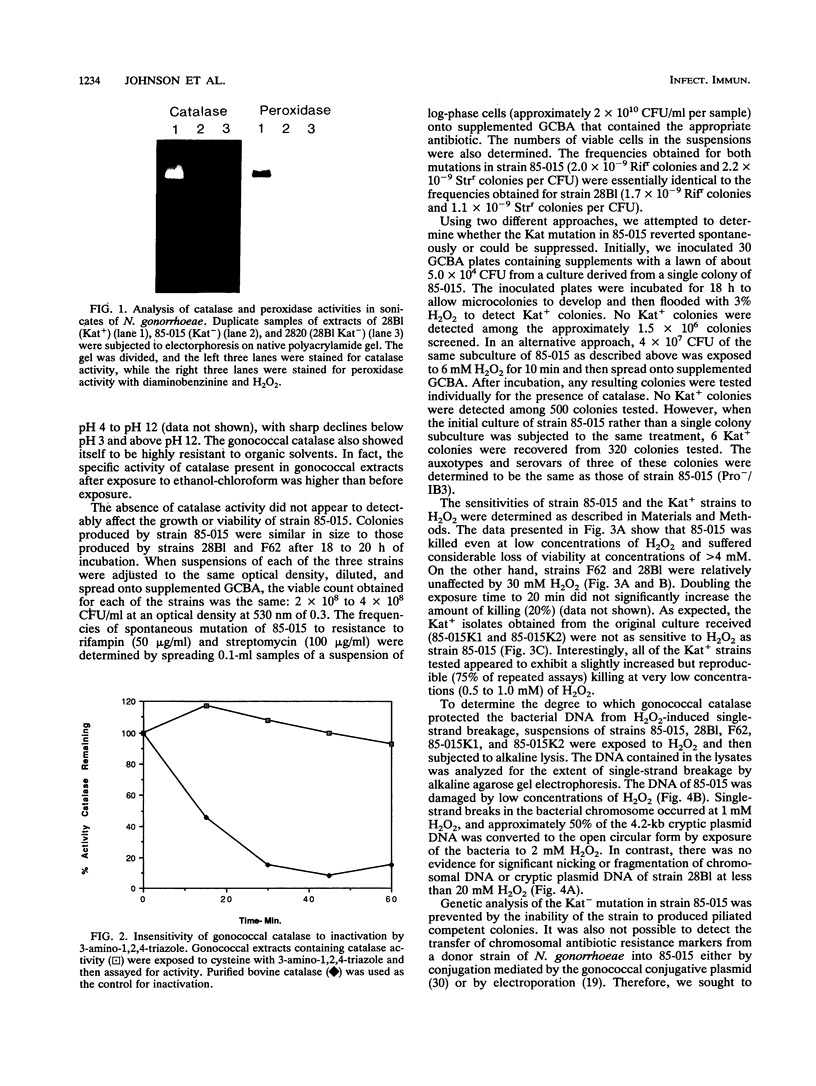
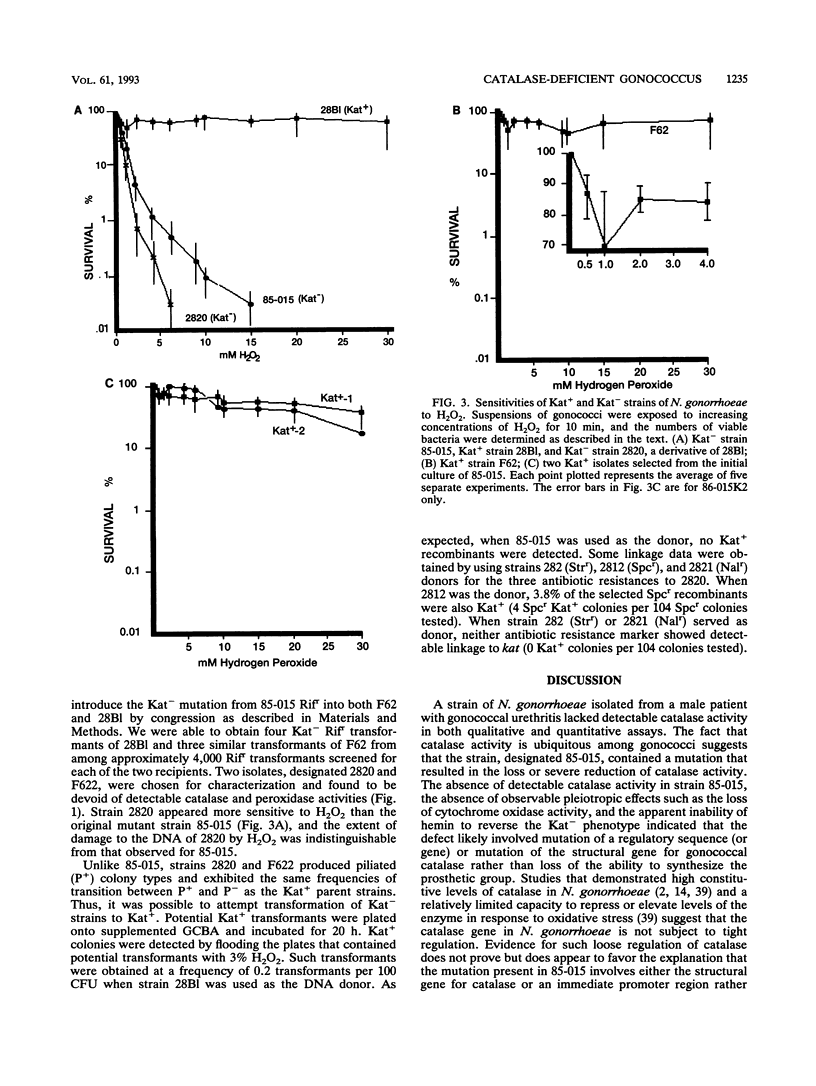
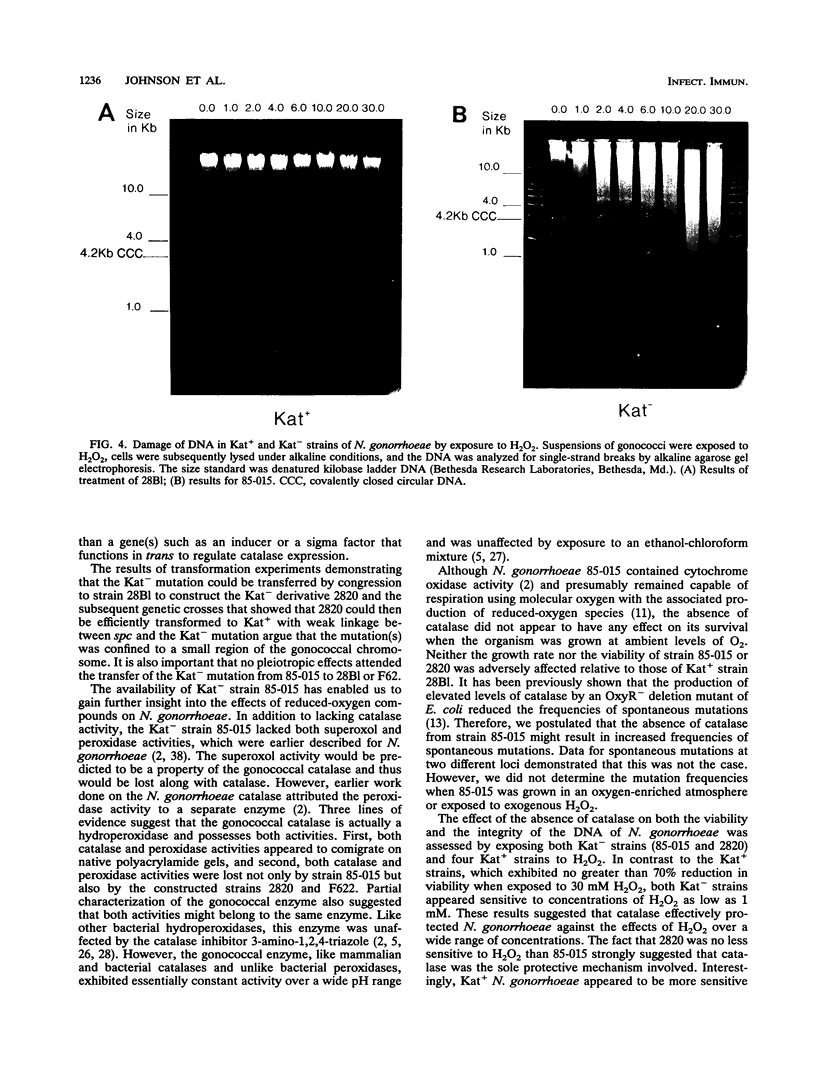
Abstract
We obtained a catalase-deficient (Kat-) strain of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolated from a patient who had been unsuccessfully treated with penicillin. Quantitative enzyme assays and electrophoresis of cell extracts on native polyacrylamide gels subsequently stained for catalase and peroxidase activities failed to detect both enzymes. The strain exhibited no growth anomalies or unusual requirements when grown under ordinary laboratory conditions. However, the Kat- strain proved extremely sensitive to exogenous hydrogen peroxide, and analysis of the bacterial DNA after such exposure showed extensive single-strand breakage in both chromosomal and plasmid DNAs. Partial characterization of the gonococcal catalase from a Kat+ laboratory strain revealed that the enzyme had the physical and chemical properties of both catalase and peroxidase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ananthaswamy H. N., Eisenstark A. Repair of hydrogen peroxide-induced single-strand breaks in Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):187–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.187-191.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald F. S., Duong M. N. Superoxide dismutase and oxygen toxicity defenses in the genus Neisseria. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):631–641. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.631-641.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEERS R. F., Jr, SIZER I. W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp C., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):276–287. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Sies H., Boveris A. Hydroperoxide metabolism in mammalian organs. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):527–605. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman M. F., Morgan R. W., Jacobson F. S., Ames B. N. Positive control of a regulon for defenses against oxidative stress and some heat-shock proteins in Salmonella typhimurium. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Halbrook J. Inducible repair of oxidative DNA damage in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):466–468. doi: 10.1038/304466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Linn S. 5,6-Saturated thymine lesions in DNA: production by ultraviolet light or hydrogen peroxide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3781–3789. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields P. I., Swanson R. V., Haidaris C. G., Heffron F. Mutants of Salmonella typhimurium that cannot survive within the macrophage are avirulent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5189–5193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzon V. L., Arondel J., Sansonetti P. J. Contribution of superoxide dismutase and catalase activities to Shigella flexneri pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):529–535. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.529-535.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. The biology of oxygen radicals. Science. 1978 Sep 8;201(4359):875–880. doi: 10.1126/science.210504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Sansonetti P. Transposon mutagenesis as a tool to study the role of hemolysin in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. T., Demple B. Overproduction of peroxide-scavenging enzymes in Escherichia coli suppresses spontaneous mutagenesis and sensitivity to redox-cycling agents in oxyR-mutants. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2611–2617. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03111.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassett D. J., Charniga L., Cohen M. S. recA and catalase in H2O2-mediated toxicity in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7293–7296. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7293-7296.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A., Linn S. Bimodal pattern of killing of DNA-repair-defective or anoxically grown Escherichia coli by hydrogen peroxide. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):519–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.519-527.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A., Linn S. Mutagenesis and stress responses induced in Escherichia coli by hydrogen peroxide. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):2967–2976. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.2967-2976.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail G., Sawyer W. D., Wegener W. S. Effect of hydrogen peroxidase and superoxide radical on viability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and related bacteria. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Jun;155(2):264–269. doi: 10.3181/00379727-155-39786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Kitagawa S. Molecular basis for the enhanced respiratory burst of activated macrophages. Fed Proc. 1985 Nov;44(14):2927–2932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Hollstein M., Christman M. F., Schwiers E. A., Ames B. N. A new Salmonella tester strain (TA102) with A X T base pairs at the site of mutation detects oxidative mutagens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7445–7449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S. A. Isolation and characterization of catalase deficient mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 18;150(2):205–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00695400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C. Isolation of catalase-deficient Escherichia coli mutants and genetic mapping of katE, a locus that affects catalase activity. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):622–626. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.622-626.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIASH E., NOVOGRODSKY A., SCHEJTER A. Irreversible reaction of 3-amino-1:2:4-triazole and related inhibitors with the protein of catalase. Biochem J. 1960 Feb;74:339–348. doi: 10.1042/bj0740339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Catalase, superoxide dismutase, and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. In vitro and in vivo studies with emphasis on staphylococcal--leukocyte interaction. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):561–566. doi: 10.1172/JCI107963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra H. P., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase and peroxidase: a positive activity stain applicable to polyacrylamide gel electropherograms. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Oct;183(2):511–515. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrod P., Morse S. A. Absence of superoxide dismutase in some strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 29;90(4):1287–1294. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Falkow S. Plasmid-mediated chromosomal gene transfer in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):66–70. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.66-70.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short H. B., Ploscowe V. B., Weiss J. A., Young F. E. Rapid method for auxotyping multiple strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):244–248. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.3.244-248.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Christman M. F., Sies H., Ames B. N. Spontaneous mutagenesis and oxidative damage to DNA in Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8917–8921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teebor G. W., Boorstein R. J., Cadet J. The repairability of oxidative free radical mediated damage to DNA: a review. Int J Radiat Biol. 1988 Aug;54(2):131–150. doi: 10.1080/09553008814551591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., LoBuglio A. F. Phagocyte-generated oxygen metabolites and cellular injury. Lab Invest. 1982 Jul;47(1):5–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist L., Rannug U., Rannug A., Ramel C. Protection from toxic and mutagenic effects of H2O2 by catalase induction in Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1984 Nov-Dec;141(3-4):145–147. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(84)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury W., Spencer A. K., Stahman M. A. An improved procedure using ferricyanide for detecting catalase isozymes. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90375-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonei S., Yokota R., Sato Y. The distinct role of catalase and DNA repair systems in protection against hydrogen peroxide in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 13;143(2):638–644. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91401-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H., Harris A. B., Tapsall J. W. Differentiation of gonococcal and non-gonococcal neisseriae by the superoxol test. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Apr;60(2):87–89. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.2.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng H. Y., Hassett D. J., Bean K., Cohen M. S. Regulation of catalase in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Effects of oxidant stress and exposure to human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1000–1006. doi: 10.1172/JCI115912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]