Abstract
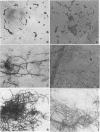
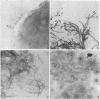
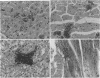
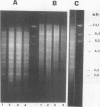
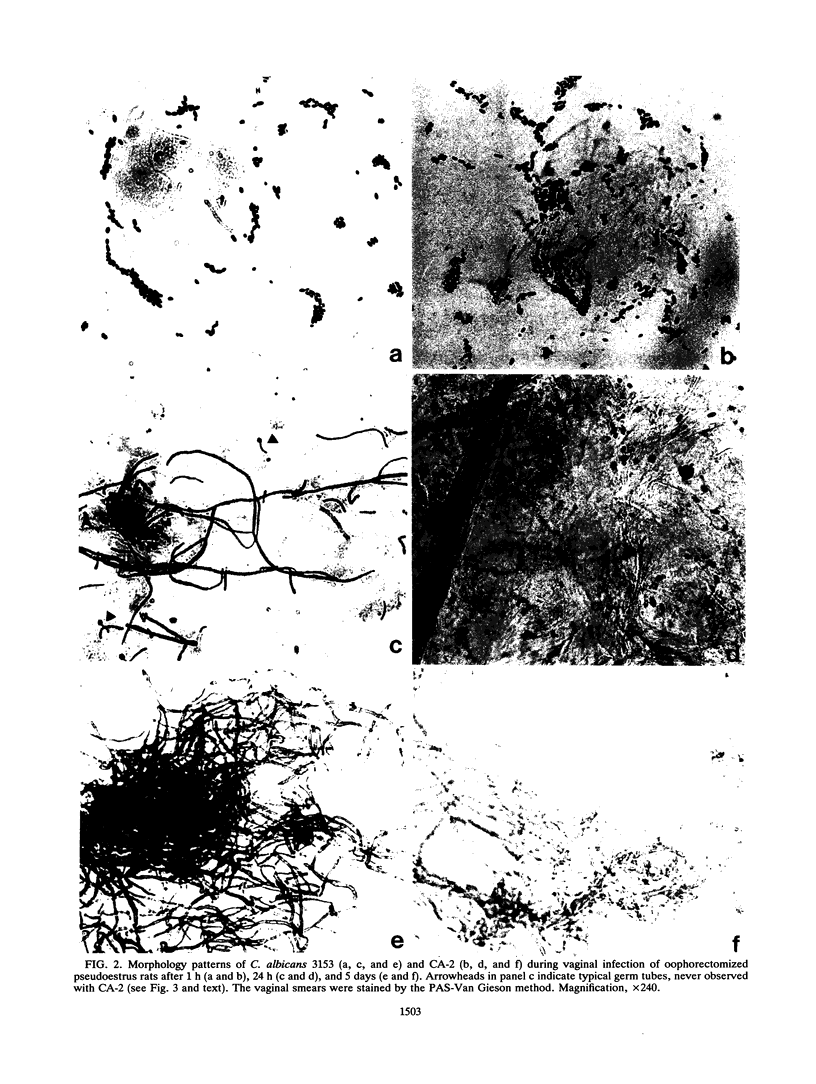
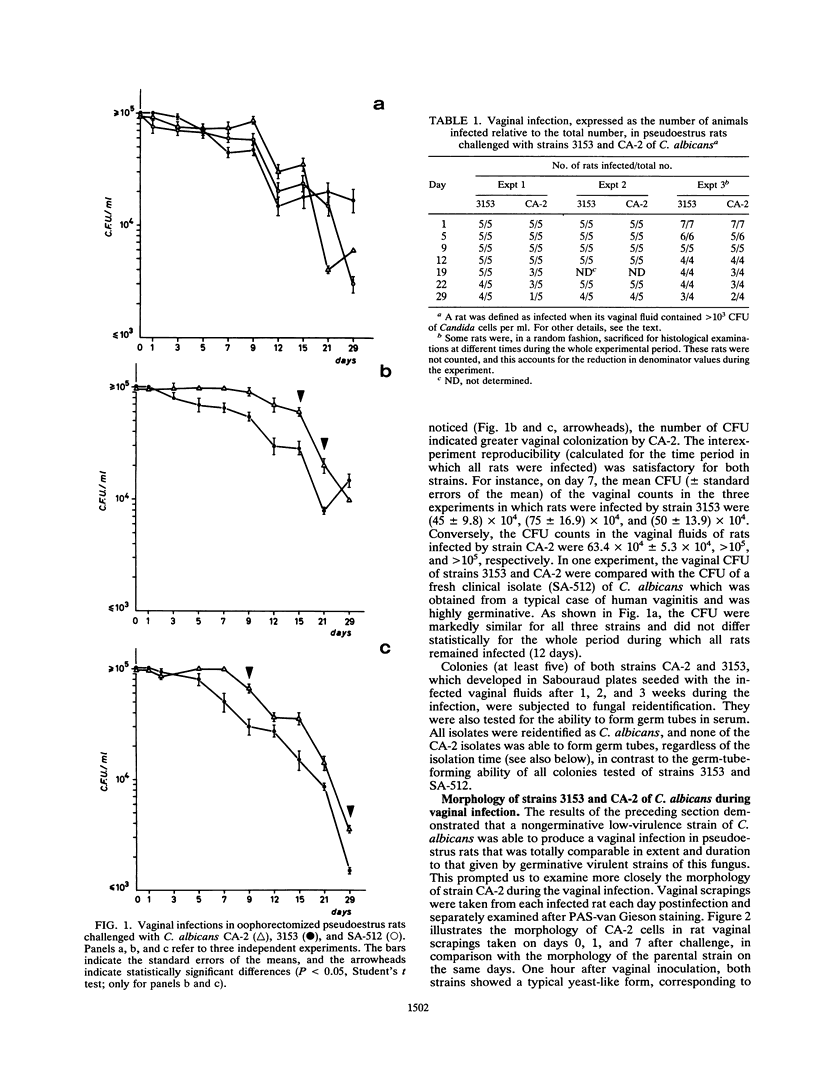
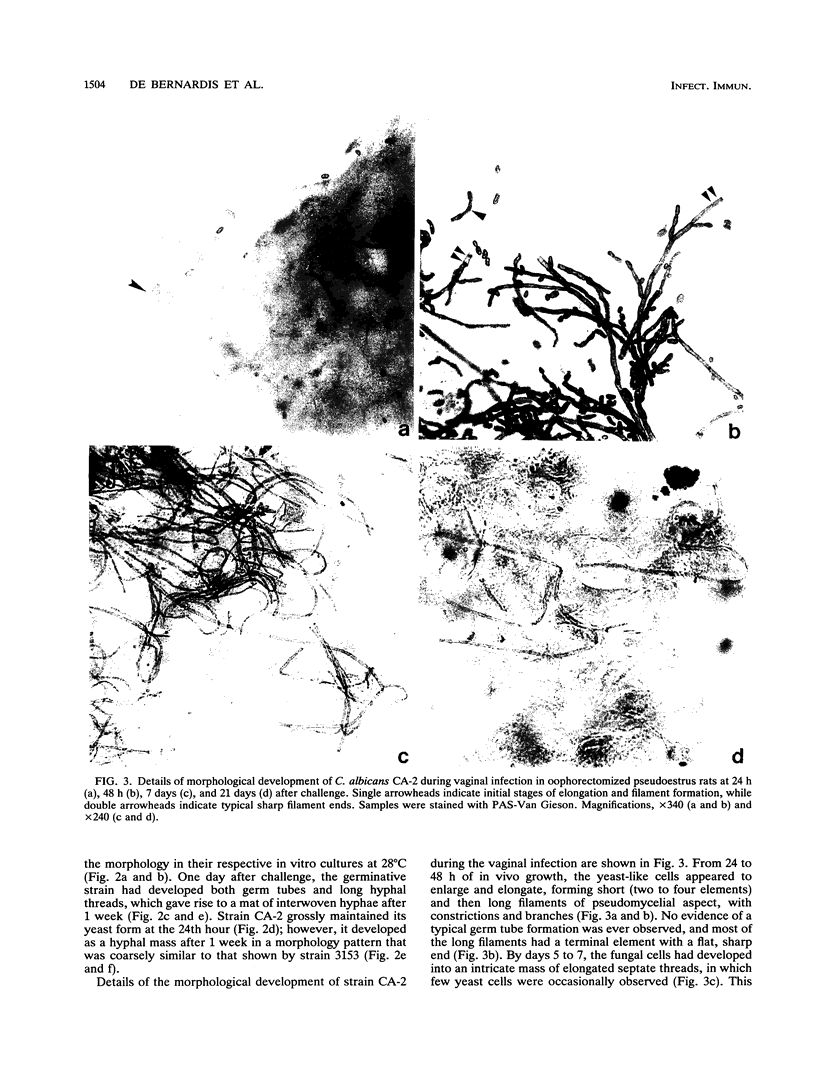
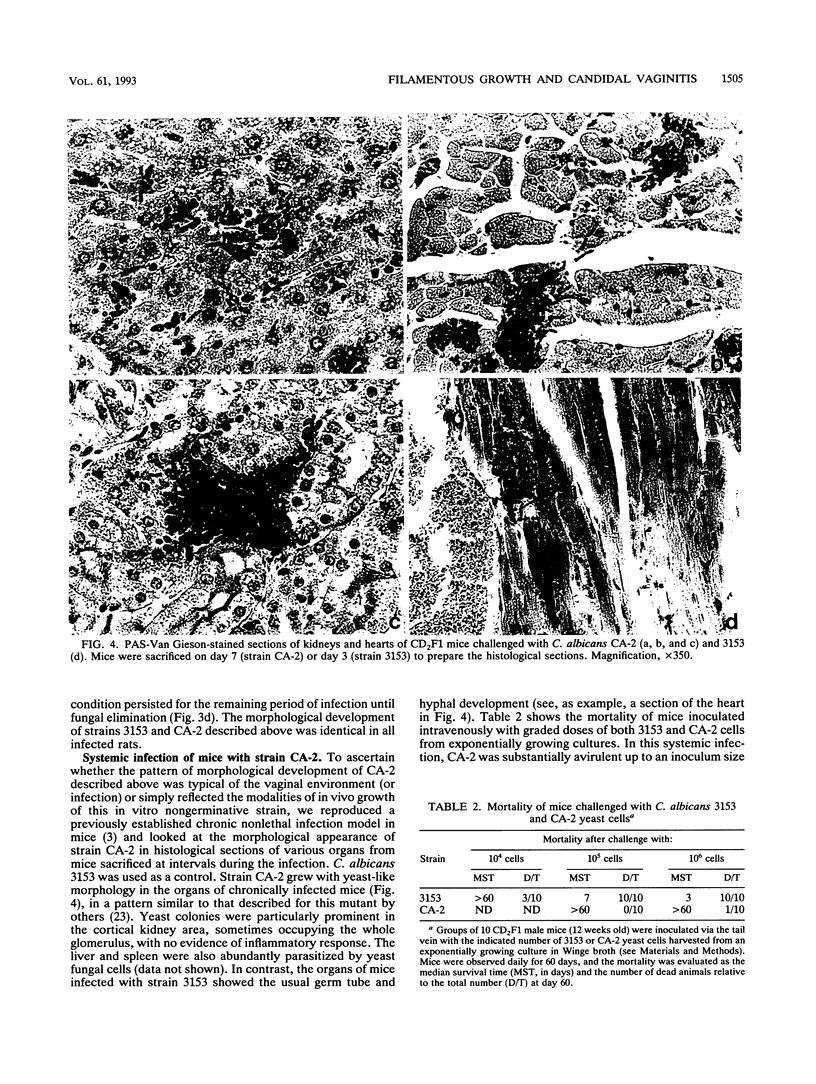
The vaginopathic potential and the intravaginal morphology of a nongerminative variant of Candida albicans, strain CA-2, were studied in a rat vaginitis model. Although it expressed low virulence in systemic infections, strain CA-2 was capable of causing a vaginal infection of the same duration and extent as that obtained in rats challenged with the germ-tube-forming strain C. albicans 3153 from the stock collection or with a fresh clinical isolate of C. albicans from a case of human vaginitis. During the experimental infection, the CA-2 cells did not maintain their yeast morphology but gave rise to single enlarged-elongated elements (1 to 2 days) which grew predominantly as coarse, short, pseudomycelium-like filaments (2 to 3 days) and then as long threads (7 days). These latter filaments were ultimately indistinguishable from the hyphal filaments formed by the germ-tube-forming strains, which, however, initially developed in the vagina by typical germ tube formation. This peculiar morphological development of strain CA-2 was not observed in organs of systemically infected mice, where, in contrast to strain 3153 which formed typical hyphae, strain CA-2 maintained a typical pattern of yeast growth. Vaginal isolates of strain CA-2 taken at different days of infection were found to be identical to the challenging CA-2 cells, in terms of biochemical characteristics, inability to form germ tubes in any medium at 37 degrees C in vitro, echinocandin resistance, DNA biotype, and low virulence in systemic infections in mice. Thus, experimental vaginitis by strain CA-2 is associated with a peculiar filamentous growth in the vagina, through an apparently novel morphological development bypassing classical germ tube formation but ultimately leading to ordinary hyphae. The elevated vaginopathic potential of strain CA-2, in contrast to its low virulence in systemic infection, also suggests that different Candida virulence factors (and host responses) come into play in local and disseminated candidal infections.
Full text
PDF


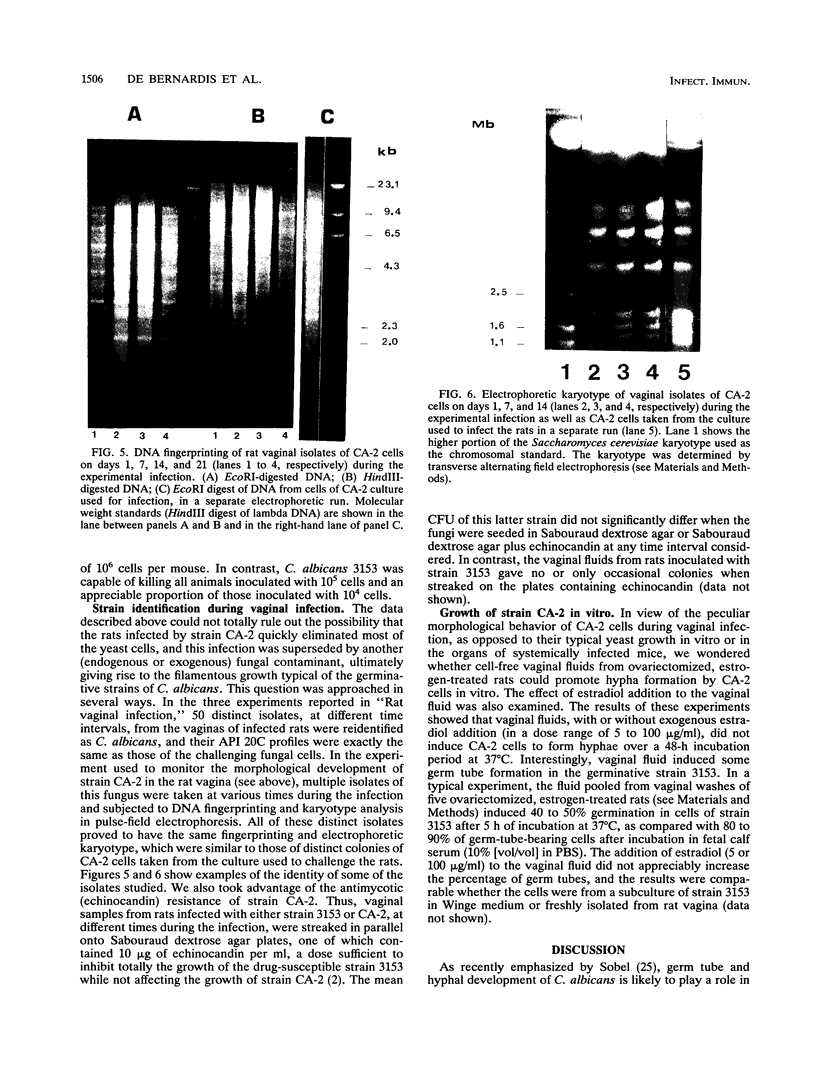


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agatensi L., Franchi F., Mondello F., Bevilacqua R. L., Ceddia T., De Bernardis F., Cassone A. Vaginopathic and proteolytic Candida species in outpatients attending a gynaecology clinic. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Oct;44(10):826–830. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.10.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bistoni F., Vecchiarelli A., Cenci E., Puccetti P., Marconi P., Cassone A. Evidence for macrophage-mediated protection against lethal Candida albicans infection. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):668–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.668-674.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E. Ultrastructural and biochemical studies of two dynamically expressed cell surface determinants on Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):327–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.327-336.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantorna M. T., Balish E. Mucosal and systemic candidiasis in congenitally immunodeficient mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1093–1100. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1093-1100.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruba G., Pontieri E., De Bernardis F., Martino P., Cassone A. DNA fingerprinting and electrophoretic karyotype of environmental and clinical isolates of Candida parapsilosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):916–922. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.916-922.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassone A. Cell wall of Candida albicans: its functions and its impact on the host. Curr Top Med Mycol. 1989;3:248–314. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-3624-5_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassone A., De Bernardis F., Mondello F., Ceddia T., Agatensi L. Evidence for a correlation between proteinase secretion and vulvovaginal candidosis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):777–783. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassone A., Mason R. E., Kerridge D. Lysis of growing yeast-form cells of Candida albicans by echinocandin: a cytological study. Sabouraudia. 1981 Jun;19(2):97–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cenci E., Romani L., Vecchiarelli A., Puccetti P., Bistoni F. Role of L3T4+ lymphocytes in protective immunity to systemic Candida albicans infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3581–3587. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3581-3587.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Acute systemic candidiasis in normal and congenitally thymic-deficient (nude) mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Feb;19(2):121–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bernardis F., Agatensi L., Ross I. K., Emerson G. W., Lorenzini R., Sullivan P. A., Cassone A. Evidence for a role for secreted aspartate proteinase of Candida albicans in vulvovaginal candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1276–1283. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bernardis F., Lorenzini R., Verticchio R., Agatensi L., Cassone A. Isolation, acid proteinase secretion, and experimental pathogenicity of Candida parapsilosis from outpatients with vaginitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2598–2603. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2598-2603.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. D., Lee J. C., Morris A. L. Adherence of Candida albicans and other Candida species to mucosal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):667–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.667-674.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsman O. S., Collard A. E. Hormonal factors in vaginal candidiasis in rats. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):498–504. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.498-504.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattia E., Carruba G., Angiolella L., Cassone A. Induction of germ tube formation by N-acetyl-D-glucosamine in Candida albicans: uptake of inducer and germinative response. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):555–562. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.555-562.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. M., Starko K. M., Zinner S. H. Symptoms associated with vaginal colonization with yeast. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Jan;158(1):31–33. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(88)90770-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D., Hopwood V., Vernes A. Antigenic variability of Candida albicans. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;12(3):223–270. doi: 10.3109/10408418509104430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross I. K., De Bernardis F., Emerson G. W., Cassone A., Sullivan P. A. The secreted aspartate proteinase of Candida albicans: physiology of secretion and virulence of a proteinase-deficient mutant. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Apr;136(4):687–694. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-4-687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryley J. F., Ryley N. G. Candida albicans--do mycelia matter? J Med Vet Mycol. 1990;28(3):225–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Aug 1;152(7 Pt 2):924–935. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(85)80003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Muller G., Buckley H. R. Critical role of germ tube formation in the pathogenesis of candidal vaginitis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):576–580. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.576-580.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Myers P. G., Kaye D., Levison M. E. Adherence of Candida albicans to human vaginal and buccal epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):76–82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D. Pathogenesis of Candida vulvovaginitis. Curr Top Med Mycol. 1989;3:86–108. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-3624-5_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Langtimm C. J., McDowell J., Hicks J., Galask R. High-frequency switching in Candida strains isolated from vaginitis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1611–1622. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1611-1622.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torosantucci A., Palma C., Boccanera M., Ausiello C. M., Spagnoli G. C., Cassone A. Lymphoproliferative and cytotoxic responses of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells to mannoprotein constituents of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Nov;136(11):2155–2163. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-11-2155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin S. S., Hirsch J., Ledger W. J. A macrophage defect in women with recurrent Candida vaginitis and its reversal in vitro by prostaglandin inhibitors. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Oct;155(4):790–795. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(86)80022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bernardis F., Morelli L., Ceddia T., Lorenzini R., Cassone A. Experimental pathogenicity and acid proteinase secretion of vaginal isolates of Candida parapsilosis. J Med Vet Mycol. 1990;28(2):125–137. doi: 10.1080/02681219080000171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]