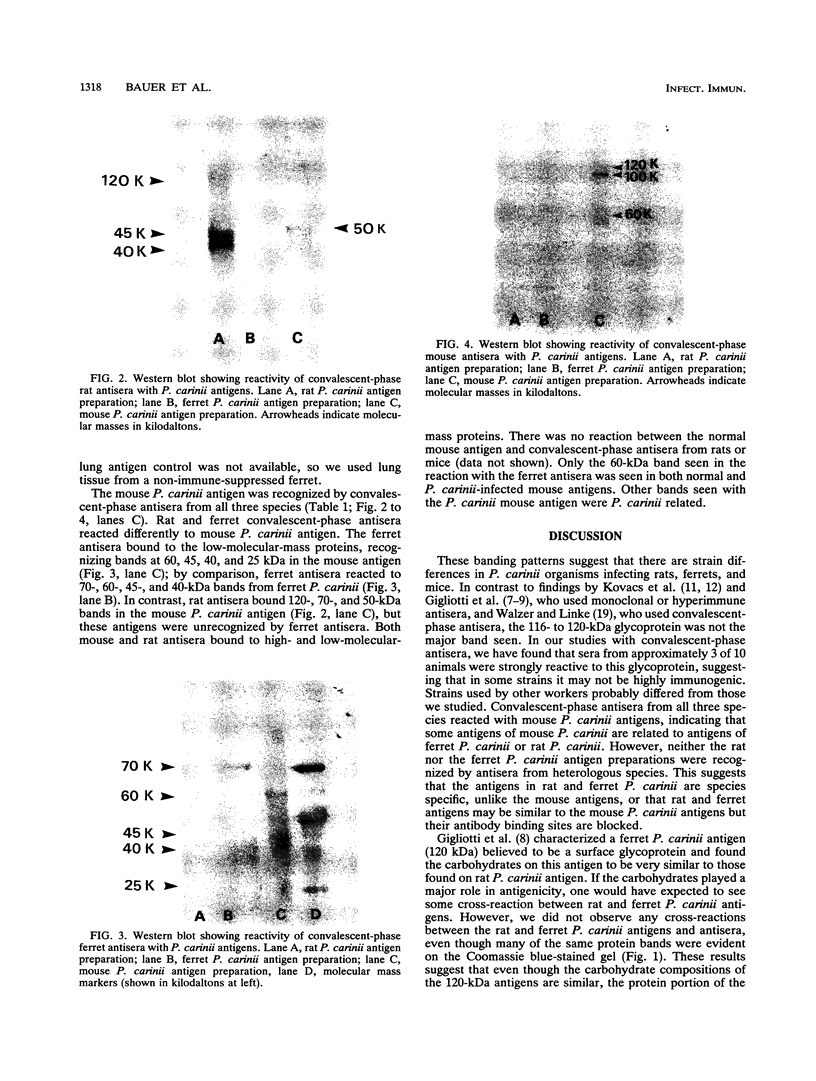
Abstract
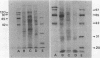
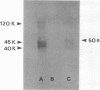
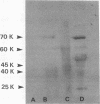
Pneumocystis carinii infections were developed in animals immunosuppressed by dexamethasone treatment either from activation of latent infection (ferret) or by transtracheal inoculation with P. carinii-infected lung tissue from the homologous species (rat or mouse). Convalescent-phase antisera were obtained by stopping dexamethasone treatment after 2 to 4 weeks and allowing animals 5 to 8 weeks for recovery. P. carinii harvests from infected lungs were purified by differential filtration, solubilized in buffer containing urea, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and 2-mercaptoethanol, subjected to SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and blotted to polyvinylidene difluoride sheets for Western immunoblot analysis. These lung preparations are hereafter referred to as P. carinii antigens. Convalescent-phase antisera from each animal species were reacted on Western blots of P. carinii antigens prepared from organisms isolated from rats, ferrets, or mice. Each combination of P. carinii antigens and antisera from the same species of animal reacted with three or more P. carinii antigen proteins. Convalescent-phase mouse antisera reacted with P. carinii antigens from mice but not rats or ferrets. Convalescent-phase rat antisera reacted with P. carinii antigens from rats and mice but not ferrets, and convalescent-phase ferret antisera showed reactions with ferret and mouse P. carinii antigens but not rat antigens. These findings indicate antigenic differences among P. carinii strains infecting these animals.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett M. S., Fishman J. A., Queener S. F., Durkin M. M., Jay M. A., Smith J. W. New rat model of Pneumocystis carinii infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1100–1102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1100-1102.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Queener S. F., Durkin M. M., Shaw M. A., Smith J. W. Inoculated mouse model of Pneumocystis carinii infection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Feb;15(2):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(92)90036-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer N. L., Paulsrud J. R., Bartlett M. S., Smith J. W., Wilde C. E., 3rd Immunologic comparisons of Pneumocystis carinii strains obtained from rats, ferrets, and mice using convalescent sera from the same sources. J Protozool. 1991 Nov-Dec;38(6):166S–168S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman J. A. Cross-reactive antigens of the rat and human Pneumocystis carinii. J Protozool. 1989 Jan-Feb;36(1):66S–67S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta T., Ueda K. Intra- and inter-species transmission and antigenic difference of Pneumocystis carinii derived from rat and mouse. Jpn J Exp Med. 1987 Feb;57(1):11–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Ballou L. R., Hughes W. T., Mosley B. D. Purification and initial characterization of a ferret Pneumocystis carinii surface antigen. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):848–854. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F. Host species-specific antigenic variation of a mannosylated surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1992 Feb;165(2):329–336. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Stokes D. C., Cheatham A. B., Davis D. S., Hughes W. T. Development of murine monoclonal antibodies to Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):315–322. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C., McNabb S. J., Worley M. A., Downs T. D., Ivey M. H. Analyses of rat Pneumocystis carinii antigens recognized by human and rat antibodies by using western immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):96–103. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.96-103.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Halpern J. L., Lundgren B., Swan J. C., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Monoclonal antibodies to Pneumocystis carinii: identification of specific antigens and characterization of antigenic differences between rat and human isolates. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jan;159(1):60–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Lundgren B., Masur H. Identification of antigens specific for Pneumocystis carinii. J Protozool. 1989 Jan-Feb;36(1):67S–69S. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1989.tb02706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linke M. J., Cushion M. T., Walzer P. D. Properties of the major antigens of rat and human Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1547–1555. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1547-1555.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth A., Janitschke K. Detection of antibody formation in mice, rats and rabbits immunized with different Pneumocystis carinii antigens. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1991 Apr;275(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80776-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair K., Wakefield A. E., Banerji S., Hopkin J. M. Pneumocystis carinii organisms derived from rat and human hosts are genetically distinct. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Mar;45(1):183–184. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield A. E., Pixley F. J., Banerji S., Sinclair K., Miller R. F., Moxon E. R., Hopkin J. M. Amplification of mitochondrial ribosomal RNA sequences from Pneumocystis carinii DNA of rat and human origin. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Nov;43(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Linke M. J. A comparison of the antigenic characteristics of rat and human Pneumocystis carinii by immunoblotting. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2257–2265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E. Comparison of rat, mouse, and human Pneumocystis carinii by immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):449–449. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E. Humoral immunity in experimental Pneumocystis carinii infection. I. Serum and bronchial lavage fluid antibody responses in rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Jun;97(6):820–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E. Serum antibody responses to Pneumocystis carinii among different strains of normal and athymic mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):620–626. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.620-626.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]