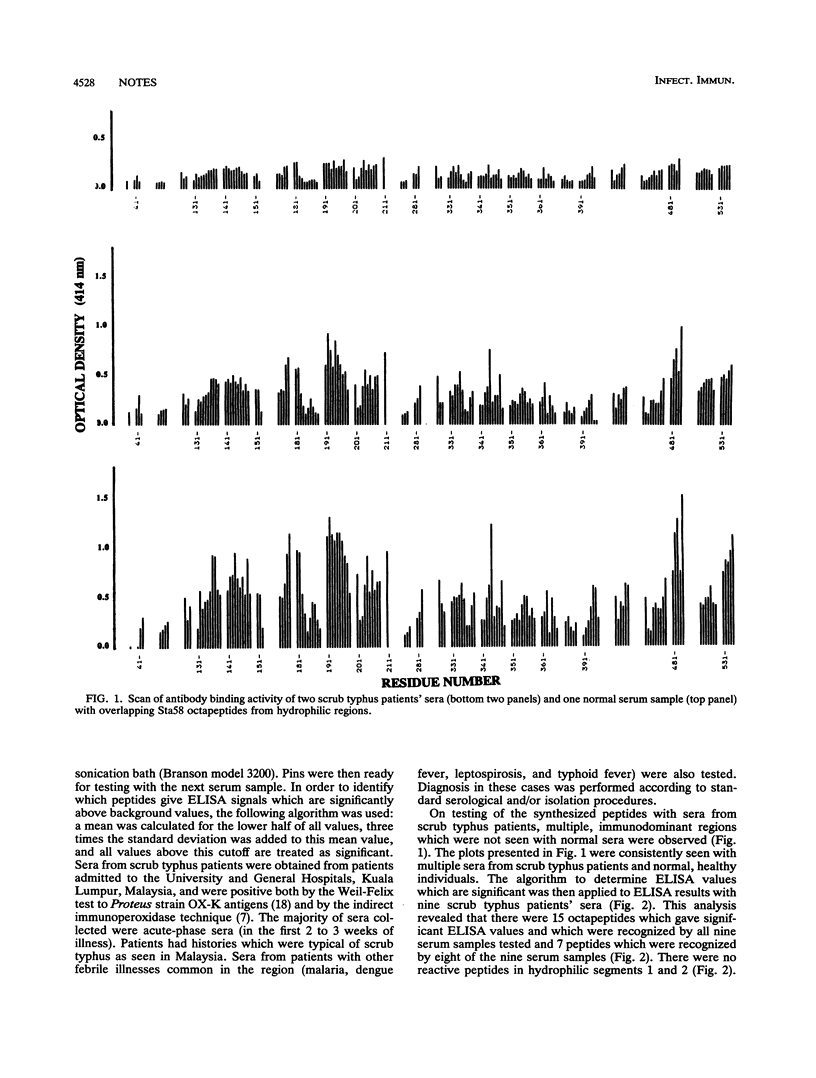
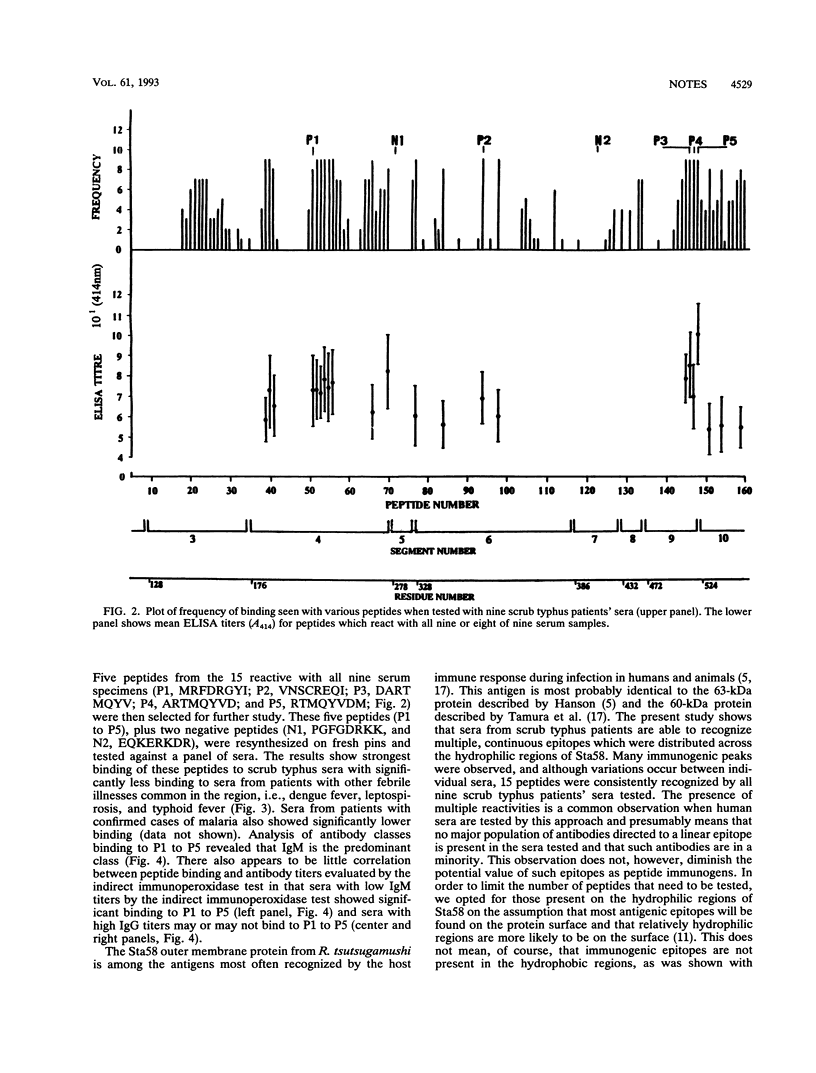
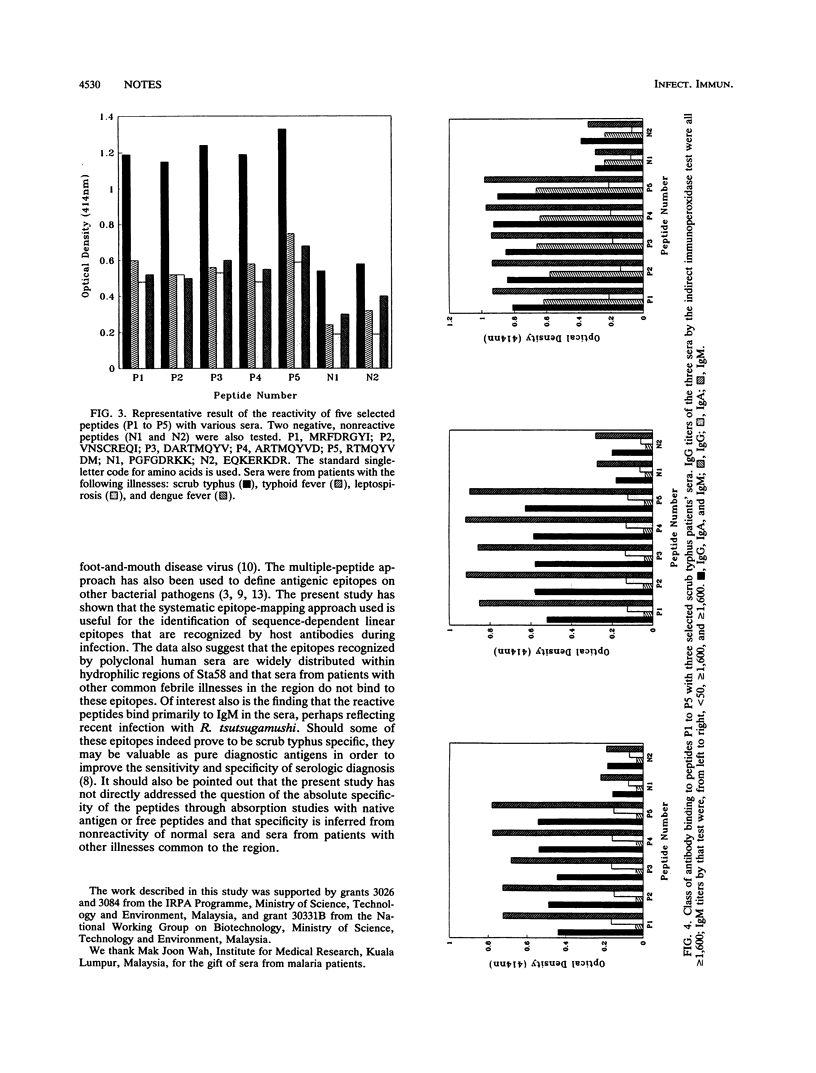
Abstract
Binding studies of 160 overlapping, synthetic octapeptides from the hydrophilic regions of the Sta58 major outer membrane protein of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi with sera from patients with scrub typhus revealed 15 immunodominant peptides which are recognized by all the sera tested. Further analysis of the specificity of peptide binding with five of these peptides indicated that the peptides showed significantly stronger binding to scrub typhus patients' sera than they did to sera from patients with other febrile illnesses common in the region, i.e., malaria, dengue fever, typhoid fever, and leptospirosis. The main antibody class binding to these peptides appears to be immunoglobulin M, and there appears to be little correlation between reactivity with peptides and antibody titers measured by the indirect immunoperoxidase test.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown G. W., Shirai A., Jegathesan M., Burke D. S., Twartz J. C., Saunders J. P., Huxsoll D. L. Febrile illness in Malaysia--an analysis of 1,629 hospitalized patients. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Mar;33(2):311–315. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L. Epidemiology of drug resistance: implications for a post-antimicrobial era. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1050–1055. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan J. W., Clarke I. N., Ward M. E. Epitope mapping with solid-phase peptides: identification of type-, subspecies-, species- and genus-reactive antibody binding domains on the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):673–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J., Tribbick G., Schoofs P. G. Strategies for epitope analysis using peptide synthesis. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Sep 24;102(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. Identification and partial characterization of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi major protein immunogens. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):603–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.603-609.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazár J., Brezina R. Control of rickettsial diseases. Eur J Epidemiol. 1991 May;7(3):282–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00145678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. J., Wong P. W., Gan E., Chye C. T., Cowan D., Lewis G. E., Jr Multi-laboratory evaluation of a scrub typhus diagnostic kit. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Sep;43(3):301–307. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.43.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E. Diagnosis of rickettsial diseases: a perspective. Eur J Epidemiol. 1991 May;7(3):270–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00145676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness B., Barlow A. K., Clarke I. N., Farley J. E., Anilionis A., Poolman J. T., Heckels J. E. Deduced amino acid sequences of class 1 protein (PorA) from three strains of Neisseria meningitidis. Synthetic peptides define the epitopes responsible for serosubtype specificity. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):1871–1882. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloen R. H., Barteling S. J. Epitope mapping of the outer structural protein VP1 of three different serotypes of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virology. 1986 Feb;149(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Rice R. M., Kelly D. J., Stover C. K. Antigenic and genetic relatedness of eight Rickettsia tsutsugamushi antigens. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3116–3122. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3116-3122.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radford A. J., Wood P. R., Billman-Jacobe H., Geysen H. M., Mason T. J., Tribbick G. Epitope mapping of the Mycobacterium bovis secretory protein MPB70 using overlapping peptide analysis. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Feb;136(2):265–272. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D. Antibiotic treatment of rickettsiosis, recent advances and current concepts. Eur J Epidemiol. 1991 May;7(3):276–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00145677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapmund G. Rickettsial diseases of the Far East: new perspectives. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):330–338. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stover C. K., Marana D. P., Dasch G. A., Oaks E. V. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the Sta58 major antigen gene of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi: sequence homology and antigenic comparison of Sta58 to the 60-kilodalton family of stress proteins. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1360–1368. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1360-1368.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Ohashi N., Urakami H., Takahashi K., Oyanagi M. Analysis of polypeptide composition and antigenic components of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):671–675. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.671-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


