Abstract
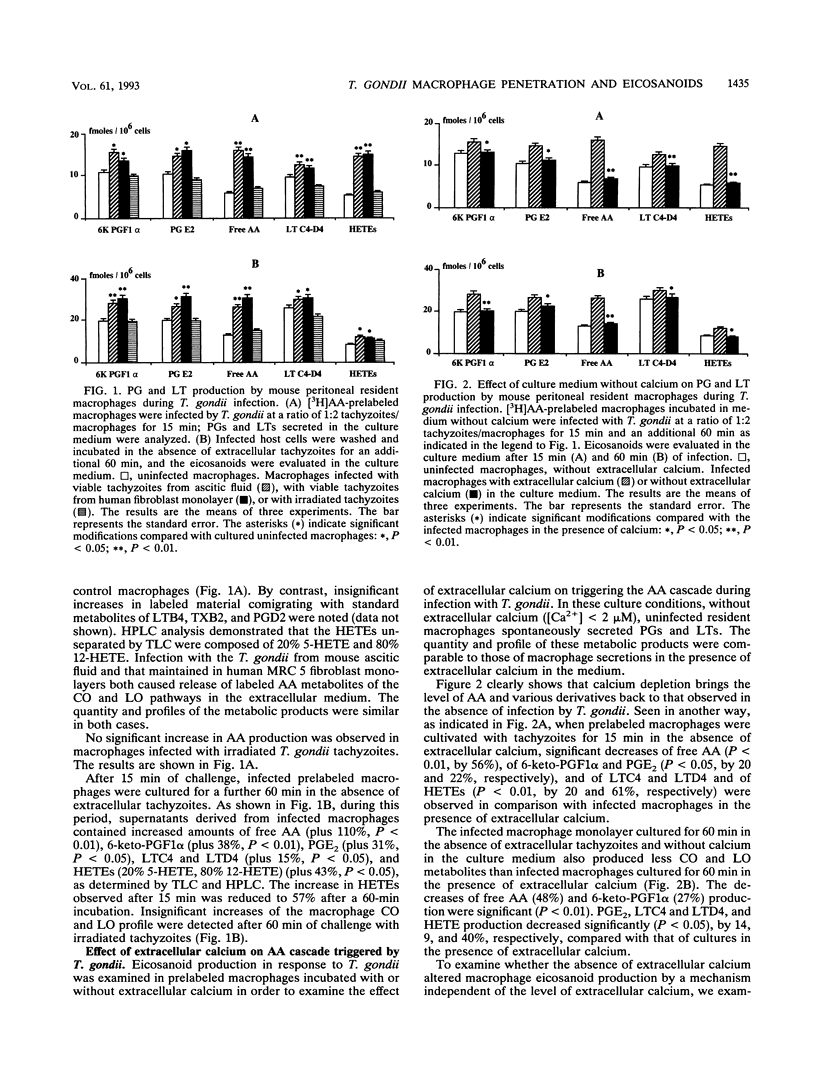
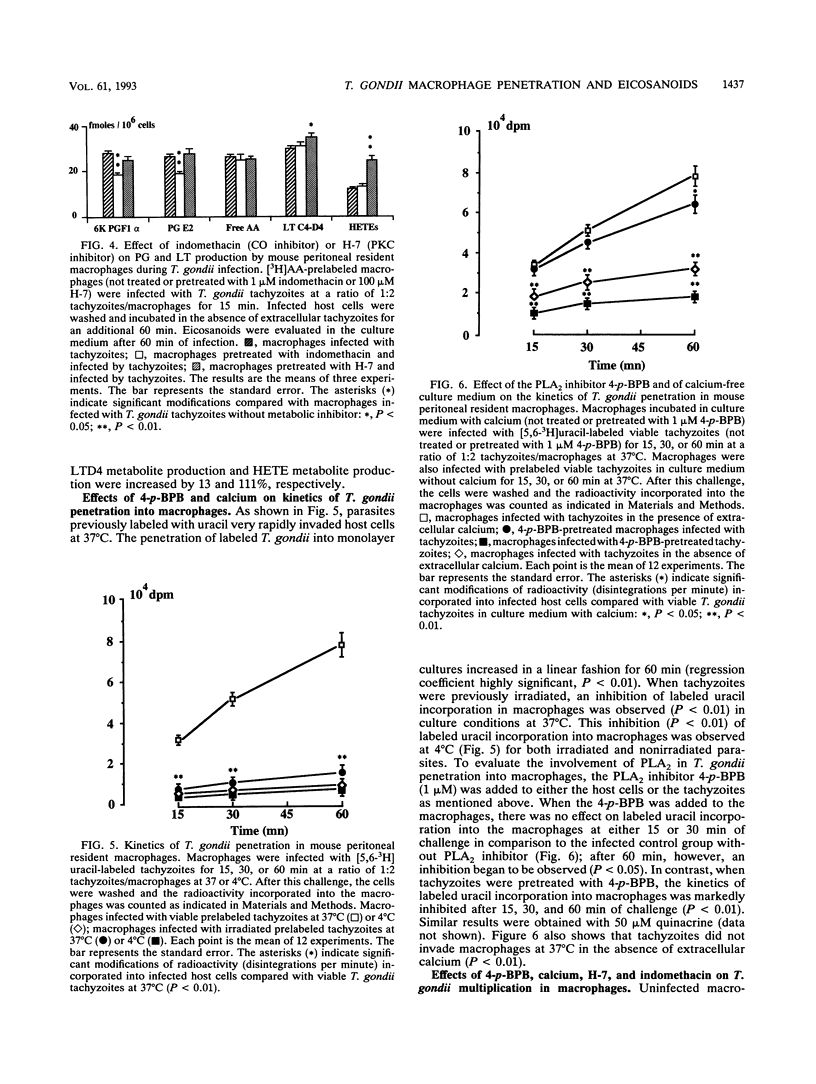
The metabolism of endogenous arachidonic acid by mouse resident peritoneal macrophages infected in vitro with Toxoplasma gondii was studied. Prelabeling of macrophages with [5,6,8,9,11,12,14,15-3H]arachidonic acid and challenge with tachyzoites for 15 min resulted in a high mobilization of free labeled arachidonic acid (178%) in the culture medium. The parasites also triggered the synthesis of 6-keto-prostaglandin F1 alpha (47%), prostaglandin E2 (44%), leukotrienes C4 and D4 (33%) and 5-, 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (155%). The study indicated that during the intracellular development phase of the parasites, 6-keto-prostaglandin F1 alpha (38%), prostaglandin E2 (31%) leukotrienes C4 and D4 (15%), hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (43%), and free arachidonic acid (110%) were secreted into the culture medium. Pretreatment of tachyzoites with phospholipase A2 inhibitors (4-p-bromophenacyl bromide and quinacrine) and no calcium in the culture medium resulted in inhibition of tachyzoite penetration into the macrophages and a decrease of the arachidonic acid metabolism. The triggering of the arachidonic acid cascade by T. gondii was dependent on the active penetration of the parasites into the macrophages, whereas preincubation of the macrophages with phospholipase A2 inhibitors did not affect penetration or free arachidonic acid release, thereby supporting a role for parasite phospholipase in the penetration process and in arachidonic acid mobilization from macrophage membrane phospholipids. Moreover, treatment of macrophages with phospholipase A2 inhibitors decreased the activities of the cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase pathways, also suggesting an activation of host cell phospholipase A2 by the parasite.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwell G. J., Flower R. J. Inhibition of phospholipase. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jul;39(3):260–264. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonser R. W., Siegel M. I., Chung S. M., McConnell R. T., Cuatrecasas P. Esterification of an endogenously synthesized lipoxygenase product into granulocyte cellular lipids. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 1;20(18):5297–5301. doi: 10.1021/bi00521a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonta I. L., Parnham M. J. Prostaglandins and chronic inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(12):1611–1623. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Morgan A. The control of free arachidonic acid levels. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):365–366. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90227-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derouin F., Mazeron M. C., Garin Y. J. Comparative study of tissue culture and mouse inoculation methods for demonstration of Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1597–1600. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1597-1600.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgue M. F., Pipy B., Beraud M., Pinelli E., Cambon C., Didier A., Souqual M. C., Vandaele J. Possible implication of arachidonic acid metabolism in the decrease of chemiluminescence production after exposure of murine peritoneal macrophages to diethylnitrosamine and tumour promoter, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Mar;12(3):449–457. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgue M. F., Pipy B., Beraud M., Souqual M. C., Combis J. M. 1-naphthyl N-methyl carbamate effect on intra- and extracellular concentrations of arachidonic acid metabolites, and on the chemiluminescence generation by mouse peritoneal macrophages. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1990;12(2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(90)90049-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fusco A. C., Salafsky B., Delbrook K. Schistosoma mansoni: production of cercarial eicosanoids as correlates of penetration and transformation. J Parasitol. 1986 Jun;72(3):397–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuse I., Iwanaga T., Tai H. H. Phorbol ester, 1,2-diacylglycerol, and collagen induce inhibition of arachidonic acid incorporation into phospholipids in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3890–3895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanni C., Becker E. L. Inhibition of neutrophil phospholipase A2 by p-bromophenylacyl bromide, nordihydroguaiaretic acid, 5,8,11,14-eicosatetraynoic acid and quercetin. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;76(3):214–217. doi: 10.1159/000233694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locksley R. M., Fankhauser J., Henderson W. R. Alteration of leukotriene release by macrophages ingesting Toxoplasma gondii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6922–6926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Naot Y., Araujo F. G., Stinson E. B., Remington J. S. Primary and reactivated toxoplasma infection in patients with cardiac transplants. Clinical spectrum and problems in diagnosis in a defined population. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):27–31. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Remington J. S. AIDS commentary. Toxoplasmic encephalitis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur S. N., Albright E., Field F. J. Incorporation of lipoxygenase products into cholesteryl esters by acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase in cholesterol-rich macrophages. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):807–814. doi: 10.1042/bj2560807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. A., Chiappino M. L. Cytoskeleton of Toxoplasma gondii. J Protozool. 1987 May;34(2):217–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1987.tb03162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. A., Chiappino M. L., O'Connor G. R. Secretion from the rhoptries of Toxoplasma gondii during host-cell invasion. J Ultrastruct Res. 1983 Apr;83(1):85–98. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(83)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby R. Host Cell Penetration of Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):250–255. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.250-255.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby R. Immunological Study on the Host Cell Penetration Factor of Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):278–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.278-286.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfannkuche H. J., Kaever V., Gemsa D., Resch K. Regulation of prostaglandin synthesis by protein kinase C in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 1;260(2):471–478. doi: 10.1042/bj2600471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Malemud C. J. Arachidonic acid metabolism by murine peritoneal macrophages infected with Leishmania donovani: in vitro evidence for parasite-induced alterations in cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase pathways. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):556–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Malemud C. J. Arachidonic acid metabolism in murine leishmaniasis (Donovani): ex-vivo evidence for increased cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase activity in spleen cells. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 15;88(2):501–510. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Schultz L. A., Malemud C. J. Eicosanoid metabolism by Leishmania donovani-infected macrophages: mouse strain responses in prostanoid synthesis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Jan;38(1):59–64. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. V., Henkle K. J., Herrmann V., McLaren D. J., Mitchell G. F. Evidence that a 16-kilodalton integral membrane protein antigen from Schistosoma japonicum adult worms is a type A2 phospholipase. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1442–1447. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1442-1447.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer L. D., Long Krug S. A., Schwartzman J. D. The role of phospholipase in host cell penetration by Toxoplasma gondii. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Feb;40(2):145–149. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.40.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer L. D., Schwartzman J. D. A soluble phospholipase of Toxoplasma gondii associated with host cell penetration. J Protozool. 1991 Sep-Oct;38(5):454–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1991.tb04816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salafsky B., Wang Y. S., Fusco A. C., Antonacci J. The role of essential fatty acids and prostaglandins in cercarial penetration (Schistosoma mansoni). J Parasitol. 1984 Oct;70(5):656–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. A., Flower R. J. Extraction and thin-layer chromatography of arachidonic acid metabolites. Methods Enzymol. 1982;86:477–493. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)86219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzman J. D. Inhibition of a penetration-enhancing factor of Toxoplasma gondii by monoclonal antibodies specific for rhoptries. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):760–764. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.760-764.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. D., Catterall J. R., Remington J. S. Parasiticidal activity of macrophages against Toxoplasma. Methods Enzymol. 1986;132:626–637. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)32046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Krahenbuhl J. L., Adams G. M., Weidner E. Toxoplasma modifies macrophage phagosomes by secretion of a vesicular network rich in surface proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):867–874. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Santucci L. A., Meyers N., Sekeyova Z. Penetration of host cells by Rickettsia rickettsii appears to be mediated by a phospholipase of rickettsial origin. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2733–2740. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2733-2740.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenson W. F., Nickells M. W., Atkinson J. P. Esterification of monohydroxyfatty acids into the lipids of a macrophage cell line. Prostaglandins. 1983 Aug;26(2):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(83)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Firth W. T., Ballard J. G., Hegarty B. C. Role of phospholipase-associated penetration mechanism in cell injury by Rickettsia rickettsii. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):840–842. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.840-842.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanke C., Tuazon C. U., Kovacs A., Dina T., Davis D. O., Barton N., Katz D., Lunde M., Levy C., Conley F. K. Toxoplasma encephalitis in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome: diagnosis and response to therapy. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 May;36(3):509–516. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werk R. How does Toxoplasma gondii enter host cells? Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):449–457. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.4.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maroussem D., Pipy B., Beraud M., Derache P., Mathieu J. R. [1-14C]Arachidonic acid incorporation into glycerolipids and prostaglandin synthesis in peritoneal macrophages: effect of chloramphenicol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Mar 27;834(1):8–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


