Abstract
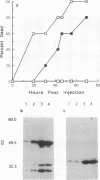
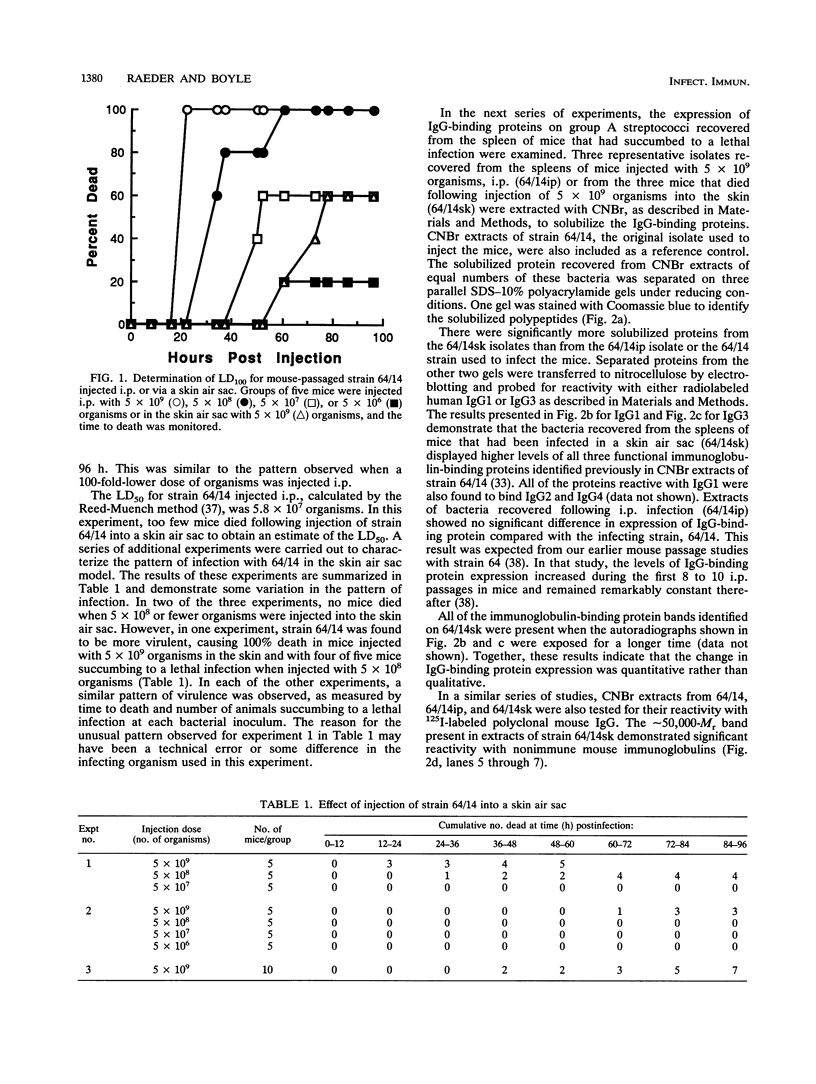
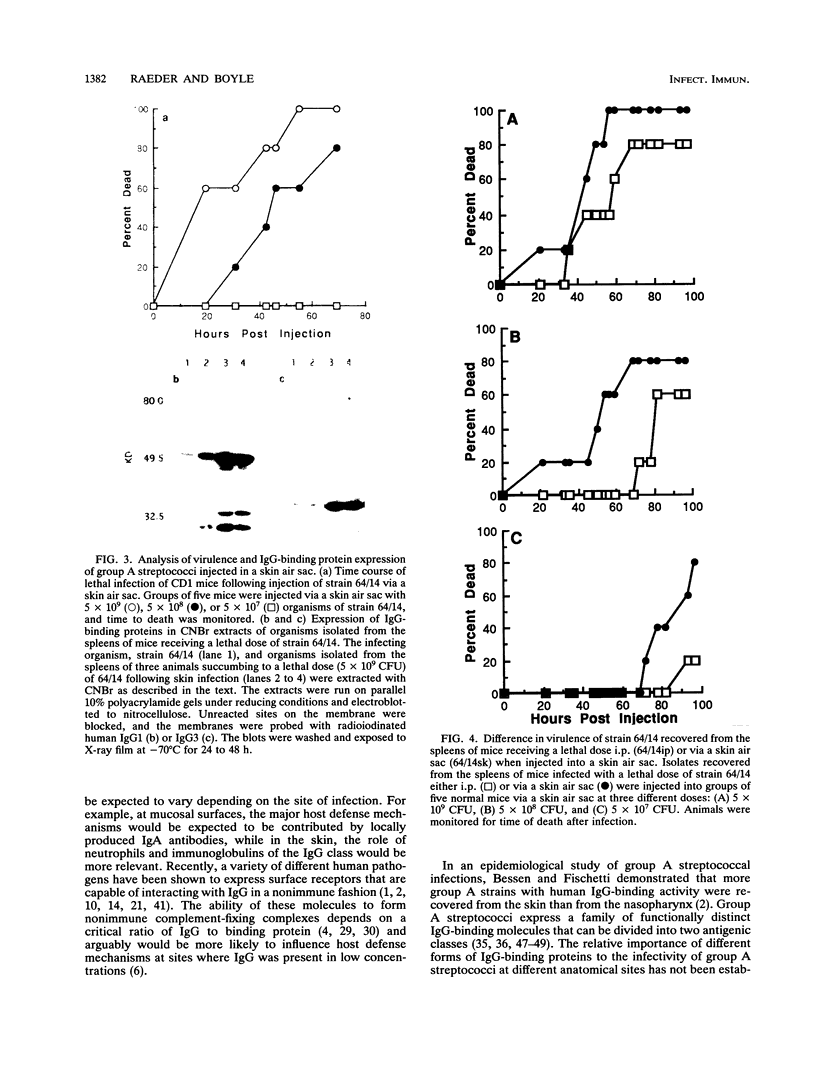
In this study, we developed a mouse model of skin infection to test the association between expression of immunoglobulin-binding proteins by and infectivity of group A streptococci. Group A streptococci capable of crossing tissue barriers and establishing a lethal systemic infection in mice showed a higher level of immunoglobulin-binding protein expression. The group A streptococci recovered from the spleen of a mouse that died following a skin infection were found to be more virulent when injected into the skin of naive mice. Together, these results suggest that immunoglobulin-binding protein expression by group A streptococci correlates with their ability to establish invasive skin infections.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balber A. E., Sturtevant J. E. A surface glycoprotein of Trypanosoma lewisi binds immunoglobulin G from the serum of uninfected rats. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):420–426. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.420-426.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessen D., Fischetti V. A. A human IgG receptor of group A streptococci is associated with tissue site of infection and streptococcal class. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):747–754. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisno A. L. Group A streptococcal infections and acute rheumatic fever. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 12;325(11):783–793. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109123251106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Chiodo V. A., Lawman M. J., Gee A. P., Young M. Urokinase: a chemotactic factor for polymorphonuclear leukocytes in vivo. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Lawman M. J., Gee A. P., Young M. Measurement of leukocyte chemotaxis in vivo. Methods Enzymol. 1988;162:101–114. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)62068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bricker B. J., Tabatabai L. B., Mayfield J. E. Immunoglobulin G binding activity of Brucella abortus. Mol Immunol. 1991 Jan-Feb;28(1-2):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90084-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder C. C., Lottenberg R., von Mering G. O., Johnston K. H., Boyle M. D. Isolation of a prokaryotic plasmin receptor. Relationship to a plasminogen activator produced by the same micro-organism. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4922–4928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Geist R. T., Perez-Casal J., Scott J. R. Environmental regulation of virulence in group A streptococci: transcription of the gene encoding M protein is stimulated by carbon dioxide. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5693–5701. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5693-5701.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Identification of a gene that regulates expression of M protein, the major virulence determinant of group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8677–8681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Menduke H., Wheelock E. F. A new method for quantitation of cell-mediated immunity in the mouse. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Mar;25(3):255–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehrer S. L., Boyle M. D., Halliwell R. E. Identification of protein A from Staphylococcus intermedius isolated from canine skin. Am J Vet Res. 1988 May;49(5):697–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A. Pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus mutants in general and local infections. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(4):564–570. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Quie P. G. Effects of staphylococcal protein A on heat labile opsonins. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1177–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G. N., Rehm S. R., Toews G. B., Hart D. A., Pierce A. K. Lung clearance of Staphylococcus aureus strains with differing protein A content: protein A effect on in vivo clearance. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):7–9. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.7-9.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higginbotham R. D. Mast cells and local resistance to Russell's viper venom. J Immunol. 1965 Nov;95(5):867–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm S. E., Norrby A., Bergholm A. M., Norgren M. Aspects of pathogenesis of serious group A streptococcal infections in Sweden, 1988-1989. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jul;166(1):31–37. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh S., Goldstein E., Lippert W., Margulies L. Effect of protein A on the antistaphylococcal defence mechanisms of the murine lung. J Infect Dis. 1978 Dec;138(6):754–759. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.6.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan E. L., Johnson D. R., Cleary P. P. Group A streptococcal serotypes isolated from patients and sibling contacts during the resurgence of rheumatic fever in the United States in the mid-1980s. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jan;159(1):101–103. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. R., Morens D. M. Severe streptococcal infections in historical perspective. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):298–307. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J., Boyle M. D., Borsos T. Studies on the interaction between protein A and immunoglobulin G. I. Effect of protein A on the functional activity of IgG. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):327–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J., Boyle M. D., Borsos T. Studies on the interaction between protein A and immunoglobulin G. II. Composition and activity of complexes formed between protein A and IgG. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):333–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J. Protein A of Staphylococcus aureus and related immunoglobulin receptors produced by streptococci and pneumonococci. Adv Immunol. 1982;32:157–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawman M. J., Boyle M. D., Gee A. P., Young M. A rapid technique for measuring leukocyte chemotaxis in vivo. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Apr 27;69(2):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90318-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottenberg R., Broder C. C., Boyle M. D. Identification of a specific receptor for plasmin on a group A streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1914–1918. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1914-1918.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten R. A., Raeder R., Heath D. G., Lottenberg R., Cleary P. P., Boyle M. D. Identification of two type IIa IgG-binding proteins expressed by a single group A streptococcus. J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):3174–3182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Casal J., Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Mry, a trans-acting positive regulator of the M protein gene of Streptococcus pyogenes with similarity to the receptor proteins of two-component regulatory systems. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2617–2624. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2617-2624.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeder R., Faulmann E. L., Boyle M. D. Evidence for functional heterogeneity in IgG Fc-binding proteins associated with group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1247–1253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeder R., Otten R. A., Chamberlin L., Boyle M. D. Functional and serological analysis of type II immunoglobulin G-binding proteins expressed by pathogenic group A streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Dec;30(12):3074–3081. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.12.3074-3081.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis K. J., Yarnall M., Ayoub E. M., Boyle M. D. Effect of mouse passage on Fc receptor expression by group A streptococci. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Nov;20(5):433–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb01022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. C., Spanier J. G., Jones S. J., Simpson W. J., Cleary P. P. Streptococcus pyogenes type 12 M protein gene regulation by upstream sequences. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5633–5640. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5633-5640.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., LaPenta D., Chen C., Cleary P. P. Coregulation of type 12 M protein and streptococcal C5a peptidase genes in group A streptococci: evidence for a virulence regulon controlled by the virR locus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):696–700. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.696-700.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stannard L. M., Hardie D. R. An Fc receptor for human immunoglobulin G is located within the tegument of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3411–3415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3411-3415.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L. Invasive group A streptococcus infections. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):2–11. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömberg A., Romanus V., Burman L. G. Outbreak of group A streptococcal bacteremia in Sweden: an epidemiologic and clinical study. J Infect Dis. 1991 Sep;164(3):595–598. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.3.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P., Kim Y., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Opsonic requirements for staphylococcal phagocytosis. Heterogeneity among strains. Immunology. 1977 Aug;33(2):191–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widders P. R., Dorrance L. A., Yarnall M., Corbeil L. B. Immunoglobulin-binding activity among pathogenic and carrier isolates of Haemophilus somnus. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):639–642. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.639-642.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarnall M., Boyle M. D. Identification of a unique receptor on a group A streptococcus for the Fc region of human IgG3. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2670–2673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarnall M., Boyle M. D. Isolation and characterization of type IIa and type IIb Fc receptors from a group A streptococcus. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Nov;24(5):549–557. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarnall M., Boyle M. D. Isolation and partial characterization of a type II Fc receptor from a group A streptococcus. Mol Cell Biochem. 1986 Apr;70(1):57–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00233803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]