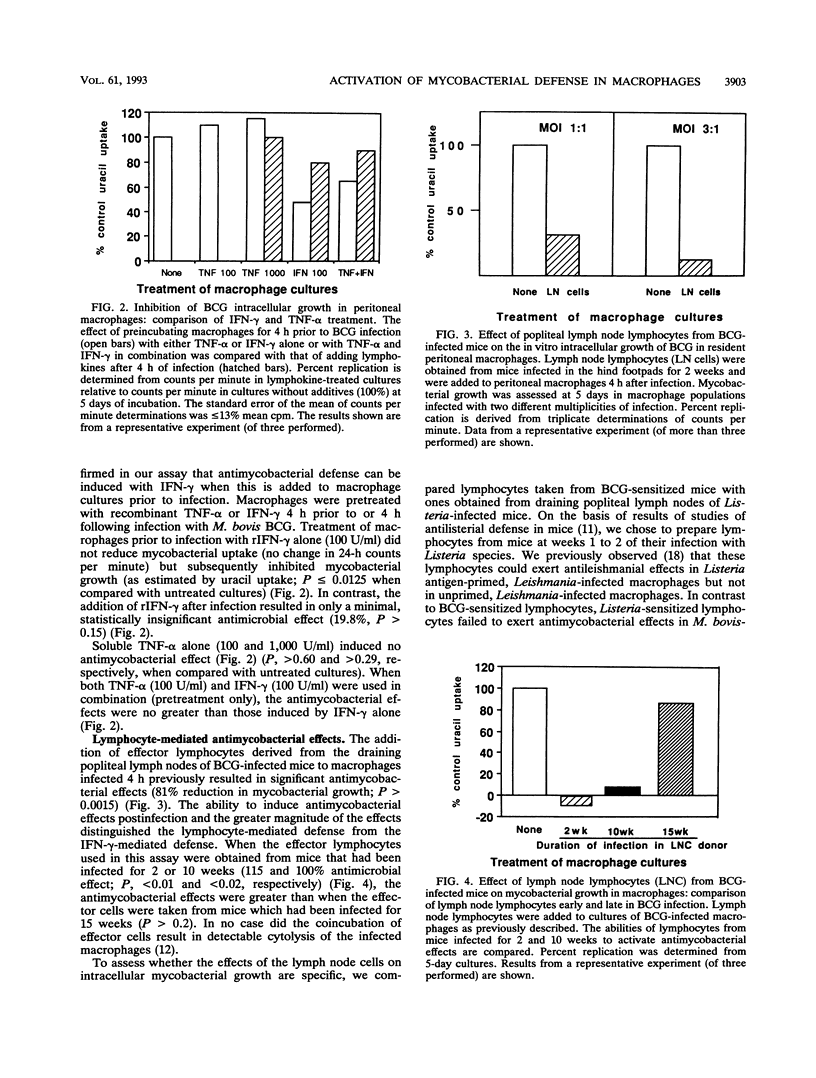
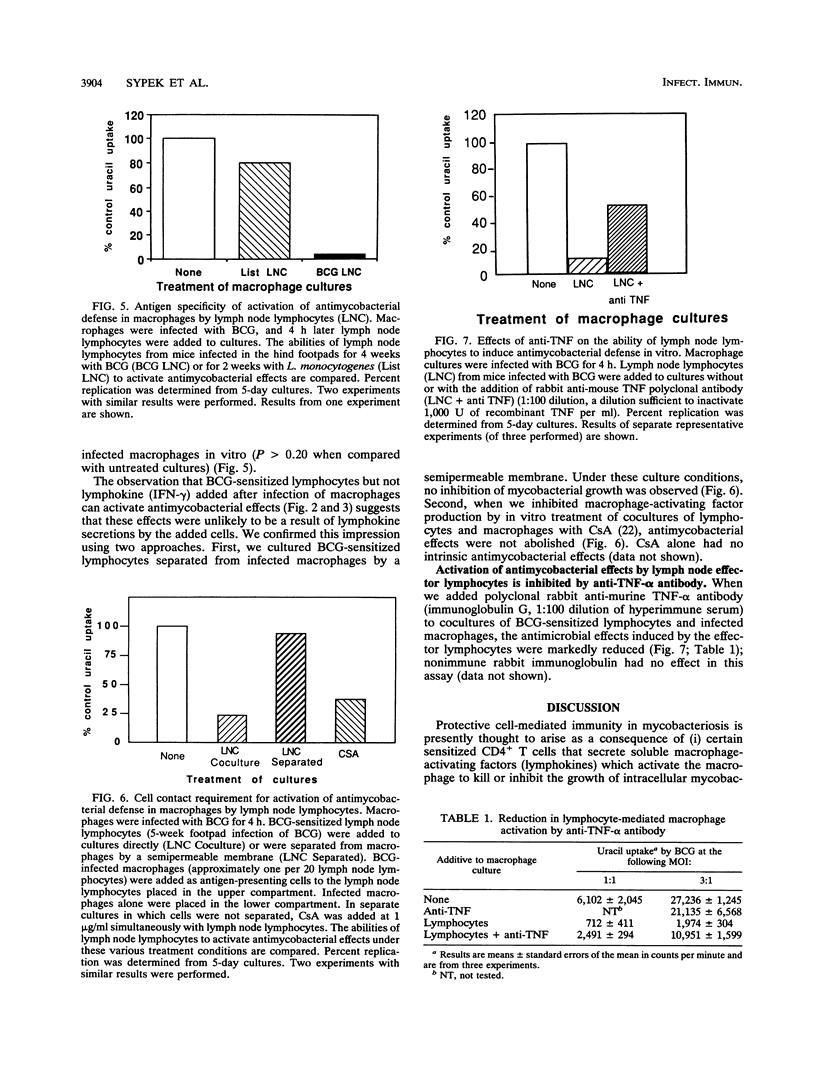
We compared the abilities of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and sensitized murine lymph node lymphocytes to activate syngeneic murine peritoneal macrophages to inhibit the growth of intracellular Mycobacterium bovis BCG in vitro. IFN-gamma could activate antimycobacterial defense only when added to macrophage cultures prior to their infection with BCG. TNF-alpha was without any effect. In contrast, BCG-sensitized lymphocytes could induce antimycobacterial defenses when added after macrophages had been infected with BCG. The cell-mediated effect required direct contact between effector lymphocytes and the targets (BCG-infected macrophages), as revealed in studies in which these cell populations were separated by a semipermeable membrane. Cyclosporin A, which inhibits the production of relevant macrophage-activating lymphokines, did not abrogate the ability of sensitized lymphocytes to activate antimycobacterial effects in infected macrophages. Furthermore, only BCG-sensitized lymphocytes, and not Listeria-sensitized lymphocytes, could activate the antimycobacterial effects. These lymphocytes were not cytotoxic to the infected macrophages. The presence of anti-TNF-alpha antibody in cocultures reduced the antimicrobial effects. We propose that the activation of antimycobacterial defense in macrophages can occur by direct physical contact with sensitized lymphocytes. This process may be due to lymphocyte membrane-associated TNF-alpha, as we previously demonstrated in our studies of antileishmanial defense.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boom W. H., Wallis R. S., Chervenak K. A. Human Mycobacterium tuberculosis-reactive CD4+ T-cell clones: heterogeneity in antigen recognition, cytokine production, and cytotoxicity for mononuclear phagocytes. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2737–2743. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2737-2743.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., May M. H. Replication of lyophilized and cultured BCG in human macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Oct;128(4):673–679. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.4.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Libero G., Flesch I., Kaufmann S. H. Mycobacteria-reactive Lyt-2+ T cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):59–66. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Activation of tuberculostatic macrophage functions by gamma interferon, interleukin-4, and tumor necrosis factor. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2675–2677. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2675-2677.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Stimulation of antibacterial macrophage activities by B-cell stimulatory factor 2 (interleukin-6). Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):269–271. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.269-271.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I., Kaufmann S. H. Mycobacterial growth inhibition by interferon-gamma-activated bone marrow macrophages and differential susceptibility among strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4408–4413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. The role of cell-mediated immunity in bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1221–1250. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janis E. M., Kaufmann S. H., Schwartz R. H., Pardoll D. M. Activation of gamma delta T cells in the primary immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):713–716. doi: 10.1126/science.2524098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Flesch I. Function and antigen recognition pattern of L3T4+ T-cell clones from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-immune mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):291–296. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.291-296.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Cellular mediators of anti-Listeria immunity as an enlarged population of short lived, replicating T cells. Kinetics of their production. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):342–355. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panosian C. B., Sypek J. P., Wyler D. J. Cell contact-mediated macrophage activation for antileishmanial defense. I. Lymphocyte effector mechanism that is contact dependent and noncytotoxic. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3358–3365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Champion B. R., Steele J., Varey A. M., Stanford J. L. I-A restricted activation by T cell lines of anti-tuberculosis activity in murine macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Feb;59(2):414–420. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. B., Sheagren J. N. Cellular immunity in vitro. I. Immunologically mediated enhancement of macrophage bactericidal capacity. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1377–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. B., Sheagren J. N. Enhancement of macrophage bactericidal capacity by antigenically stimulated immune lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jun;4(2):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sypek J. P., Panosian C. B., Wyler D. J. Antigen recognition by effector T cells in antileishmanial defense. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):1057–1063. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sypek J. P., Panosian C. B., Wyler D. J. Cell contact-mediated macrophage activation for antileishmanial defense. II. Identification of effector cell phenotype and genetic restriction. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3351–3357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sypek J. P., Wyler D. J. Antileishmanial defense in macrophages triggered by tumor necrosis factor expressed on CD4+ T lymphocyte plasma membrane. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):755–759. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sypek J. P., Wyler D. J. Cell contact-mediated macrophage activation for antileishmanial defence: mapping of the genetic restriction to the I region of the MHC. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Dec;62(3):449–457. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sypek J. P., Wyler D. J. T-cell hybridomas reveal two distinct mechanisms of antileishmanial defense. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1146–1152. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1146-1152.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler D. J., Beller D. I., Sypek J. P. Macrophage activation for antileishmanial defense by an apparently novel mechanism. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1246–1249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Althage A., Adler B., Blanden R. V., Davidson W. F., Kees U., Dunlop M. B., Shreffler D. C. H-2 restriction of cell-mediated immunity to an intracellular bacterium: effector T cells are specific for Listeria antigen in association with H-21 region-coded self-markers. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1353–1367. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


