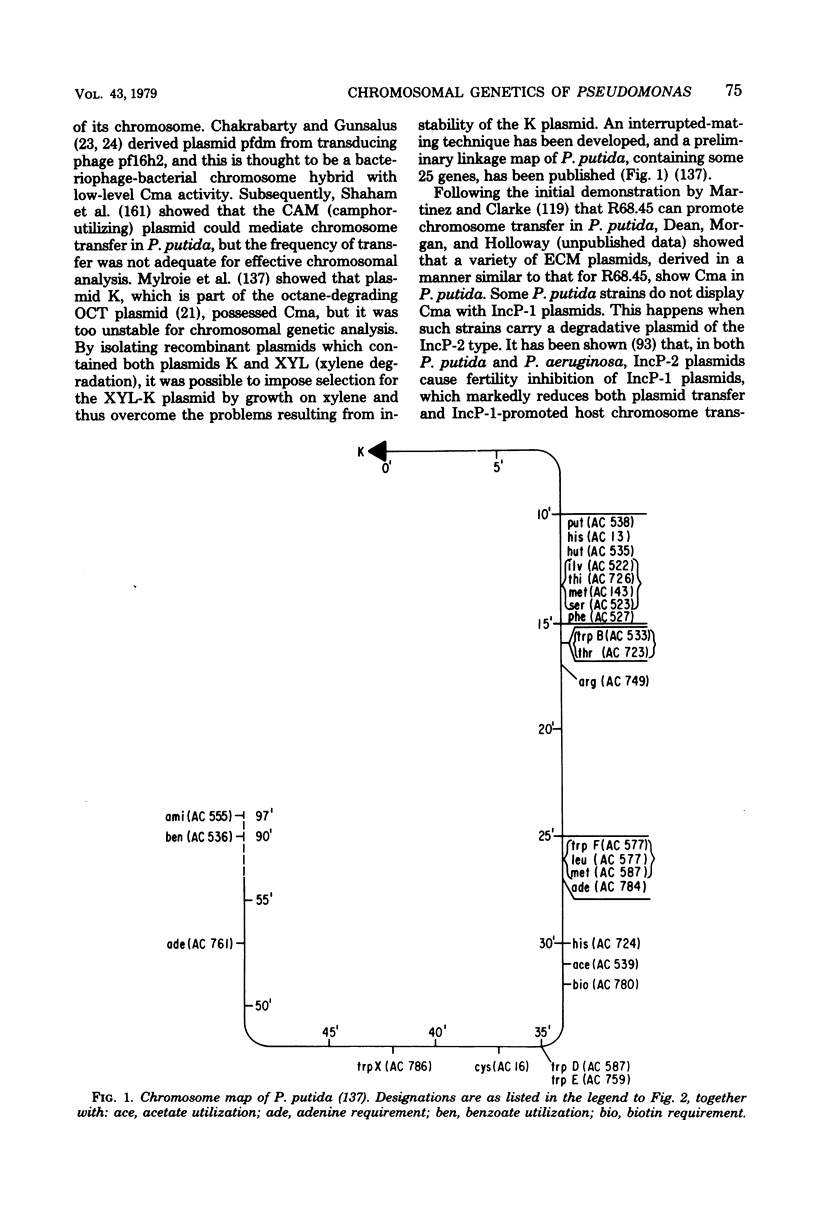
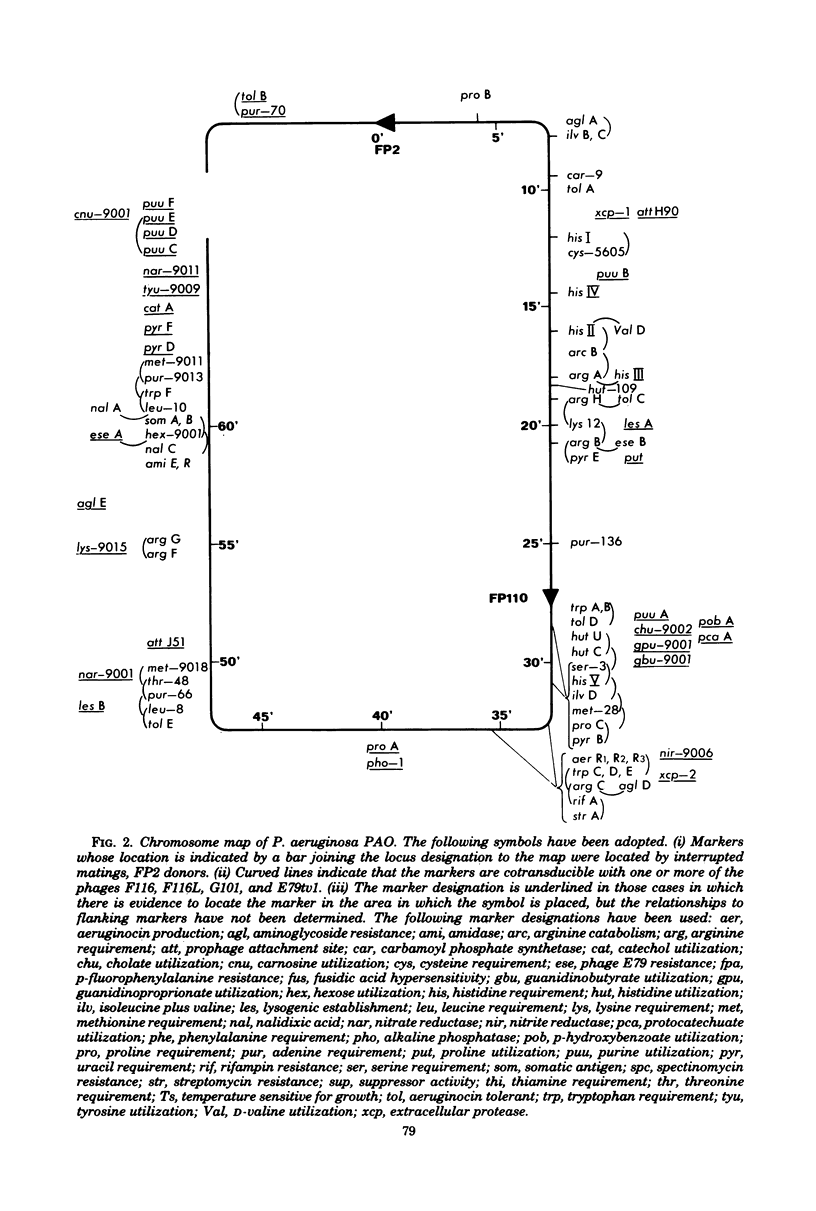
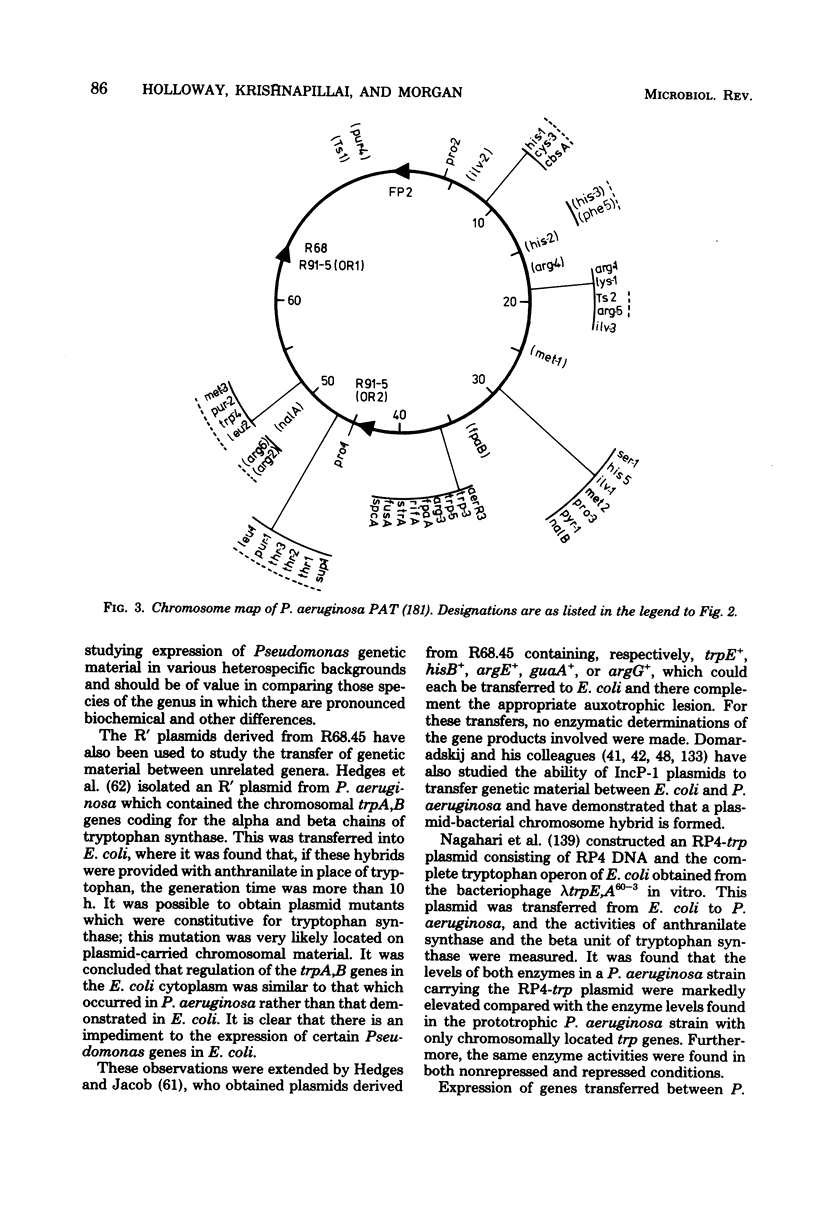
Full text
PDF


























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B., Taylor A. L. Recalibrated linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):116–167. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.116-167.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barksdale L., Arden S. B. Persisting bacteriophage infections, lysogeny, and phage conversions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):265–299. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson S., Shapiro J. TOL is a broad-host-range plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):278–280. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.278-280.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz J. L., Brown J. E., Clarke P. H., Day M. Genetic analysis of amidase mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1974 Jun;23(3):335–359. doi: 10.1017/s001667230001497x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz J. L., Brown P. R., Smyth M. J., Clarke P. H. Evolution in action. Nature. 1974 Feb 1;247(5439):261–264. doi: 10.1038/247261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blevins W. T., Feary T. W., Phibbs P. V., Jr 6-Phosphogluconate dehydratase deficiency in pleiotropic carbohydrate-negative mutant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):942–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.942-949.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher C. A., Sequeira L. Evidence for the cotransfer of genetic markers in Pseudomonas solanacearum strain K60. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Jan;24(1):69–72. doi: 10.1139/m78-013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brammar W. J., Clarke P. H., Skinner A. J. Biochemical and genetic studies with regulator mutants of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa 8602 amidase system. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Apr;47(1):87–102. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Semaka S. D., Van den Elzen H. M., Kinnear J. E., Whitehouse R. L. Characteristics of R931 and other Pseudomonas aeruginosa R factors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 May;3(5):625–637. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.5.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van Den Elzen H. M. Effects of membrane-energy mutations and cations on streptomycin and gentamicin accumulation by bacteria: a model for entry of streptomycin and gentamicin in susceptible and resistant bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):163–177. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. H., Pierson D. L., Jensen R. A. The regulation of tryptophan biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Mar 1;121(2):117–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00277526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J. M., Geisselsoder J., Zusman D. R. Isolation of bacteriophage MX4, a generalized transducing phage for Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey K. E., Krishnapillai V. Chromosomal location of prophage J51 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. Genet Res. 1975 Apr;25(2):179–187. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300015573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey K. E., Krishnapillai V. Location of prophage H90 on the chromosome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. Genet Res. 1974 Apr;23(2):155–164. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300014774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrigan J. M., Helman Z. M., Krishnapillai V. Transfer-deficient mutants of the narrow-host-range plasmid R91-5 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):911–919. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.911-919.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M., Friello D. A., Bopp L. H. Transposition of plasmid DNA segments specifying hydrocarbon degradation and their expression in various microorganisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3109–3112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M., Friello D. A. Dissociation and interaction of individual components of a degradative plasmid aggregate in Pseudomonas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3410–3414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M., Gunsalus C. F., Gunsalus I. C. Transduction and the clustering of genes in fluorescent Pseudomonads. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):168–175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M., Gunsalus I. C. Autonomous replication of a defective transducing phage in Pseudomonas putida. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):92–104. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M., Gunsalus I. C. Defective phage and chromosome mobilization in Pseudomonas putida. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1217–1223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M., Gunsalus I. C. Transduction and genetic homology between Pseudomonas species putida and aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):830–832. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.830-832.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M., Mylroie J. R., Friello D. A., Vacca J. G. Transformation of Pseudomonas putida and Escherichia coli with plasmid-linked drug-resistance factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3647–3651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M. Plasmids in Pseudomonas. Annu Rev Genet. 1976;10:7–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.10.120176.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler P. M., Krishnapillai V. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa derepressed R-plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):596–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.596-603.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler P. M., Krishnapillai V. Phenotypic properties of R factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: R factors readily transferable between Pseudomonas and the Enterobacteriaceae. Genet Res. 1974 Jun;23(3):239–250. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300014890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang B. J., Holloway B. W. Bacterial mutation affecting plasmid maintenance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):943–945. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.943-945.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosloy S. D., Oishi M. The nature of the transformation process in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Jul 31;124(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00267159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I. P. Gene rearrangements in the evolution of the tryptophan synthetic pathway. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Jun;39(2):87–120. doi: 10.1128/br.39.2.87-120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean H. F., Royle P., Morgan A. F. Detection of FP plasmids in hospital isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):249–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.249-250.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett R. G. Incidence of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa from clinical sources. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):936–937. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.936-937.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggleby C. J., Bayley S. A., Worsey M. J., Williams P. A., Broda P. Molecular sizes and relationships of TOL plasmids in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1274–1280. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1274-1280.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARGIE B., HOLLOWAY B. W. ABSENCE OF CLUSTERING OF FUNCTIONALLY RELATED GENES IN PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. Genet Res. 1965 Jul;6:284–299. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300004158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farin F., Clarke P. H. Positive regulation of amidase synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):379–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.379-392.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell R., Gunsalus I. C., Crawford I. P., Johnston J. B., Ito J. Restriction endonuclease sites and aromatic metabolic plasmid structure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 30;82(2):411–416. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90891-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennewald M., Prevatt W., Meyer R., Shapiro J. Isolation of inc P-2 plasmid DNA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Plasmid. 1978 Feb;1(2):164–173. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fil'kova E. V., Berezkina N. E., Domaradskii I. V. Transgenoz s uchastiem plazmidy RP1; ukazanie na nalichie "sostavnoi plazmidy" u mezhrodovogo gibrida Escherichia coli. Biull Eksp Biol Med. 1977 Sep;84(9):360–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulbright D. W., Leary J. V. Linkage analysis of Pseudomonas glycinea. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):497–500. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.497-500.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R. Antibiotic therapy and cystic fibrosis: increased resistance of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa to carbenicillin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):215–217. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Fyfe J. A., McMillan C. The instability of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa: fluctuation test and improved stability of the mucoid form in shaken culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jan;110(1):229–232. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-1-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Fyfe J. A. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and cystic fibrosis: resistance of the mucoid from to carbenicillin, flucloxacillin and tobramycin and the isolation of mucoid variants in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4(3):233–240. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLOWAY B. W., EGAN J. B., MONK M. Lysogeny in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1960 Aug;38:321–329. doi: 10.1038/icb.1960.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLOWAY B. W. Self-fertility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Aug;15(1):221–224. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-1-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Holloway B. W. Chromosome mobilization by the R plasmid R68.45: a tool in Pseudomonas genetics. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jan 17;158(3):229–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00267194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Holloway B. W. R factor variants with enhanced sex factor activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Mar 30;144(3):243–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00341722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Holloway B. W., Schamböck A., Leisinger T. The genetic organization of arginine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jul 7;154(1):7–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00265571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. IncP2 group of Pseudomonas, a class of uniquely large plasmids. Nature. 1978 Aug 17;274(5672):715–717. doi: 10.1038/274715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Jacob A. E., Barth P. T., Grinter N. J. Compatibility properties of P1 and PhiAMP prophages. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Dec 1;141(3):263–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00341804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Jacob A. E., Crawford I. P. Wide ranging plasmid bearing the Pseudomonas aeruginosa tryptophan synthase genes. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):283–284. doi: 10.1038/267283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heil A., Zillig W. Reconstitution of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase from isolated subunits as a tool for the elucidation of the role of the subunits in transcription. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec;11(3):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80519-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W. A genetic approach to the study of the bacterial membrane. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1971 Oct;49(5):429–434. doi: 10.1038/icb.1971.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W. Genetics of Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Sep;33(3):419–443. doi: 10.1128/br.33.3.419-443.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W. Isolation and characterization of an R' plasmid in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1078–1082. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1078-1082.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Stanisich V. Pseudomonas genetics. Annu Rev Genet. 1971;5:425–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.05.120171.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W. Plasmids that mobilize bacterial chromosome. Plasmid. 1979 Jan;2(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Rossiter H., Burgess D., Dodge J. Aeruginocin tolerant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1973 Dec;22(3):239–253. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300013069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Van de Putte P. Transducing phage for Pseudomonas putida. Nature. 1968 Feb 3;217(5127):459–460. doi: 10.1038/217459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y., Shionoya H. Relationship between pyocine and temperate phage of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 3. Serological relationship between pyocines and temperate phages. Jpn J Exp Med. 1967 Oct;37(5):395–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Chater K. F., Dowding J. E., Vivian A. Advances in Streptomyces coelicolor genetics. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):371–405. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.371-405.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Sadoff J., Bjorn M. J., Maxwell E. S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S: an adenosine diphosphate ribosyltransferase distinct from toxin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3211–3215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Tomizawa J. Prophage P1, and extrachromosomal replication unit. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:791–798. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaac J. H., Holloway B. W. Control of pyrimidine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1732–1741. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1732-1741.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., WOLLMAN E. L. Sur les processus de conjugaison et de recombinaison chez Escherichia coli. I. L'induction par conjugaison ou induction zygotique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Oct;91(4):486–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A. Properties of R plasmids determining gentamicin resistance by acetylation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):239–252. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Rogers J. E., Jacob A. E., Hedges R. W. Transposition of Pseudomonas toluene-degrading genes and expression in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):179–180. doi: 10.1038/274179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K., Kropinski A. M. The chemical composition of the lipopolysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO and a spontaneously derived rough mutant. Microbios. 1977;19(76):103–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K., Kropinski A. M. The isolation and characterization of a lipopolysaccharide-specific Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage. J Gen Virol. 1976 Oct;33(1):99–106. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston A. W., Bibb M. J., Beringer J. E. Tryptophan genes in Rhizobium--their organization and their transfer to other bacterial genera. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 24;165(3):323–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00332533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. B., Gunsalus I. C. Isolation of metabolic plasmid DNA from Pseudomonas putida. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 7;75(1):13–19. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91282-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp M. B., Hegeman G. D. Genetic control of the beta-ketoadipate pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1488–1499. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1488-1499.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koval S. F., Meadow P. M. The isolation and characterization of lipopolysaccharide-defective mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAC1. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Feb;98(2):387–398. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-2-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnapillai V. A novel transducing phage. Its role in recognition of a possible new host-controlled modification system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(2):134–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00332784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnapillai V., Carey K. E. Chromosomal location of a prophage in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. Genet Res. 1972 Aug;20(1):137–140. doi: 10.1017/s001667230001363x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Chan L., Jarrell K., Milazzo F. H. The nature of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO bacteriophage receptors. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Jun;23(6):653–658. doi: 10.1139/m77-098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Chan L., Milazzo F. H. Susceptibility of lipopolysaccharide-defective mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO to dyes, detergents, and antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):494–499. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy G. H., Leary J. V. Plasmid-mediated transmission of chromosomal genes in Pseudomonas glycinea. Genet Res. 1976 Jun;27(3):363–368. doi: 10.1017/s001667230001658x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leidigh B. J., Wheelis M. L. The clustering on the Pseudomonas putida chromosome of genes specifying dissimilatory functions. J Mol Evol. 1973 Nov 27;2(4):235–242. doi: 10.1007/BF01654092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litchrield J. H. Comparative technical and economic aspects of single-cell protein processes. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1977;22:267–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. II. Effects of lecithinase and protease. J Infect Dis. 1966 Feb;116(1):112–116. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loutit J. S. Investigation of the mating system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 1. IV. Mapping of distal markers. Genet Res. 1969 Feb;13(1):91–98. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300002767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSUSHIRO A., SATO K., ITO J., KIDA S., IMAMOTO F. ON THE TRANSCRIPTION OF THE TRYTOPHAN OPERON IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. THE TRYPTOPHAN OPERATOR. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jan;11:54–63. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoharan T. H., Jayaraman K. Mapping of the locus involved in the catabolic oxidation of D-amino acids in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Aug 4;164(1):51–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00267598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinus M. G., Loutit J. S. Regulation of isoleucine-valine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Characterisation and mapping of mutants. Genetics. 1969 Nov;63(3):547–556. doi: 10.1093/genetics/63.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S. M., Macrina F. L., Phibbs P. V., Jr R-factor inheritance and plasmid content in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):530–539. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.530-539.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. R. Mucoid variation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa induced by the action of phage. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):111–118. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Ohta S., Kobayashi R., Terawaki Y. Chromosomal location of genes participating in the degradation of purines in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 29;167(2):165–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00266910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Tazaki T. FP5 factor, an undescribed sex factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Microbiol. 1973 Sep;17(5):409–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1973.tb00792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mee B. J., Lee B. T. A map order for his I, one of the genetic regions controlling histidine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, using the transducing phage F116. Genetics. 1969 Jul;62(3):687–696. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mee B. J., Lee B. T. An analysis of histidine requiring mutants in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genetics. 1967 Apr;55(4):709–722. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.4.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergeay M., Boyen A., Legrain C., Glansdorff N. Expression of Escherichia coli K-12 arginine genes in Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1187–1188. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1187-1188.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergeay M., Gerits J. F'-plasmid transfer from Escherichia coli to Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):18–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.18-28.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Ku C. M. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants deficient in the establishment of lysogeny. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):875–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.875-883.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Pemberton J. M., Clark A. J. Prophage F116: evidence for extrachromosomal location in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):844–847. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.844-847.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills B. J., Holloway B. W. Mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that show specific hypersensitivity to aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Sep;10(3):411–416. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Cohen J., Weisburd M. Isolation of nonsense suppressor mutants in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):177–182. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.177-182.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minina T. S., Andreevskaia E. A., Domaradskii I. V. Novye ukazaniia na uchastie plazmid R gruppy P v perenose khromosomnykh genov pri mezhrodovykh skreshchivaniiakh. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1978 Oct;(10):61–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moillo A. M. Isolation of a transducing phage forming plaques on Pseudomonas maltophilia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1973 Jun;21(3):287–289. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300013471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mylroie J. R., Friello D. A., Chakrabarty A. M. Transformation of Pseudomonas putida with chromosomal DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 15;82(1):281–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90606-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahari K., Sakaguchi K. RSF1010 plasmid as a potentially useful vector in Pseudomonas species. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1527–1529. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1527-1529.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahari K., Sano Y., Sakaguchi K. Derepression of E. coli trp operon on interfamilial transfer. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):745–746. doi: 10.1038/266745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahari K., Tanaka T., Hishinuma F., Kuroda M., Sakaguchi K. Control of tryptophan synthetase amplified by varying the numbers of composite plasmids in Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1977 Mar;1(2):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa T., Hayashi E., Yokota T., Ebina Y., Nakazawa A. Isolation of TOL and RP4 recombinants by integrative suppression. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):270–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.270-277.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa T. TOL plasmid in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO: thermosensitivity of self-maintenance and inhibition of host cell growth. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):527–535. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.527-535.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi M., Cosloy S. D. The genetic and biochemical basis of the transformability of Escherichia coli K12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Dec 18;49(6):1568–1572. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90520-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Hansen J. Evolution and utility of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa drug resistance factor. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):837–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.837-844.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Metcalf E. S. Conversion of mesophilic to psychrophilic bacteria. Science. 1968 Dec 13;162(3859):1288–1289. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3859.1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Metcalf E. S., Todd J. K. Characteristics of bacteriophages attacking psychrophilic and mesophilic pseudomonads. J Virol. 1968 Apr;2(4):357–364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.4.357-364.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palchaudhuri S. Molecular characterization of hydrocarbon degradative plasmids in Pseudomonas putida. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):518–525. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton J. M., Holloway B. W. Chromosome mapping in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1972 Jun;19(3):251–260. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300014518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton J. M. Size of the chromosome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):748–752. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.748-752.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, McCowen S. M., Feary T. W., Blevins W. T. Mannitol and fructose catabolic pathways of Pseudomonas aeruginosa carbohydrate-negative mutants and pleiotropic effects of certain enzyme deficiencies. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):717–728. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.717-728.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: persisting problems and current research to find new therapies. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jun;82(6):819–831. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-6-819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravin V. K., Shulga M. G. Evidence for extrachromosomal location of prophage N15. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):800–807. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M., Solomon L., Zipkas D. Relationship between gene function and gene location in Escherichia coli. J Mol Evol. 1978 May 12;11(1):47–56. doi: 10.1007/BF01768024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. L., Hegeman G. D. Clustering of functionally related genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):353–355. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.353-355.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Hartman P. E. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition V. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):471–519. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.471-519.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieger H. Phage P22-mutants with increased or decreased transduction abilities. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(1):75–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00270447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaham M., Chakrabarty A. M., Gunsalus I. C. Camphor plasmid-mediated chromosomal transfer in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):944–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.944-949.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomiya T., Osumi M., Kageyama M. Defective pyocin particles produced by some mutant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1508–1521. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1508-1521.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair M. I., Morgan A. F. Transformation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO with bacteriophage and plasmid DNA. Aust J Biol Sci. 1978 Dec;31(6):679–688. doi: 10.1071/bi9780679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth P. F., Clarke P. H. Catabolite repression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa amidase: isolation of promotor mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Sep;90(1):91–99. doi: 10.1099/00221287-90-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobieski R. J., Olsen R. H. Cold-sensitive Pseudomonas RNA polymerase. II. Cold-promoted restriction of bacteriophage CB3 and the lack of host-dependent bacteriophage-specific RNA transcription. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1384–1394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1384-1394.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Ornston L. N. The beta-ketoadipate pathway. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9(0):89–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V. A., Bennett P. M., Richmond M. H. Characterization of a translocation unit encoding resistance to mercuric ions that occurs on a nonconjugative plasmid in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1227–1233. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1227-1233.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V. A., Holloway B. W. A mutant sex factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1972 Feb;19(1):91–108. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300014294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V. A., Holloway B. W. Chromosome transfer in Pseudomonas aeruginosa mediated by R factors. Genet Res. 1971 Apr;17(2):169–172. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300012179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V., Holloway B. W. Genetic effects of acridines on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1969 Feb;13(1):57–70. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300002731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker R., Rørvig O., Kahlon P., Gunsalus I. C. NIC, a conjugative nicotine-nicotinate degradative plasmid in Pseudomonas convexa. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):289–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.289-290.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurm P., Garro A. J. Isolation and characterization of prophage mutants of the defective Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage PBSX. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):184–191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.184-191.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicente M., Pedro M. A., Torrontegui G., Cánovas J. L. The uptake of glucose and gluconate by Pseudomonas putida. Mol Cell Biochem. 1975 Apr 30;7(1):59–64. doi: 10.1007/BF01732164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voellmy R., Leisinger T. Dual role for N-2-acetylornithine 5-aminotransferase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in arginine biosynthesis and arginine catabolism. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):799–809. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.799-809.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. M., Holloway B. W. Chromosome mapping in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAT. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1113–1125. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1113-1125.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. M., Holloway B. W. Linkage map of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAT. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):507–521. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.507-521.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. M., Holloway B. W. Suppressor mutations in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):780–786. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.780-786.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. D., Scaife J. G. Chromosomal transfer promoted by the promiscuous plasmid RP4. Plasmid. 1978 Feb;1(2):226–237. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelis L. The genetics of dissimilarity pathways in Pseudomonas. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:505–524. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelis M. L., Stanier R. Y. The genetic control of dissimilatory pathways in Pseudomonas putida. Genetics. 1970 Oct;66(2):245–266. doi: 10.1093/genetics/66.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods W. H., Egan J. B. Prophage induction of noninducible coliphage 186. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1349–1356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1349-1356.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Sjöberg L., Wadström T. Protease-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: pleiotropic changes in activity of other extracellular enzymes. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Dec;103(2):329–336. doi: 10.1099/00221287-103-2-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Wadström T. Purification and properties of a protease with elastase activity from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Dec;103(2):319–327. doi: 10.1099/00221287-103-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T. A model for three-point analysis of random general transduction. Genetics. 1966 Aug;54(2):405–410. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh W. K., Davis G., Fletcher P., Ornston L. N. Homologous amino acid sequences in enzymes mediating sequential metabolic reactions. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4920–4923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Torrontegui G., Diaz R., Wheelis M. L., Cánovas J. L. Supra-operonic clustering of genes specifying glucose dissimilation in Pseudomonas putida. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Mar 30;144(3):307–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00341729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hartingsveldt J., Stouthamer A. H. Mapping and characerization of mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa affected in nitrate respiration in aerobic or anaerobic growth. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):97–106. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


