Abstract
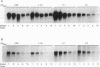
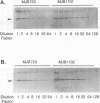
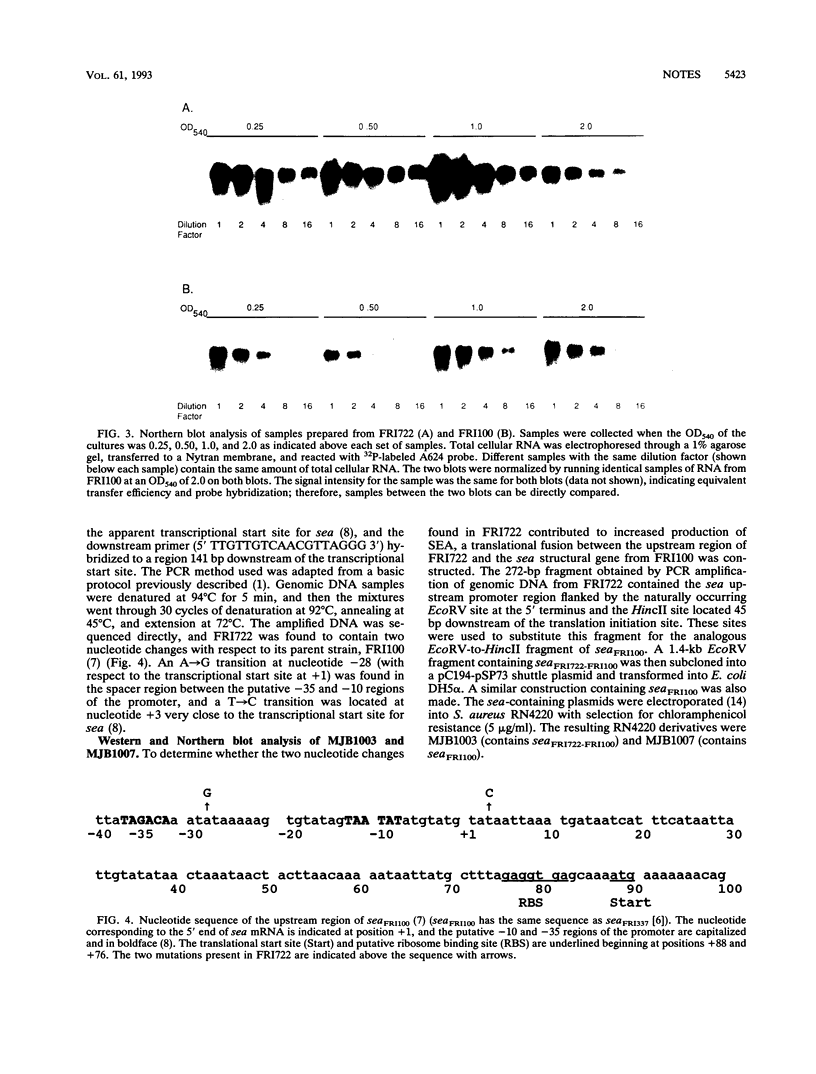
The mechanism leading to increased production of staphylococcal enterotoxin type A (SEA) in mutant Staphylococcus aureus FRI722 compared within its wild-type parent strain, FRI100, was examined. Sequence analysis revealed two mutations in the upstream promoter region of FRI722 at nucleotides -28 and +3 with respect to the transcriptional initiation site at An sea translational fusion of the upstream region of FRI722 to the structural gene from FRI100 showed an increase in sea expression by Northern (RNA) analysis and in SEA production by Western (immunoblot) analysis. To independently evaluate the effect of each mutation, site-directed mutagenesis was done and revealed that each mutation was responsible for an increase in SEA production.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayers D. G., Auble D. T., deHaseth P. L. Promoter recognition by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Role of the spacer DNA in functional complex formation. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):749–756. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90241-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Mekalanos J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the type A staphylococcal enterotoxin gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):34–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.34-41.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Mekalanos J. J. Staphylococcal enterotoxin A is encoded by phage. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.3160112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Kammerer W., Gentz R., Bujard H. Promoters of Escherichia coli: a hierarchy of in vivo strength indicates alternate structures. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2987–2994. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04596.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. E., Howard M. B. Induction of mutants of Staphylococcus aureus 100 with increased ability to produce enterotoxin A. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):289–291. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.289-291.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkin T. M., Sonenshein A. L. Mutations of the Escherichia coli lacUV5 promoter resulting in increased expression in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):467–474. doi: 10.1007/BF00331151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hufnagle W. O., Tremaine M. T., Betley M. J. The carboxyl-terminal region of staphylococcal enterotoxin type A is required for a fully active molecule. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2126–2134. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2126-2134.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iordănescu S. Recombinant plasmid obtained from two different, compatible staphylococcal plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):597–601. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.597-601.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer W., Deuschle U., Gentz R., Bujard H. Functional dissection of Escherichia coli promoters: information in the transcribed region is involved in late steps of the overall process. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2995–3000. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regassa L. B., Couch J. L., Betley M. J. Steady-state staphylococcal enterotoxin type C mRNA is affected by a product of the accessory gene regulator (agr) and by glucose. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):955–962. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.955-962.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler P., Weisblum B. Erythromycin-induced stabilization of ermA messenger RNA in Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):905–915. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]