Abstract
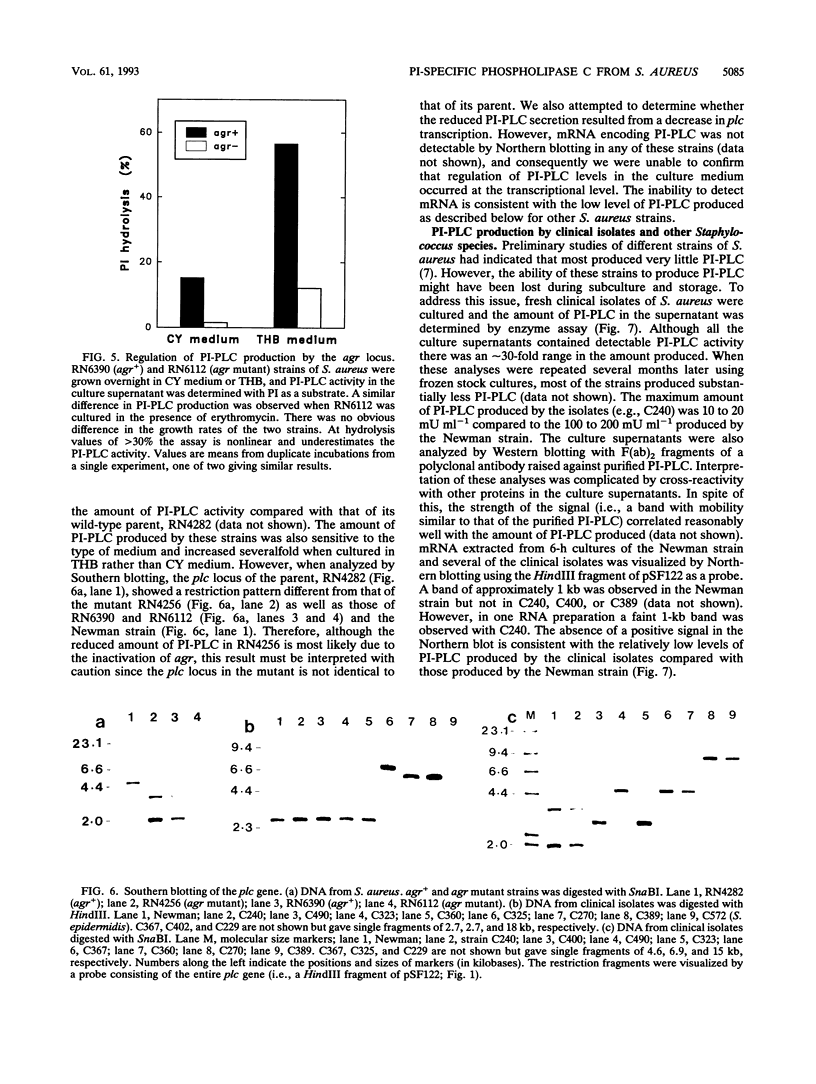
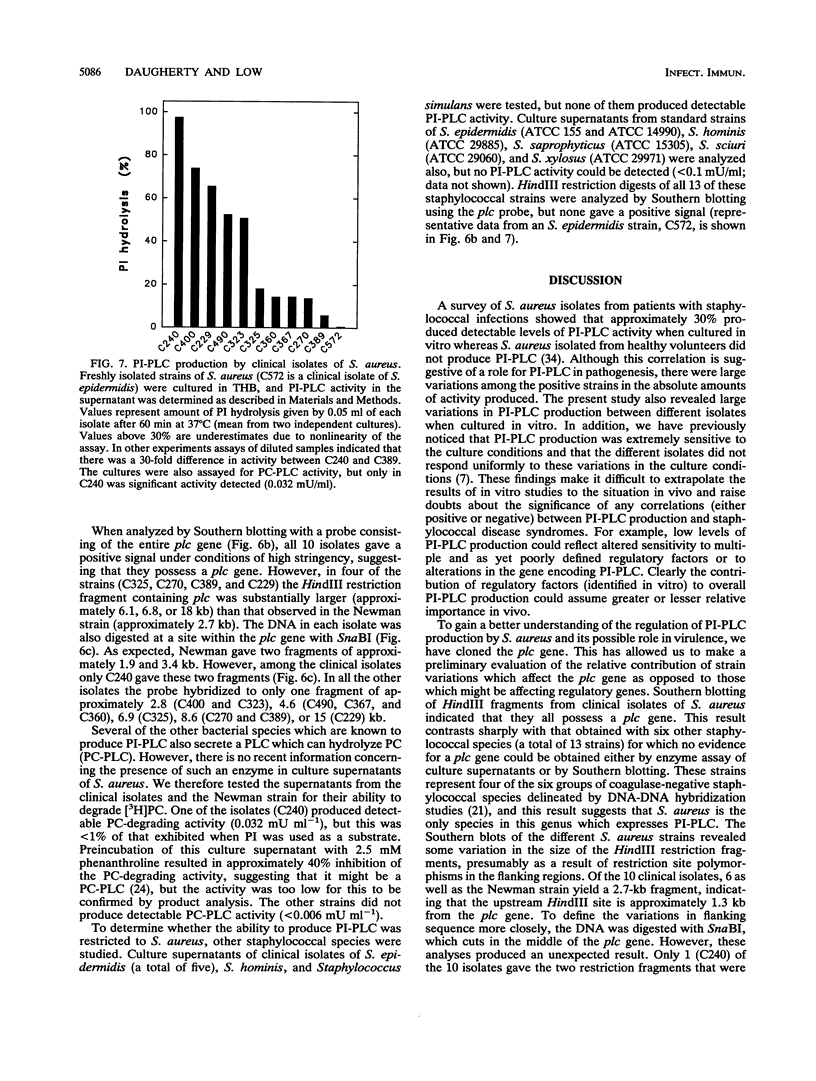
Staphylococcus aureus secretes a phosphatidylinositol (PI)-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) which is able to hydrolyze the membrane lipid PI and membrane protein anchors containing glycosyl-PI. The gene for PI-PLC (plc) was cloned from S. aureus into Escherichia coli. Oligonucleotide probes based on partial protein sequence and polyclonal antibodies raised against the purified protein were used to identify positive clones. E. coli transformed with a plasmid containing the plc gene expressed PI-PLC enzyme activity which was abolished by mutagenesis with a tetracycline resistance gene. The plc gene was present in all 15 S. aureus strains examined but not in any of 6 coagulase-negative staphylococcal species. The plc gene contained 984 bp and coded for a mature protein with a calculated molecular mass of 34,107 Da. Amino acid sequence comparisons indicated that the staphylococcal plc gene was similar (51 to 56%) to the PI-PLCs from Bacillus cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis, and Listeria monocytogenes. The recombinant PI-PLC expressed in E. coli was purified and exhibited biochemical properties identical to those of the native PI-PLC from S. aureus. PI-PLC production was decreased in agr mutant strains of S. aureus. However, PI-PLC production by both agr+ and agr mutant strains exhibited a similar dependence on the type of medium used. These data suggested that PI-PLC production was regulated by both agr-dependent and agr-independent mechanisms.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bengualid V., Hatcher V. B., Diamond B., Blumberg E. A., Lowy F. D. Staphylococcus aureus infection of human endothelial cells potentiates Fc receptor expression. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4279–4283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buisman H. P., Buys L. F., Langermans J. A., van den Broek P. J., van Furth R. Effect of probenecid on phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli by human monocytes and granulocytes. Immunology. 1991 Oct;74(2):338–341. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caird J. D., Wiseman G. M. Purification of the delta toxin os Staphylococcus aureus. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Aug;16(8):703–708. doi: 10.1139/m70-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilli A., Goldfine H., Portnoy D. A. Listeria monocytogenes mutants lacking phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C are avirulent. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):751–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilli A., Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Dual roles of plcA in Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Apr;8(1):143–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. L., Koomey J. M., Butler C. A., Projan S. J., Fischetti V. A. Regulation of exoprotein expression in Staphylococcus aureus by a locus (sar) distinct from agr. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6462–6466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doery H. M., Magnusson B. J., Gulasekharam J., Pearson J. E. The properties of phospholipase enzymes in staphylococcal toxins. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Aug;40(2):283–296. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard D. A., Cooper C. L., Low M. G., Holz R. W. Evidence that the inositol phospholipids are necessary for exocytosis. Loss of inositol phospholipids and inhibition of secretion in permeabilized cells caused by a bacterial phospholipase C and removal of ATP. Biochem J. 1990 May 15;268(1):15–25. doi: 10.1042/bj2680015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Cross G. A. Glycosyl-sn-1,2-dimyristylphosphatidylinositol is covalently linked to Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14547–14555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Raveneau J., Beretti J. L., Lecroisey A., Vazquez-Boland J. A., Alouf J. E., Berche P. Purification and characterization of an extracellular 29-kilodalton phospholipase C from Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2382–2388. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2382-2388.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine H., Johnston N. C., Knob C. Nonspecific phospholipase C of Listeria monocytogenes: activity on phospholipids in Triton X-100-mixed micelles and in biological membranes. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4298–4306. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4298-4306.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine H., Knob C. Purification and characterization of Listeria monocytogenes phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4059–4067. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4059-4067.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. H., Volwerk J. J., Kuppe A. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipases C from Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis. Methods Enzymol. 1991;197:493–502. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)97175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guddal P. H., Johansen T., Schulstad K., Little C. Apparent phosphate retrieval system in Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5702–5706. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5702-5706.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill R. J., Vann J. M., Proctor R. A. Phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus by cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells: model for postadherence events in endovascular infections. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):833–836. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.833-836.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner D. J., Yang M., Chen E., Hellmiss R., Rodriguez H., Low M. G. Sequence of the Bacillus thuringiensis phosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase C. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10383–10383. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereld D., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. cDNA encoding the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Trypanosoma brucei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8914–8918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiemstra P. S., Annema A., Schippers E. F., van Furth R. Pertussis toxin partially inhibits phagocytosis of immunoglobulin G-opsonized Staphylococcus aureus by human granulocytes but does not affect intracellular killing. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):202–205. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.202-205.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Li S., Low M. G. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D. Methods Enzymol. 1991;197:567–575. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)97184-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E. Natural populations of the genus Staphylococcus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:559–592. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppe A., Evans L. M., McMillen D. A., Griffith O. H. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Bacillus cereus: cloning, sequencing, and relationship to other phospholipases. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6077–6083. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6077-6083.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Chakraborty T. Detection of a gene encoding a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C that is co-ordinately expressed with listeriolysin in Listeria monocytogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):361–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Finean J. B. Modification of erythrocyte membranes by a purified phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (Staphylococcus aureus). Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):235–240. doi: 10.1042/bj1620235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Stiernberg J., Waneck G. L., Flavell R. A., Kincade P. W. Cell-specific heterogeneity in sensitivity of phosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane antigens to release by phospholipase C. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Oct 4;113(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. The glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor of membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 6;988(3):427–454. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy F. D., Fant J., Higgins L. L., Ogawa S. K., Hatcher V. B. Staphylococcus aureus--human endothelial cell interactions. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1988 Feb;98(2):137–146. doi: 10.1016/s0889-1605(88)80906-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques M. B., Weller P. F., Parsonnet J., Ransil B. J., Nicholson-Weller A. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, a possible virulence factor of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2451–2454. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2451-2454.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Braun-Breton C., Cossart P. Identification of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity in Listeria monocytogenes: a novel type of virulence factor? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesin M., Svec P., Lupski J. R., Godson G. N., Kreiswirth B., Kornblum J., Projan S. J. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of a chromosomally encoded tetracycline resistance determinant, tetA(M), from a pathogenic, methicillin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2273–2276. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S. H., Dufrenne J., Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Chakraborty T. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity as a marker to distinguish between pathogenic and nonpathogenic Listeria species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2666–2670. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2666-2670.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng H. L., Novick R. P., Kreiswirth B., Kornblum J., Schlievert P. Cloning, characterization, and sequencing of an accessory gene regulator (agr) in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4365–4372. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4365-4372.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presky D. H., Low M. G., Shevach E. M. Role of phosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins in T cell activation. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):860–868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Projan S. J., Kornblum J., Kreiswirth B., Moghazeh S. L., Eisner W., Novick R. P. Nucleotide sequence: the beta-hemolysin gene of Staphylococcus aureus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3305–3305. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recsei P., Kreiswirth B., O'Reilly M., Schlievert P., Gruss A., Novick R. P. Regulation of exoprotein gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus by agar. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jan;202(1):58–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00330517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regassa L. B., Betley M. J. Alkaline pH decreases expression of the accessory gene regulator (agr) in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5095–5100. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5095-5100.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regassa L. B., Betley M. J. High sodium chloride concentrations inhibit staphylococcal enterotoxin C gene (sec) expression at the level of sec mRNA. Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1581–1585. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1581-1585.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regassa L. B., Novick R. P., Betley M. J. Glucose and nonmaintained pH decrease expression of the accessory gene regulator (agr) in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3381–3388. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3381-3388.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Choi K. D. Regulation of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J. Signal transduction by GPI-anchored membrane proteins. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1991 Sep;15(9):761–767. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(91)90031-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J., Spencer S. C. Phosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane proteins and lymphocyte activation. Immunol Lett. 1988 Oct;19(2):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(88)90124-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross T. S., Majerus P. W. Isolation of D-myo-inositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate 2-inositolphosphohydrolase from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11119–11123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. Purification and characterization of two immunologically distinct phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases C from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12511–12518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Sorbara-Cazan L. R. Inositol glycan mimics the action of insulin on glucose utilization in rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 31;149(3):1084–1092. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90519-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvi R. J., Ahroon W., Saunders S. S., Arnold S. A. Evoked potentials: computer-automated threshold-tracking procedure using an objective detection criterion. Ear Hear. 1987 Jun;8(3):151–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler P., Weisblum B. Erythromycin-induced stabilization of ermA messenger RNA in Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):905–915. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeltzer M. S., Hart M. E., Iandolo J. J. Phenotypic characterization of xpr, a global regulator of extracellular virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):919–925. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.919-925.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiernberg J., Low M. G., Flaherty L., Kincade P. W. Removal of lymphocyte surface molecules with phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C: effects on mitogen responses and evidence that ThB and certain Qa antigens are membrane-anchored via phosphatidylinositol. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3877–3884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titball R. W. Bacterial phospholipases C. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Jun;57(2):347–366. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.2.347-366.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann J. M., Proctor R. A. Ingestion of Staphylococcus aureus by bovine endothelial cells results in time- and inoculum-dependent damage to endothelial cell monolayers. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2155–2163. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2155-2163.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Boland J. A., Kocks C., Dramsi S., Ohayon H., Geoffroy C., Mengaud J., Cossart P. Nucleotide sequence of the lecithinase operon of Listeria monocytogenes and possible role of lecithinase in cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):219–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.219-230.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volwerk J. J., Shashidhar M. S., Kuppe A., Griffith O. H. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus combines intrinsic phosphotransferase and cyclic phosphodiesterase activities: a 31P NMR study. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 4;29(35):8056–8062. doi: 10.1021/bi00487a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M., Caird J. D. Phospholipase activity of the delta hemolysin of Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jun;128(2):428–430. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M. The hemolysins of Staphylococcus aureus. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Dec;39(4):317–344. doi: 10.1128/br.39.4.317-344.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M. Y., Lövgren A., Low M. G., Landén R. Characterization of an avirulent pleiotropic mutant of the insect pathogen Bacillus thuringiensis: reduced expression of flagellin and phospholipases. Infect Immun. 1993 Dec;61(12):4947–4954. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.12.4947-4954.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]