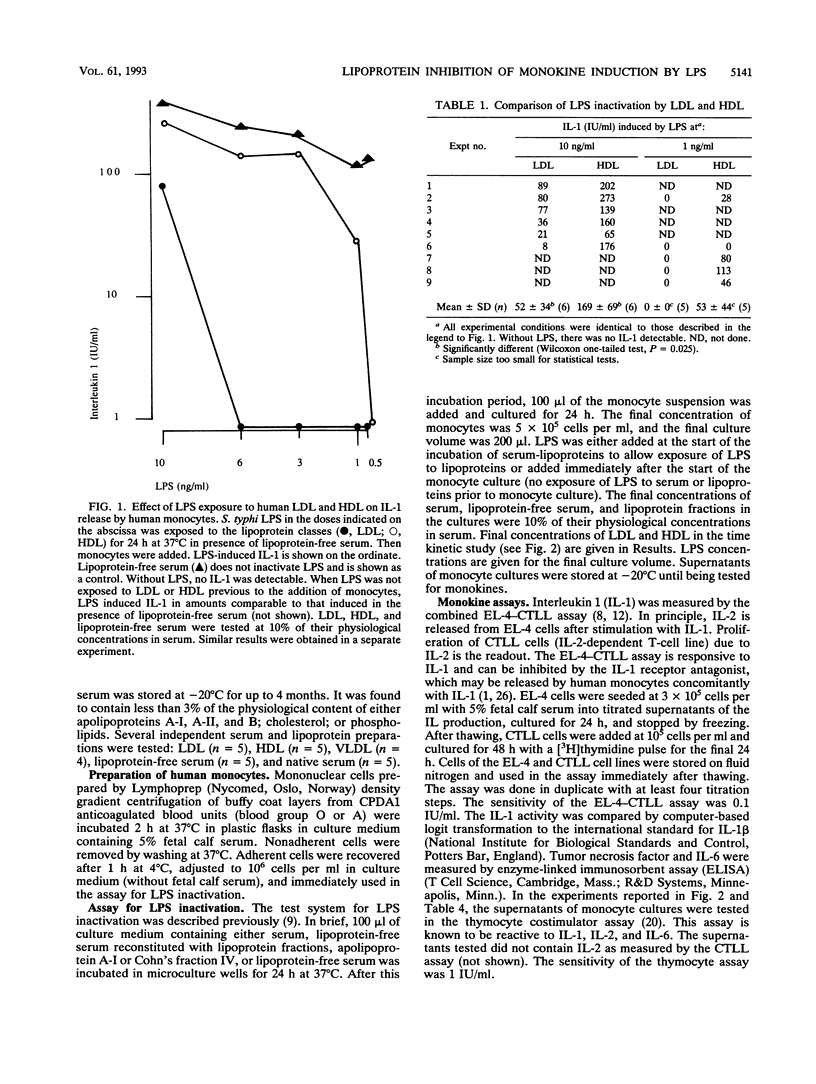
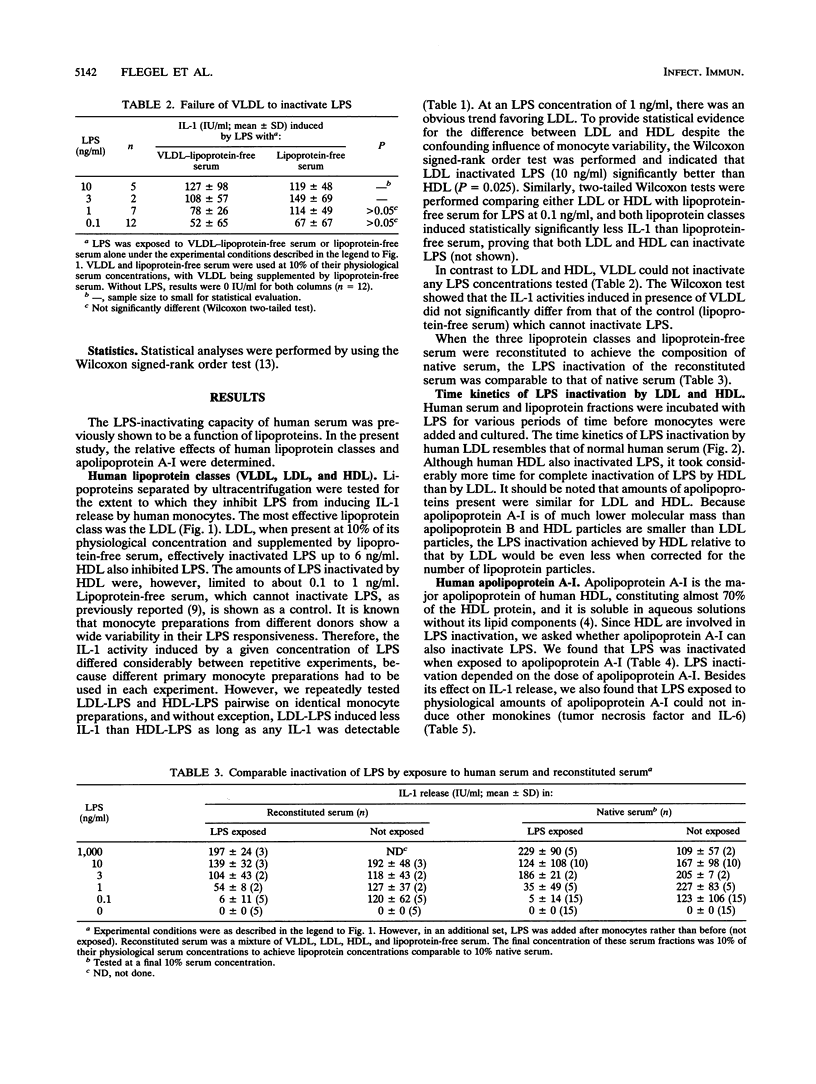
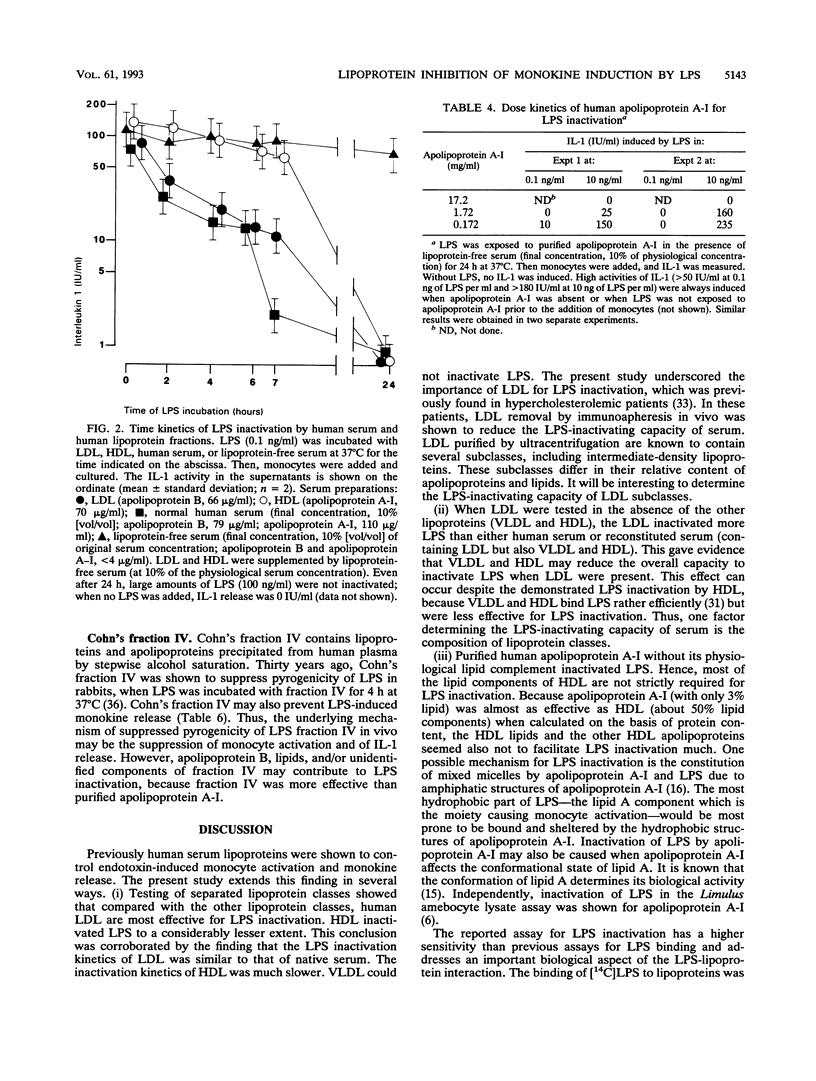
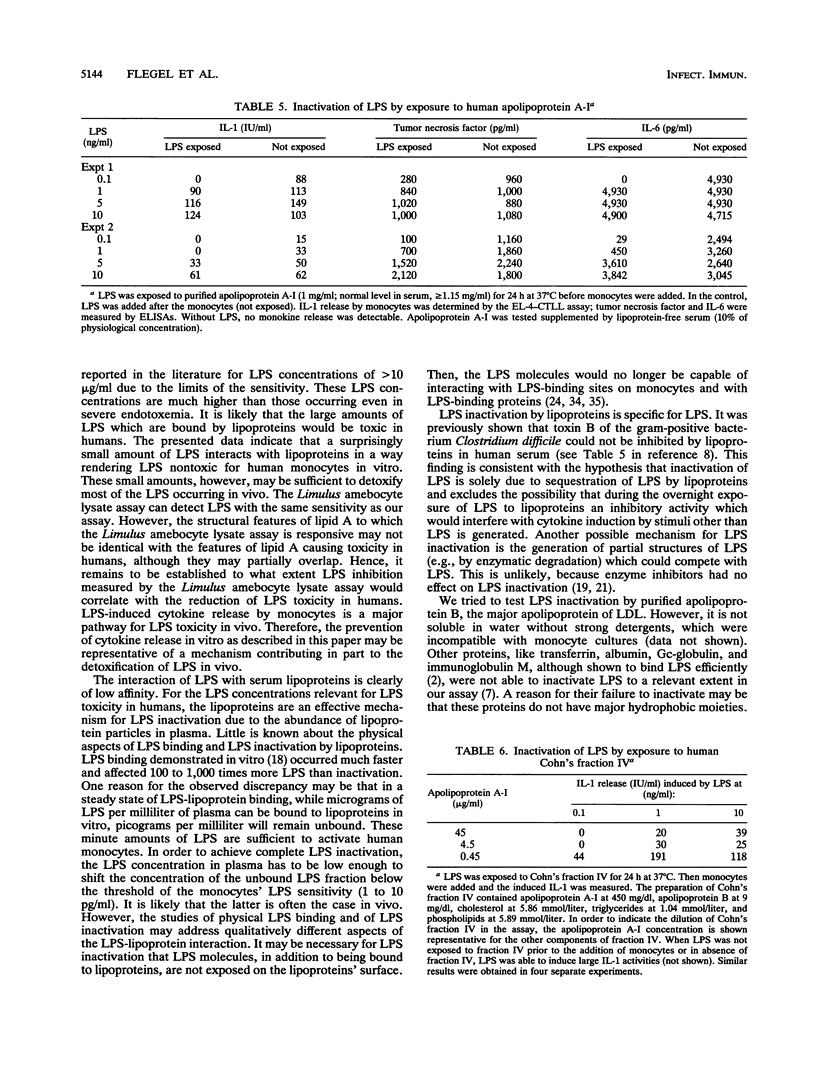
Abstract
Interaction of endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide [LPS]) with human lipoproteins is known to prevent the LPS-induced activation of human monocytes and release of cytokines (monokines). LPS was exposed to lipoprotein classes separated by ultracentrifugation and to apolipoprotein A-I. Then monocytes were added, and the LPS activation of monocytes was determined by measuring the induced monokines. Failure of LPS to induce monokine release was called LPS inactivation caused by lipoproteins or apolipoproteins. The LPS inactivation is shown to be a function of low-density lipoproteins. High-density lipoproteins inactivate LPS to a much lesser extent. The very-low-density lipoproteins cannot inactivate LPS. Lipid components seemed not absolutely required for LPS inactivation, because purified human apolipoprotein A-I without its physiological lipid complement also inhibits LPS-induced monokine release.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. A new member of the interleukin 1 family. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1445–1451. doi: 10.1172/JCI115453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger D., Beger H. G. Evidence for endotoxin binding capacity of human Gc-globulin and transferrin. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Mar 30;163(3):289–299. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J., Utermann G., Füssle R. Binding and partial inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin by human plasma low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5899–5904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow J. L. Human apolipoprotein molecular biology and genetic variation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:699–727. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaillon J. M., Fitting C., Haeffner-Cavaillon N., Kirsch S. J., Warren H. S. Cytokine response by monocytes and macrophages to free and lipoprotein-bound lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2375–2382. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2375-2382.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emancipator K., Csako G., Elin R. J. In vitro inactivation of bacterial endotoxin by human lipoproteins and apolipoproteins. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):596–601. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.596-601.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flegel W. A., Müller F., Däubener W., Fischer H. G., Hadding U., Northoff H. Cytokine response by human monocytes to Clostridium difficile toxin A and toxin B. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3659–3666. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3659-3666.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flegel W. A., Wölpl A., Männel D. N., Northoff H. Inhibition of endotoxin-induced activation of human monocytes by human lipoproteins. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2237–2245. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2237-2245.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg M. A., Bøg-Hansen T. C., Back U., Galanos C. Interaction of lipopolysaccharides with plasma high-density lipoprotein in rats. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):373–380. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.373-380.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzano-Santoro H., Parent J. B., Grinna L., Horwitz A., Parsons T., Theofan G., Elsbach P., Weiss J., Conlon P. J. High-affinity binding of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein and a recombinant amino-terminal fragment to the lipid A region of lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4754–4761. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4754-4761.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing A. J., Bird C. R., Bristow A., Poole S., Thorpe R. A simple sensitive bioassay for interleukin-1 which is unresponsive to 10(3) U/ml of interleukin-2. J Immunol Methods. 1987 May 4;99(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz T., Brandenburg K., Seydel U., Roth A., Galanos C., Rietschel E. T. Structural and physicochemical requirements of endotoxins for the activation of arachidonic acid metabolism in mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):11–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H. Plasma lipoproteins: apolipoprotein structure and function. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 1;25(12):1277–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Ulevitch R. J. The clearance, tissue distribution, and cellular localization of intravenously injected lipopolysaccharide in rabbits. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2133–2143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L., Dietschy J. M. Binding of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides to rat high-density lipoproteins. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):835–843. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.835-843.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northoff H., Carter C., Oppenheim J. J. Inhibition of concanavalin A-induced human lymphocyte mitogenic factor (Interleukin-2) production by suppressor T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1823–1828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peitsch M. C., Kress A., Lerch P. G., Morgenthaler J. J., Isliker H., Heiniger H. J. A purification method for apolipoprotein A-I and A-II. Anal Biochem. 1989 May 1;178(2):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder D. J., Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Endotoxic-lipopolysaccharide-specific binding proteins on lymphoid cells of various animal species: association with endotoxin susceptibility. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1054–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1054-1058.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann R. R., Leong S. R., Flaggs G. W., Gray P. W., Wright S. D., Mathison J. C., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.2402637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Lowenthal J. W., Williamson K., Dayer J. M., MacDonald H. R. A urine inhibitor of interleukin 1 activity that blocks ligand binding. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1546–1549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias P. S., McAdam K. P., Soldau K., Ulevitch R. J. Control of lipopolysaccharide-high-density lipoprotein interactions by an acute-phase reactant in human serum. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):73–76. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.73-76.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias P. S., Soldau K., Ulevitch R. J. Identification of a lipid A binding site in the acute phase reactant lipopolysaccharide binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10867–10871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Johnston A. R., Weinstein D. B. New function for high density lipoproteins. Isolation and characterization of a bacterial lipopolysaccharide-high density lipoprotein complex formed in rabbit plasma. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):827–837. doi: 10.1172/JCI110100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lenten B. J., Fogelman A. M., Haberland M. E., Edwards P. A. The role of lipoproteins and receptor-mediated endocytosis in the transport of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2704–2708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren H. S., Riveau G. R., de Deckker F. A., Chedid L. A. Control of endotoxin activity and interleukin-1 production through regulation of lipopolysaccharide-lipoprotein binding by a macrophage factor. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):204–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.204-212.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock C., Ullrich H., Hohe R., Berg A., Baumstark M. W., Frey I., Northoff H., Flegel W. A. Low density lipoproteins inhibit endotoxin activation of monocytes. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992 Mar;12(3):341–347. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.12.3.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Patel M., Miller D. S. Septin: a factor in plasma that opsonizes lipopolysaccharide-bearing particles for recognition by CD14 on phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):719–727. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIOKA M., JOHNSON A. G. Characteristics of endotoxin altering fractions derived from normal human serum. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:326–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


