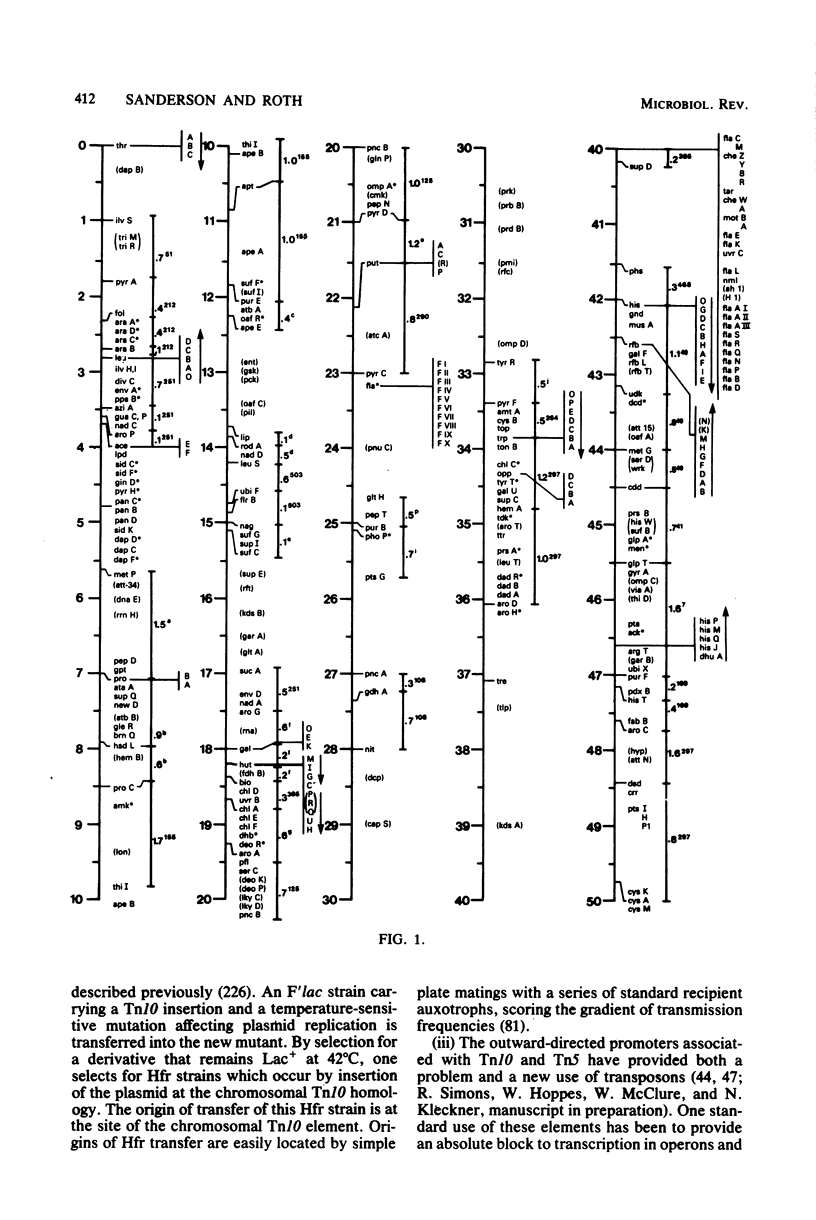
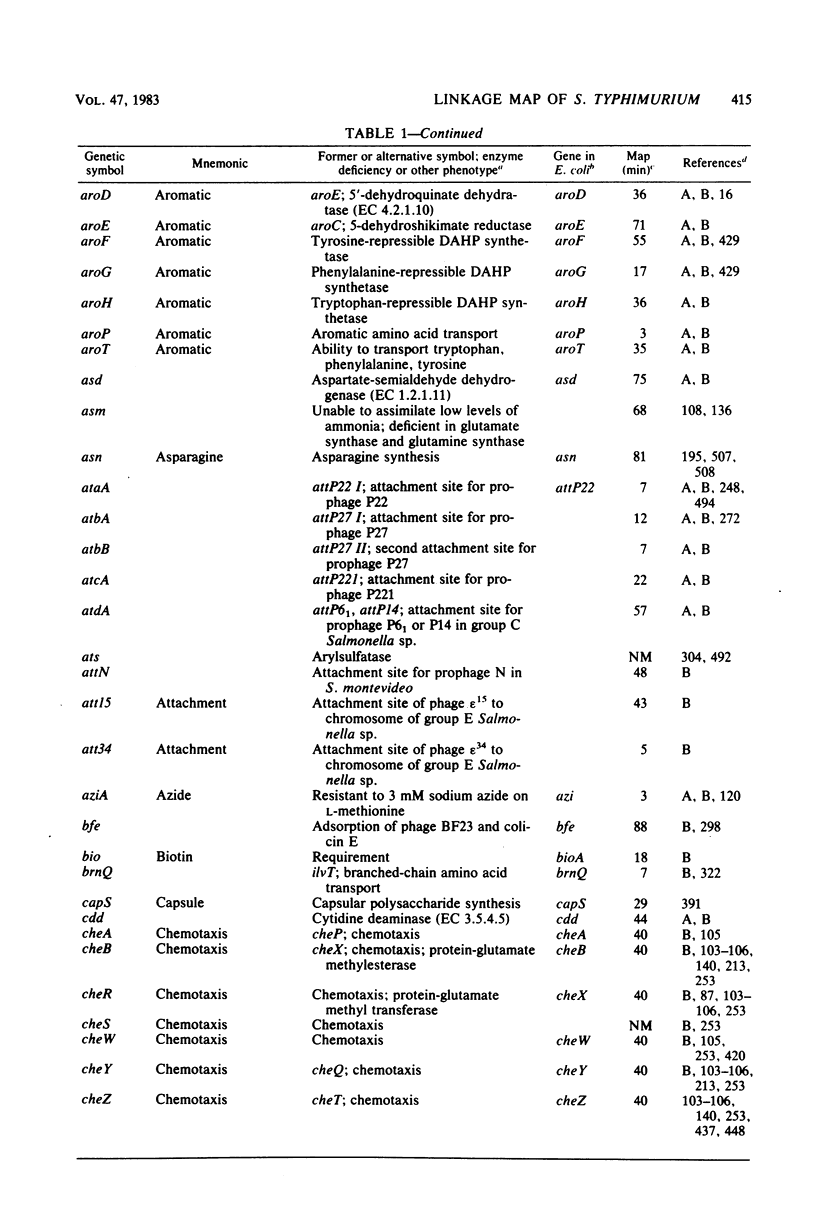
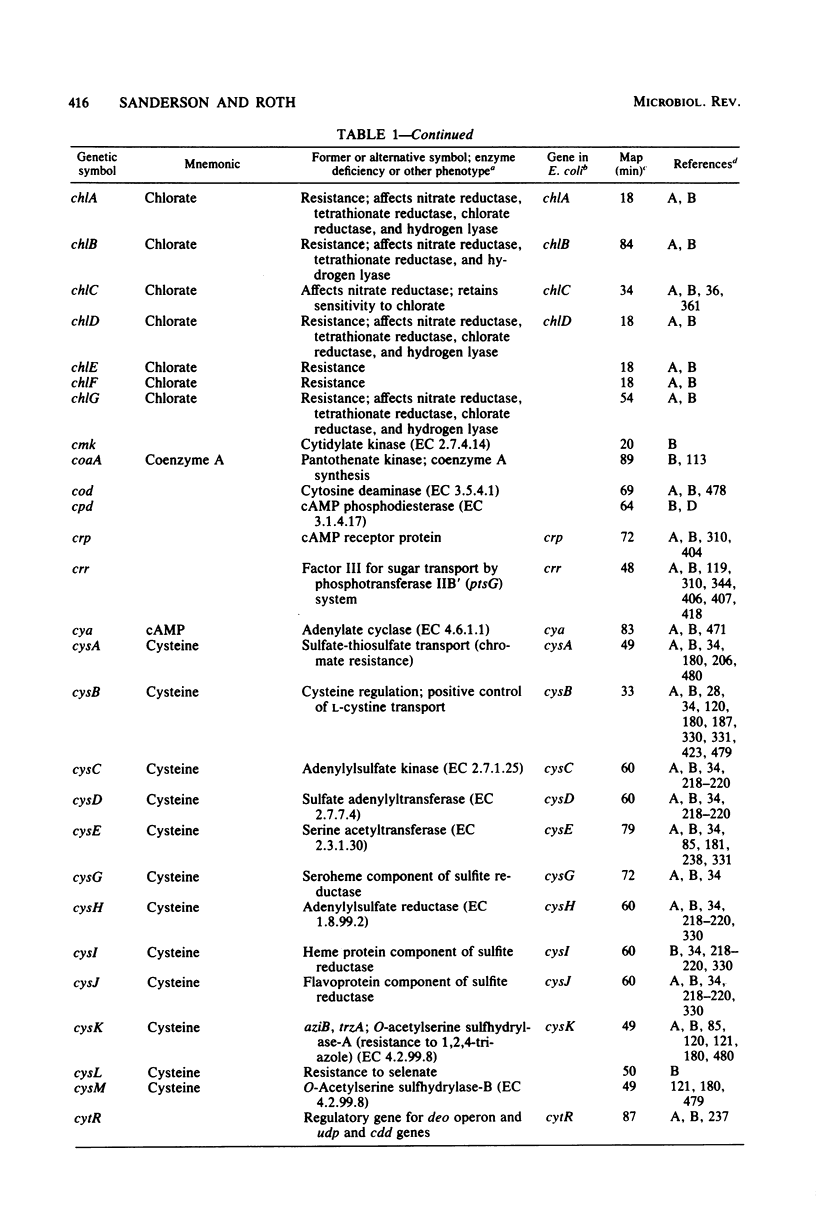
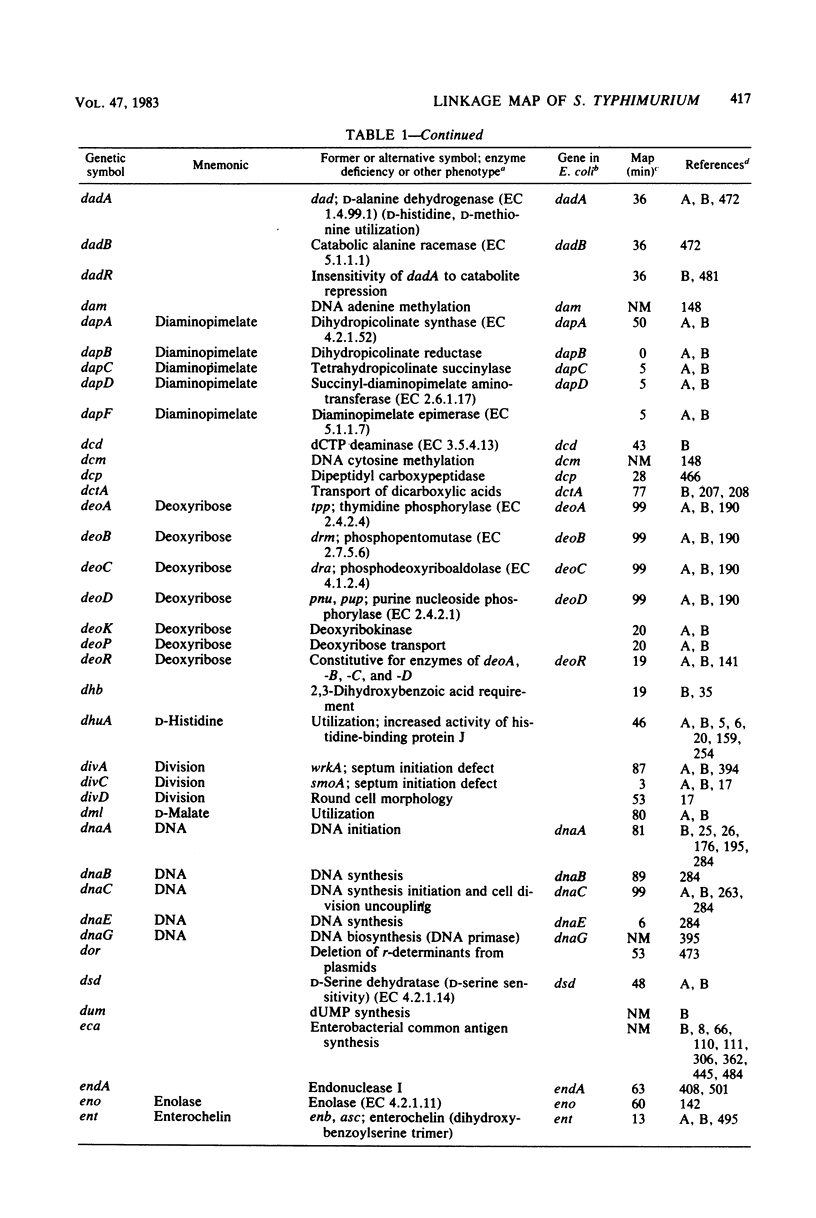
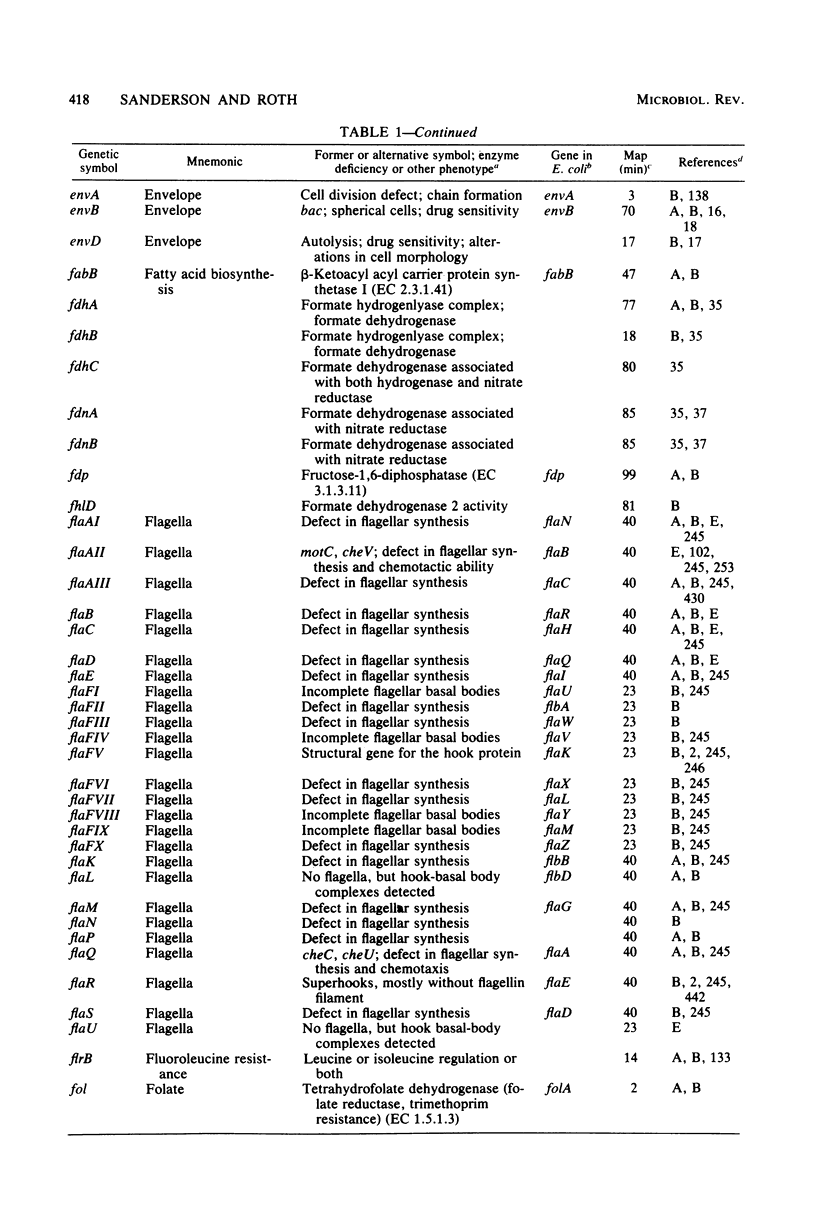
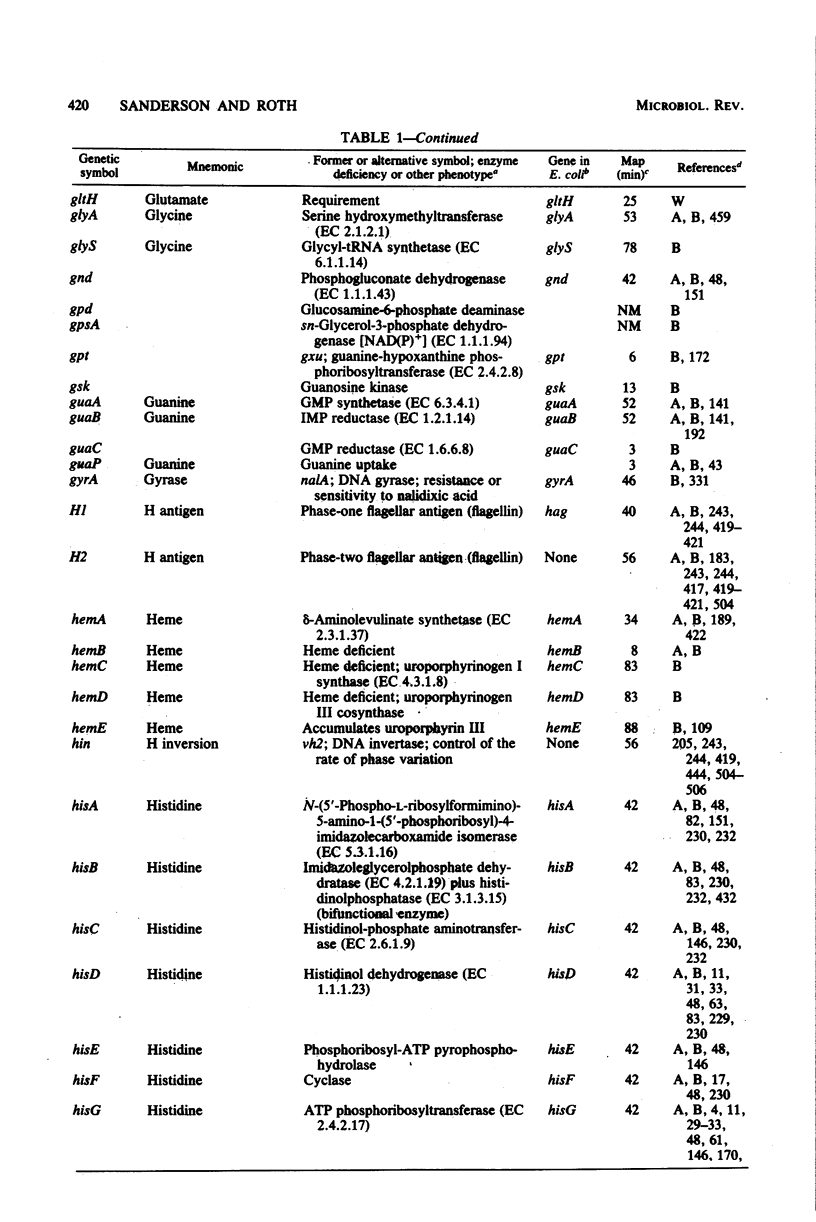
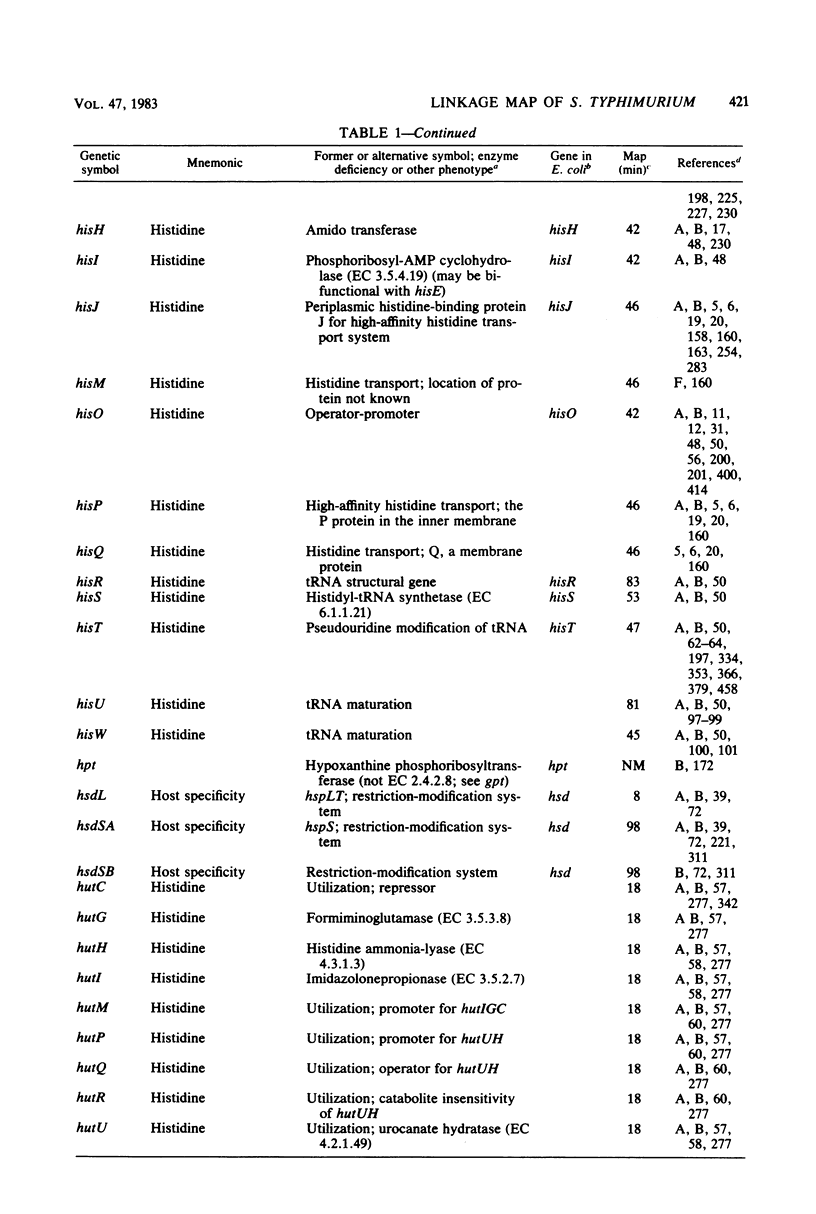
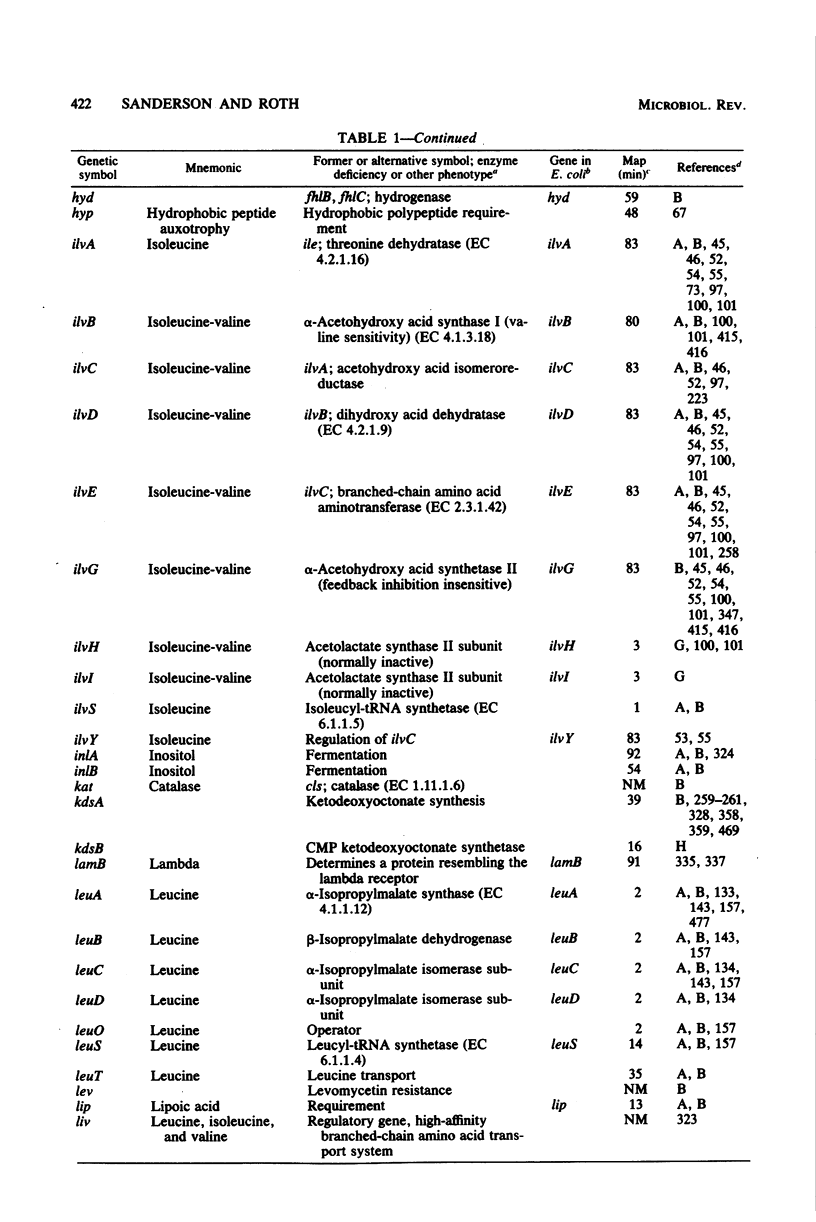
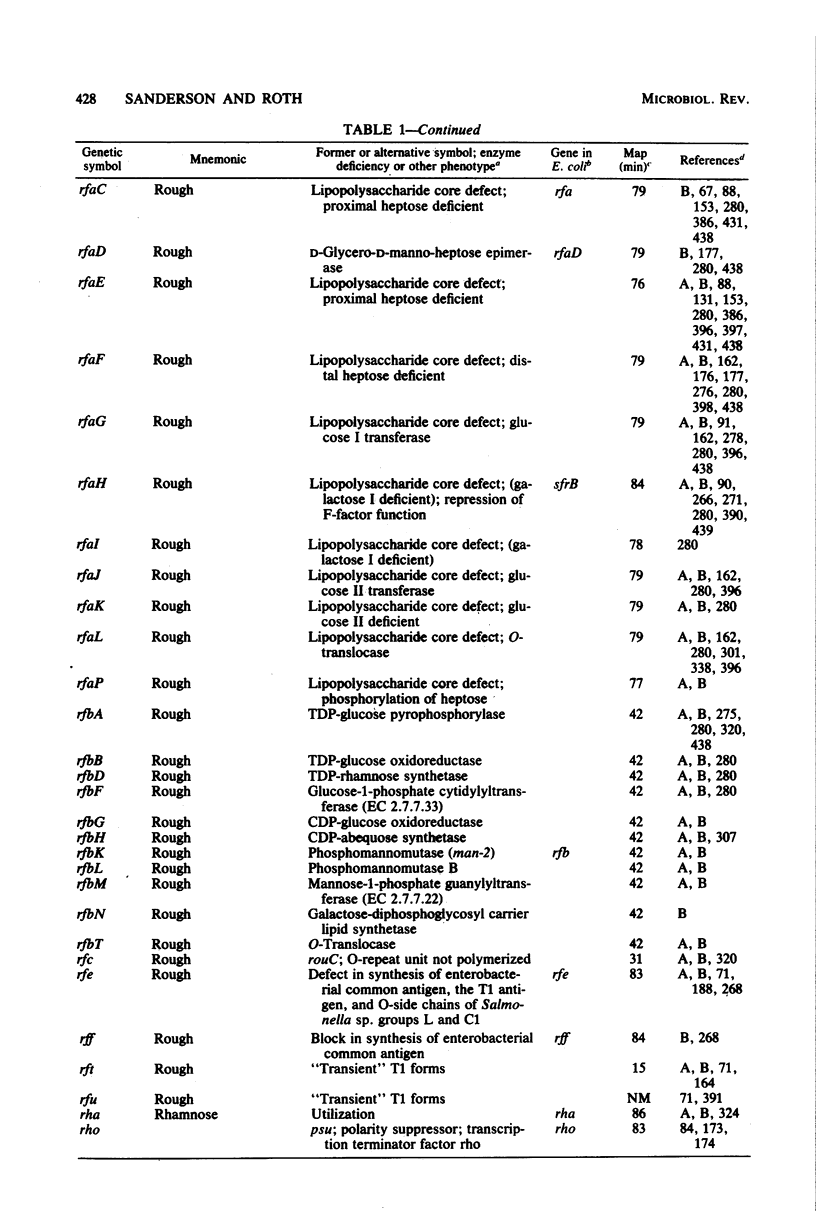
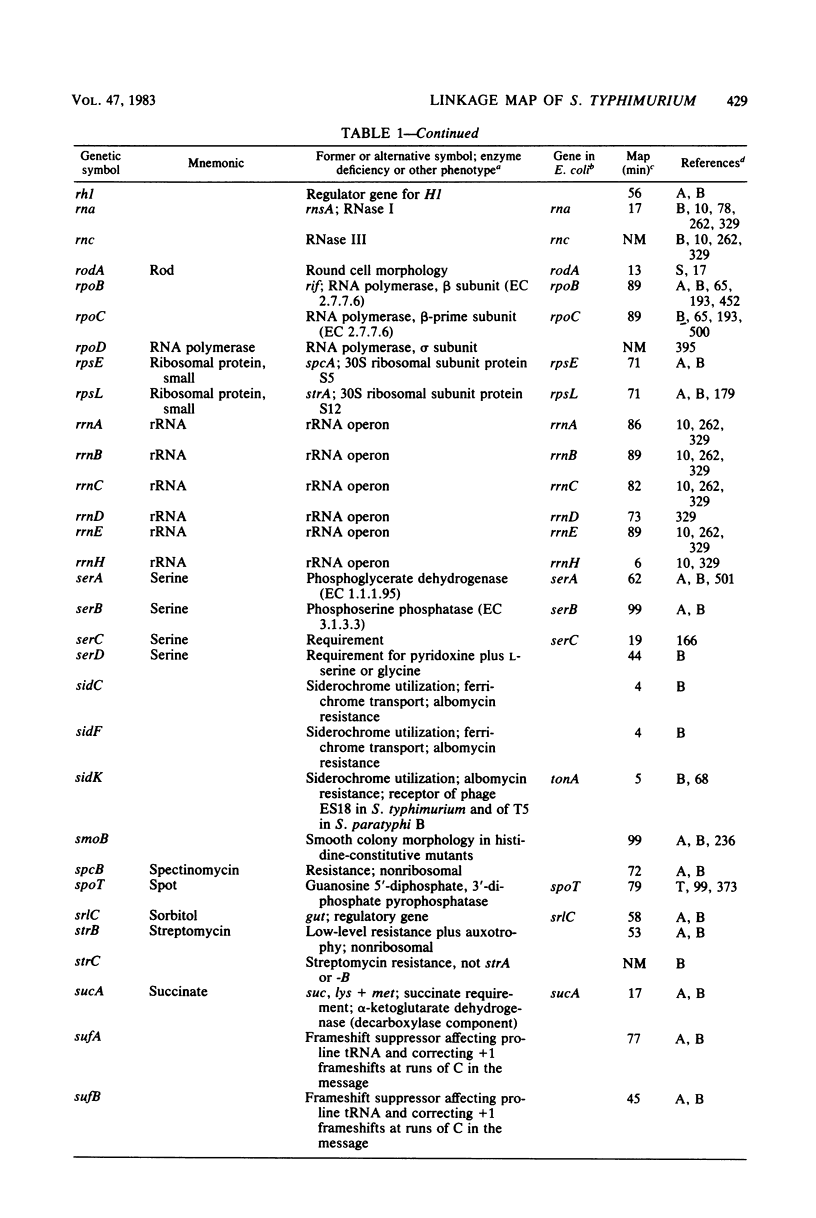
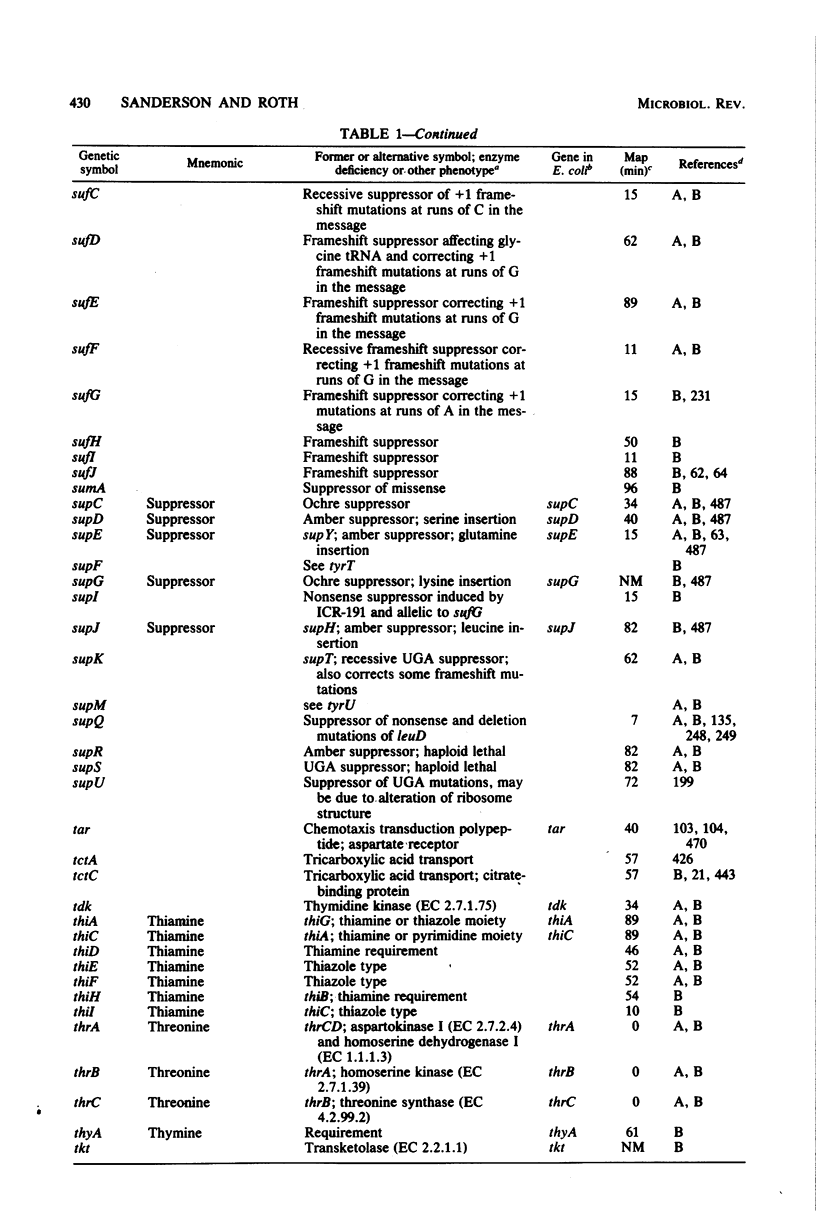
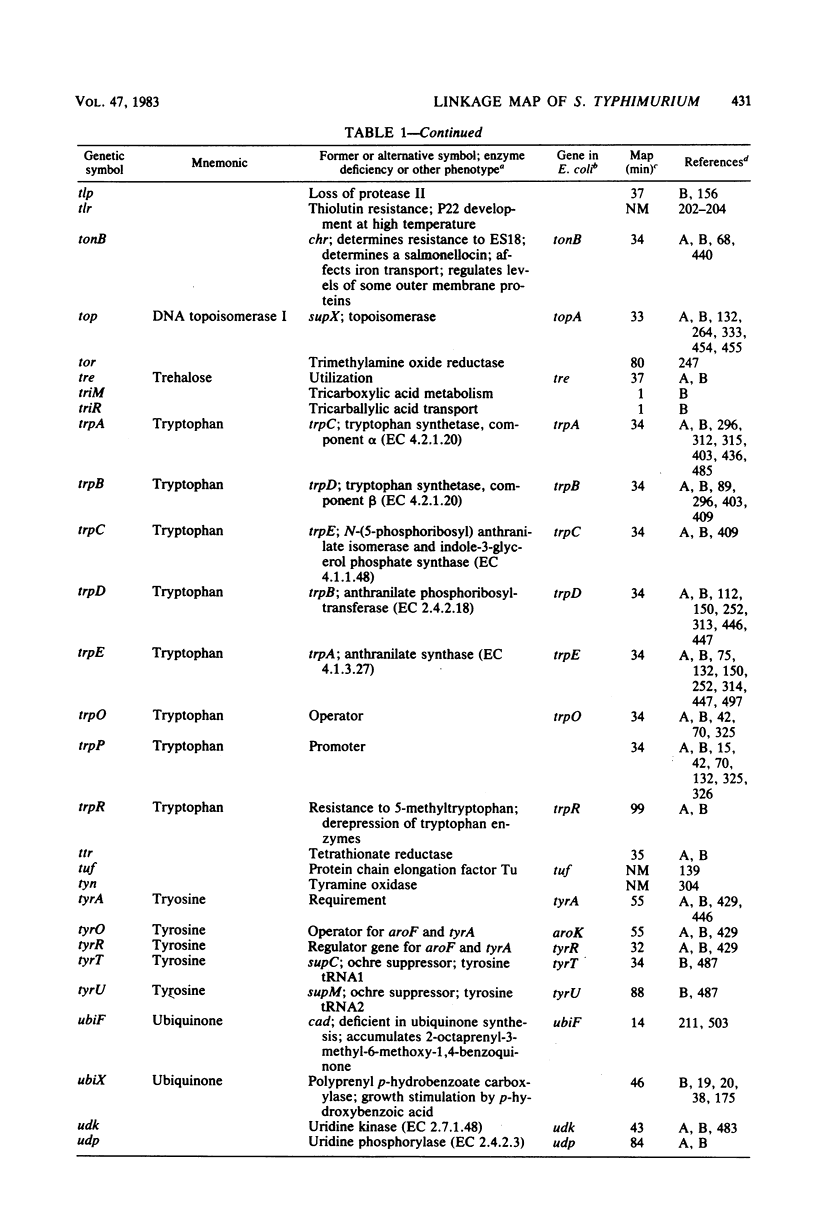
Full text
PDF






















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abstracts of papers presented at the 1980 meetings of the Genetic Society of America. Boulder, Colorado August 18-20, 1980. Genetics. 1980;94(4 Pt 2 Suppl):1–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aceves-Piña E., Ortega M. V., Artís M. Linkage of the Salmonella typhimurium chromosomal loci encoding for the cytochrome-linked L-alpha-glycerophosphate dehydrogenase and amylomaltase activities. Arch Microbiol. 1974;101(1):59–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00455925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aizawa S. I., Kato S., Asakura S., Kagawa H., Yamaguchi S. In vitro polymerization of polyhook protein from Salmonella SJW880. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 21;625(2):291–303. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90293-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksamit R. R., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of the ribose binding protein as the receptor for ribose chemotaxis in Salmonella typhimurium. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 22;13(22):4473–4478. doi: 10.1021/bi00719a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. D., Parsons S. M. Nitrocellulose filter binding: quantitation of the histidyl-tRNA-ATP phosphoribosyltransferase complex. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 1;92(1):22–30. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90620-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Biek D. P., Spudich E. N. Duplications of histidine transport genes in Salmonella typhimurium and their use for the selection of deletion mutants. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1094–1108. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1094-1108.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Identification of a membrane protein as a histidine transport component in Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5447–5451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Noel K. D., Taber H., Spudich E. N., Nikaido K., Afong J. Fine-structure map of the histidine transport genes in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1289–1297. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1289-1297.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsden A. B., Small D. K., Gomez R. F. Complex medium toxicity to some DNA repair-deficient strains of Salmonella typhimurium. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Oct;23(10):1494–1496. doi: 10.1139/m77-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. S., Smith H. R. Fertility inhibition in strains of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;118(1):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Roth J. Spontaneous tandem genetic duplications in Salmonella typhimurium arise by unequal recombination between rRNA (rrn) cistrons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3113–3117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. P., Roth J. R. Tandem chromosomal duplications in Salmonella typhimurium: fusion of histidine genes to novel promoters. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 15;119(1):147–166. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. P., Roth J. R. Tandem genetic duplications in Salmonella typhimurium: amplification of the histidine operon. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 25;126(1):53–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90279-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. R., Menzel R., Wood J. M. Biochemistry and regulation of a second L-proline transport system in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1071–1076. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1071-1076.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelosanto F. A., Torget R., Balbinder E. A mutation to 5-methyltryptophan dependence in the trp operon of Salmonella typhimurium. IV. Isolation and characterization of trp promoter mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 4;165(2):155–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00269903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardeshir F., Ames G. F. Cloning of the histidine transport genes from Salmonella typhimurium and characterization of an analogous transport system in Escherichia coli. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(1):117–130. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardeshir F., Higgins C. F., Ames G. F. Physical map of the Salmonella typhimurium histidine transport operon: correlation with the genetic map. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):401–409. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.401-409.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton D. M., Sweet G. D., Somers J. M., Kay W. W. Citrate transport in Salmonella typhimurium: studies with 2-fluoro-L-erythro-citrate as a substrate. Can J Biochem. 1980 Oct;58(10):797–803. doi: 10.1139/o80-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayling P. D. Methionine sulfoxide is transported by high-affinity methionine and glutamine transport systems in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):514–520. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.514-520.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayling P. D., Mojica-a T., Klopotowski T. Methionine transport in Salmonella typhimurium: evidence for at least one low-affinity transport system. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):227–246. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus H., Schmieger H. Bacterial DNA synthesized under phage control in a DNA-defective Salmonella-mutant and packaged into a special fraction of transducing particles of phage P22. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 27;171(3):301–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00267585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus H., Schmieger H. Replication and maturation of phage P22 in a mutant of Salmonella typhimurium temperature sensitive in initiation of DNA replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 27;171(3):295–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00267584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft S., Rhee S. G., Neumann C., Kustu S. Mutations that alter the covalent modification of glutamine synthetase in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1046–1055. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1046-1055.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baptist E. W., Hallquist S. G., Kredich N. M. Identification of the Salmonella typhimurium cysB gene product by two-dimensional protein electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):495–499. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.495-499.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Tana J., Howlett B. J., Hertz R. Ubiquinone synthetic pathway in flagellation of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):637–643. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.637-643.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M. Cloning and restriction map of the first part of the histidine operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):124–134. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.124-134.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M. Construction of an M13 histidine-transducing phage: a single-stranded cloning vehicle with one EcoRI site. Gene. 1979 Feb;5(2):127–139. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M. DNA sequence from the histidine operon control region: seven histidine codons in a row. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4281–4285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M. DNA sequencing by partial ribosubstitution. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 15;119(1):83–99. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90271-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. L., Chang G. W. Cysteine auxotrophs of Salmonella typhimurium which grow without cysteine in a hydrogen/carbon dioxide atmosphere. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Dec;115(2):513–516. doi: 10.1099/00221287-115-2-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. L., Jackson C. E., Fukumoto H. T., Chang G. W. Formate dehydrogenase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: a new medium for their isolation and new mutant classes. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):95–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00267258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. L., Riggs D. L. Evidence of a second nitrate reductase activity that is distinct from the respiratory enzyme in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.563-571.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. L., Riggs D. L. Salmonella typhimurium mutants defective in the formate dehydrogenase linked to nitrate reductase. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):554–560. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.554-560.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beacham I. R., Garrett S. Transfer of RP4::Mu to Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 May;124(1):225–228. doi: 10.1099/00221287-124-1-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C. F., Eisenhardt A. R., Neuhard J. Deoxycytidine triphosphate deaminase of Salmonella typhimurium. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):609–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C. F., Ingraham J. L. Location on the chromosome of Salmonella typhimurium of genes governing pyrimidine metabolism. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;111(4):303–316. doi: 10.1007/BF00569782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. N., Brown K. D., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of the promoter--operator region of the tryptophan operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 15;121(2):139–152. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(78)80002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson C. E., Hornick D. L., Gots J. S. Genetic separation of purine transport from phosphoribosyltransferase activity in Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Dec;121(2):357–364. doi: 10.1099/00221287-121-2-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg C. M., Shaw K. J. Organization and regulation of the ilvGEDA operon in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):984–989. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.984-989.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. E., Weiss A., Crossland L. Polarity of Tn5 insertion mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):439–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.439-446.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhaduri S., Kasai T., Schlessinger D., Raskas H. J. pMB9 plasmids bearing the Salmonella typhimurium his operon and gnd gene. Gene. 1980 Feb;8(3):239–253. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biek D., Roth J. R. Regulation of Tn5 transposition in Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6047–6051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi F., Bruni C. B. Regulation of the histidine operon: translation-controlled transcription termination (a mechanism common to several biosynthetic operons). Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;19:1–45. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152819-5.50018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt J. M., Umbarger H. E. On the role of isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase in multivalent repression. Biochem Genet. 1972 Apr;6(2):99–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00486395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazey D. L., Burns R. O. Gene ilvY of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):1015–1018. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.1015-1018.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazey D. L., Burns R. O. Genetic organization of the Salmonella typhimurium ilv gene cluster. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00267247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazey D. L., Burns R. O. Transcriptional activity of the transposable element Tn10 in the Salmonella typhimurium ilvGEDA operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5011–5015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazey D. L., Kim R., Burns R. O. Molecular cloning and expression of the ilvGEDAY genes from Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):452–462. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.452-462.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenberg M., Magasanik B. A study in evolution: the histidine utilization genes of enteric bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 25;135(1):23–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenberg M., Magasanik B. Physical maps of Klebsiella aerogenes and Salmonella typhimurium hut genes. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):664–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.664-667.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Huang H. C., Schieven G. L., Ames B. N. Positive selection for loss of tetracycline resistance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):926–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.926-933.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Savageau M. A. Inhibition of growth by imidazol(on)e propionic acid: evidence in vivo for coordination of histidine catabolism with the catabolism of other amino acids. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):87–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00267937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L., Ciampi M. S. DNA sequences at the sites of three insertions of the transposable element Tn5 in the histidine operon of Salmonella. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(2):406–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00270649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L., Kohno T., Roth J. R. Genetic characterization of the sufj frameshift suppressor in Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1983 Jan;103(1):31–42. doi: 10.1093/genetics/103.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L., Roth J. R. Four-base codons ACCA, ACCU and ACCC are recognized by frameshift suppressor sufJ. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L., Ruth J. R. The influence of codon context on genetic code translation. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):123–127. doi: 10.1038/286123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D. H., Porter L. M., Young B. S., Wright A. The in vitro detection of defects in temperature sensitive RNA polymerases from mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jun 20;173(3):279–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00268638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Hantke K., Stauder W. Identification of the sid outer membrane receptor protein in Salmonella typhimurium SL1027. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Oct 20;155(2):227–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00393164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Bennett G. N., Lee F., Schweingruber M. E., Yanofsky C. RNA polymerase interaction at the promoter--operator region of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 15;121(2):153–177. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(78)80003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruneteau M., Volk W. A., Singh P. P., Lüderitz O. Structural investigations on the Salmonella T2 lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Apr 16;43(3):501–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brãnes L. V., Somers J. M., Kay W. W. Hydrophobic peptide auxotrophy in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):986–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.986-996.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullas L. R., Colson C., Neufeld B. Deoxyribonucleic acid restriction and modification systems in Salmonella: chromosomally located systems of different serotypes. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):275–292. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.275-292.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. O., Hofler J. G., Luginbuhl G. H. Threonine deaminase from Salmonella typhimurium. Substrate-specific patterns of inhibition in an activator site-deficient form of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1074–1079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussey L. B., Ingraham J. L. A regulatory gene (use) affecting the expression of pyrA and certain other pyrimidine genes. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):144–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.144-152.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan R., 3rd, Dooley M. M. A mutation to 5-methyltryptophan dependence in the tryptophan (trp) operon of Salmonella typhimurium. II. Studies of 5-methyltryptophan-dependent mutants and their revertants. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 4;165(2):129–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00269901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Lactose genes fused to exogenous promoters in one step using a Mu-lac bacteriophage: in vivo probe for transcriptional control sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4530–4533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casse F., Pascal M. C., Chippaux M. Comparison between the chromosomal maps of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Length of the inverted segment in the trp region. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Aug 17;124(3):253–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00293096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravorty M., Suryanarayana T., Datta A. K. A ribonuclease I deficient mutant (MB24) of Salmonella typhimurium. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;12(2):153–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. K., Botstein D. Specialized transduction by bacteriophage P22 in Salmonella typhimurium: genetic and physical structure of the transducing genomes and the prophage attachment site. Genetics. 1976 Jul;83(3 PT2):433–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumley F. G., Menzel R., Roth J. R. Hfr formation directed by tn10. Genetics. 1979 Apr;91(4):639–655. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumley F. G., Roth J. R. Genetic fusions that place the lactose genes under histidine operon control. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 5;145(4):697–712. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90310-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciampi M. S., Schmid M. B., Roth J. R. Transposon Tn10 provides a promoter for transcription of adjacent sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5016–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieśla Z., Filutowicz M., Kłopotowski T. Involvement of the L-cysteine biosynthetic pathway in azide-induced mutagenesis in Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1980 May;70(3):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(80)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P., Lin H. C., Wilcox G. The nucleotide sequence of the araC regulatory gene in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Gene. 1982 May;18(2):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S., Sparrow K., Panasenko S., Koshland D. E., Jr In vitro methylation of bacterial chemotaxis proteins: characterization of protein methyltransferase activity in crude extracts of Salmonella typhimurium. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(3):315–328. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clas F., Loos M. Killing of the S and Re forms of Salmonella minnesota via the classical pathway of complement activation in guinea-pig and human sera. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):547–556. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I. P., Nichols B. P., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of the trpB gene in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 5;142(4):489–502. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeger E. S., Chen J. F., Rothfield L. I. Cloning of genes for bacterial glycosyltransferases. II. Selection of a hybrid plasmid carrying the rfah gene. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):811–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeger E. S., Rothfield L. I. Cloning of genes for bacterial glycosyltransferases. I. Selection of hybrid plasmids carrying genes for two glucosyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):804–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronan J. E., Jr, Littel K. J., Jackowski S. Genetic and biochemical analyses of pantothenate biosynthesis in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):916–922. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.916-922.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N. A third L-proline permease in Salmonella typhimurium which functions in media of elevated osmotic strength. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1433–1443. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1433-1443.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N., Howe M. M., Ingraham J. L., Pierson L. S., 3rd, Turnbough C. L., Jr Infection of Salmonella typhimurium with coliphage Mu d1 (Apr lac): construction of pyr::lac gene fusions. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):299–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.299-305.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. P., Williams L. S. Regulation of isoleucine and valine biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium: the effect of hisU on repression control. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 15;127(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90244-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. P., Williams L. S. Relaxed control of RNA synthesis during nutritional shiftdowns of hisU mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):682–687. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. P., Wilson D. J., Williams L. S. Role of a hisU gene in the control of stable RNA synthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 15;157(2):237–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90232-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L., Williams L. S. Altered regulation of isoleucine-valine biosynthesis in a hisW mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):860–866. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.860-866.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L., Williams L. S. Characterization of a cold-sensitive hisW mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):867–878. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.867-878.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Construction and behavior of strains with mutations in two chemotaxis genes. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1297–1301. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1297-1301.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Molecular cloning of chemotaxis genes and overproduction of gene products in the bacterial sensing system. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):390–400. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.390-400.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Multiple methylation in processing of sensory signals during bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2429–2433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Parkinson J. S., Koshland D. E., Jr Functional homology of chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):107–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.107-114.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean G. E., Aizawa S. I., Macnab R. M. flaAII (motC, cheV) of Salmonella typhimurium is a structural gene involved in energization and switching of the flagellar motor. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):84–91. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.84-91.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dendinger S. M., Brenchley J. E. Temperature-sensitive glutamate dehydrogenase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1043–1047. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1043-1047.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dendinger S. M., Patil L. G., Brenchley J. E. Salmonella typhimurium mutants with altered glutamate dehydrogenase and glutamate synthase activities. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):190–198. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.190-198.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrochers M., Peloquin L., Săsărman A. Mapping of the hemE locus in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1151–1153. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1151-1153.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diver W. P., MacPhee D. G. The effects of mutations in the polA and recA genes on mutagenesis by nitrosoguanidine in Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1981 Oct;83(3):349–359. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(81)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson P. P., Walker G. C. Plasmid (pKM101)-mediated Weigle reactivation in Escherichia coli K12 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2: genetic dependence, kinetics of induction, and effect of chloramphenicol. Mutat Res. 1980 Jun;71(1):25–41. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(80)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley M., Torget R., Balbinder E. Differences between the anthranilate-5-phosphoribosylpyrophosphate phosphoribosyltransferases of Salmonella typhimurium strains LT2 and LT7. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 May;112(1):171–179. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-1-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn S. D., Snell E. E. Isolation of temperature-sensitive pantothenate kinase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium and mapping of the coaA gene. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):805–808. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.805-808.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt E., Wolf M., Goldberg I. H. Mutagenesis by neocarzinostatin in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: requirement for umuC+ or plasmid pKM101. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):656–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.656-660.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst J. F., Bennett R. L., Rothfield L. I. Constitutive expression of the iron-enterochelin and ferrichrome uptake systems in a mutant strain of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):928–934. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.928-934.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faelen M., Mergeay M., Gerits J., Toussaint A., Lefèbvre N. Genetic mapping of a mutation conferring sensitivity to bacteriophage Mu in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):914–919. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.914-919.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahnestock M., Koshland D. E., Jr Control of the receptor for galactose taxis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):758–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.758-763.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feucht B. U., Saier M. H., Jr Fine control of adenylate cyclase by the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase systems in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):603–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.603-610.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filutowicz M., Cieśla Z., Kłopotowski T. Interference of azide with cysteine biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jul;113(1):45–55. doi: 10.1099/00221287-113-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filutowicz M., Wiater A., Hulanicka D. Delayed inducibility of sulphite reductase in cysM mutants of Salmonella typhimurium under anaerobic conditions. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Aug;128(8):1791–1794. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-8-1791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan D. J., Willetts N. S. Two classes of Flac mutants insensitive to transfer inhibition by an F-like R factor. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;111(3):256–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00433110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. W., Holley E. A. Genetic mapping of the Salmonella typhimurium pncB locus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):394–396. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.394-396.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. W., Kinney D. M., Moat A. G. Pyridine nucleotide cycle of Salmonella typhimurium: regulation of nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase and nicotinamide deamidase. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):957–961. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.957-961.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. W. Pyridine nucleotide cycle of Salmonella typhimurium: in vitro demonstration of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide glycohydrolase, nicotinamide mononucleotide glycohydrolase, and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide pyrophosphatase activities. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1002–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1002-1009.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Baron L. S. Genetic characterization of a bacterial locus involved in the activity of the N function of phage lambda. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R. L., Madonna M. J., Brenchley J. E. Identification of the structural genes for glutamate synthase and genetic characterization of this region of the Salmonella typhimurium chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):906–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.906-915.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushi K., Kudo H., Asano H., Sasaki J. Electron microscopy of endotoxin extracted from R mutant of Salmonella. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1977 Feb;30(1):51–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Bauerle R. Re-initiation of tryptophan operon expression in a promoter deletion strain of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jan 17;158(3):239–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00267195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N., Kemper J. Wild-type isopropylmalate isomerase in Salmonella typhimurium is composed of two different subunits. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):210–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.210-219.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N., Kwoh D. Y., Kemper J. Salmonella typhimurium newD and Escherichia coli leuC genes code for a functional isopropylmalate isomerase in Salmonella typhimurium-Escherichia coli hybrids. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1253–1262. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1253-1262.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funanage V. L., Ayling P. D., Dendinger S. M., Brenchley J. E. Salmonella typhimurium LT-2 mutants with altered glutamine synthetase levels and amino acid uptake activities. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):588–596. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.588-596.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung J. C., MacAlister T. J., Weigand R. A., Rothfield L. I. Morphogenesis of the bacterial division septum: identification of potential sites of division in lkyD mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):1019–1024. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.1019-1024.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung J., MacAlister T. J., Rothfield L. I. Role of murein lipoprotein in morphogenesis of the bacterial division septum: phenotypic similarity of lkyD and lpo mutants. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1467–1471. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1467-1471.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furano A. V. Direct demonstration of duplicate tuf genes in enteric bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3104–3108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway R. J., Taylor B. L. Histidine starvation and adenosine 5'-triphosphate depletion in chemotaxis of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1068–1075. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1068-1075.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber B. B., Gots J. S. Utilization of 2,6-diaminopurine by Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):864–871. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.864-871.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrido-Pertierra A. Isolation and properties of Salmonella typhimurium mutants defective in enolase. Rev Esp Fisiol. 1980 Mar;36(1):33–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmill R. M., Wessler S. R., Keller E. B., Calvo J. M. leu operon of Salmonella typhimurium is controlled by an attenuation mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4941–4945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman R. H., Hornick R. B., Woodard W. E., DuPont H. L., Snyder M. J., Levine M. M., Libonati J. P. Evaluation of a UDP-glucose-4-epimeraseless mutant of Salmonella typhi as a liver oral vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):717–723. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmeiner J., Schlecht S. Molecular organization of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 1;93(3):609–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goitein R. K., Parsons S. M. Possible regulation of the Salmonella typhimurium histidine operon by adenosine triphosphate phosphoribosyltransferase: large metabolic effects. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):337–345. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.337-345.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L., Miller C. G. Genetic mapping of the Salmonella typhimurium pepB locus. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1524–1526. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1524-1526.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton M. J., Floyd R. A., Clark J. B., Lancaster J. H. Studies of the fatty acid composition and membrane microviscosity in Salmonella typhimurium TA98. Chem Phys Lipids. 1980 Sep;27(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(80)90022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heasley F. A. Reducing terminus of O-hapten accumulated in a Salmonella montevideo galE mutant. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):624–627. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.624-627.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiman C., Miller C. G. Acylaminoacid esterase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Aug 4;164(1):57–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00267599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiman C., Miller C. G. Salmonella typhimurium mutants lacking protease II. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):588–594. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.588-594.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg K. M., Gemmill R., Jones J., Calvo J. M. Cloning of an EcoRI-generated fragment of the leucine operon of Salmonella typhimurium. Gene. 1980 Jan;8(2):135–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Ames G. F. Regulatory regions of two transport operons under nitrogen control: nucleotide sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1083–1087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Ames G. F. Two periplasmic transport proteins which interact with a common membrane receptor show extensive homology: complete nucleotide sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6038–6042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Haag P. D., Nikaido K., Ardeshir F., Garcia G., Ames G. F. Complete nucleotide sequence and identification of membrane components of the histidine transport operon of S. typhimurium. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):723–727. doi: 10.1038/298723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hardie M. M., Jamieson D., Powell L. M. Genetic map of the opp (Oligopeptide permease) locus of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):830–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.830-836.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho C., Giza Y., Takahashi S., Ugen K. E., Cottam P. F., Dowd S. R. A proton nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of histidine-binding protein J of Salmonella typhimurium: a model for transport of L-histidine across cytoplasmic membrane. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(2):131–145. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J., Lindberg B., Głowacka M., Deryło M., Lorkiewicz Z. Structural studies of the lipopolysaccharide from Salmonella typhimurium 902 (ColIb drd2). Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):103–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04479.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley E. A., Foster J. W. Bacteriophage P22 as a vector for Mu mutagenesis in Salmonella typhimurium: isolation of nad-lac and pnc-lac gene fusions. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):959–962. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.959-962.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Ames B. N. Localized mutagenesis of any specific small region of the bacterial chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3158–3162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe I., Johnston H. M., Biek D., Roth J. R. A refined map of the hisG gene of Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1979 May;92(1):17–26. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A. H., Heffernan L., Morandi C., Lee J. H., Timko J., Wilcox G. DNA sequence of the araBAD-araC controlling region in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Gene. 1981 Sep;14(4):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houlberg U., Jensen K. F. Role of hypoxanthine and guanine in regulation of Salmonella typhimurium pur gene expression. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):837–845. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.837-845.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housley P. R., Leavitt A. D., Whitfield H. J. Genetic analysis of a temperature-sensitive Salmonella typhimurium rho mutant with an altered rho-associated polycytidylate-dependent adenosine triphosphatase activity. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):13–24. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.13-24.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housley P. R., Whitfield H. J. Transcription termination factor rho from wild type and rho-111 strains of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2569–2577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett B. J., Bar-Tana J. Polyprenyl p-hydroxybenzoate carboxylase in flagellation of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):644–651. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.644-651.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hryniewicz M., Bagdasarian M., Bagdasarian M. Integration of F factor and cryptic LT2 plasmid into a specific site of the Salmonella typhimurium chromosome. Acta Biochim Pol. 1979;26(1-2):73–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson H. P., Lindberg A. A., Stocker B. A. Lipopolysaccharide core defects in Salmonella typhimurium mutants which are resistant to Felix O phage but retain smooth character. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Nov;109(1):97–112. doi: 10.1099/00221287-109-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes V., Meynell G. G. The contribution of plasmid and host genes to plasmid-mediated interference with phage growth. Genet Res. 1977 Oct;30(2):179–185. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300017572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulanicka M. D., Hallquist S. G., Kredich N. M., Mojica-A T. Regulation of O-acetylserine sulfhydrylase B by L-cysteine in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):141–146. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.141-146.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulanicka M. D., Kradich N. M. A mutation affecting expression of the gene coding for serine transacetylase in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Oct 18;148(2):143–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00268378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibe S. N., Sinskey A. J., Botstein D. Genetic mapping of mutations in a highly radiation-resistant mutant of Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):260–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.260-268.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T., Kamiya R., Yamaguchi S. Excretion of flagellin by a short-flagella mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):506–510. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.506-510.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham J. L., Neuhard J. Cold-sensitive mutants of Salmonella typhimurium defective in uridine monophosphate kinase (pyrH). J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6259–6265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara A., Yamaguchi S., Hotani H. Passive rotation of flagella on paralyzed Salmonella typhimurium (mot) mutants by external rotatory driving force. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1082–1084. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1082-1084.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagura G., Hulanicka D. Analysis of merodiploids of the cysB region in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Sep 20;165(1):31–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00270373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann K., Kanegasaki S., Goldemann G., Mäkelä P. H. On the effect of rfe mutation on the biosynthesis of the 08 and 09 antigens of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 28;86(4):1185–1191. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janzer J. J., Stan-Lotter H., Sanderson K. E. Isolation and characterization of hemin-permeable, envelope-defective mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Feb;27(2):226–237. doi: 10.1139/m81-034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jargiello P. Simultaneous selection of mutants in gluconeogenesis and nucleoside catabolism in Salmonella typhimurium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 24;444(1):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Schachman H. K. pryB mutations as suppressors of arginine auxotrophy in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):33–40. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.33-40.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F. Apparent involvement of purines in the control of expression of Salmonella typhimurium pyr genes: analysis of a leaky guaB mutant resistant to pyrimidine analogs. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):731–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.731-738.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F., Neuhard J., Schack L. RNA polymerase involvement in the regulation of expression of Salmonella typhimurium pyr genes. Isolation and characterization of a fluorouracil-resistant mutant with high, constitutive expression of the pyrB and pyrE genes due to a mutation in rpoBC. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):69–74. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jochimsen B., Garber B., Gots J. S. Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate (PRPP) synthetase mutant in Salmonella typhimurium. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1979;122B:131–136. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8559-2_23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joh K., Hiraga S. Genetic mapping of the chromosomal replication origin of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):297–304. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.297-304.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson V., Aarti A., Nurminen M., Mäkelä P. H. Outer membrane protein-specific bacteriophages of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Jul;107(1):183–187. doi: 10.1099/00221287-107-1-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H. M., Barnes W. M., Chumley F. G., Bossi L., Roth J. R. Model for regulation of the histidine operon of Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):508–512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H. M., Roth J. R. DNA sequence changes of mutations altering attenuation control of the histidine operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 5;145(4):735–756. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H. M., Roth J. R. Genetic analysis of the histidine operon control region of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 5;145(4):713–734. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90311-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H. M., Roth J. R. Histidine mutants requiring adenine: selection of mutants with reduced hisG expression in Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1979 May;92(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H. M., Roth J. R. UGA suppressor that maps within a cluster of ribosomal protein genes. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):300–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.300-305.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi A. R., Chakravorty M. Bacteriophage P22 development is temperature sensitive in thiolutin resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi A., Siddiqui J. Z., Verma M., Chakravorty M. Participation of the host protein(s) in the morphogenesis of bacteriophage P22. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(1):44–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00422910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi A., Verma M., Chakravorty M. Thiolutin-resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):541–547. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp D., Kahmann R. The relationship of two invertible segments in bacteriophage Mu and Salmonella typhimurium DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):564–566. doi: 10.1007/BF00352543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Cameron M. J. Transport of C4-dicarboxylic acids in salmonella typhimurium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Sep;190(1):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Cameron M. Citrate transport in Salmonella typhimurium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Sep;190(1):270–280. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90276-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelln R. A., Foltermann K. F., O'Donovan G. A. Location of the argR gene on the chromosome of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Sep 8;139(4):277–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00267967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelln R. A., Zak V. L. Arginine regulon control in a Salmonella typhimurium--Escherichia coli hybrid merodiploid. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 May 31;161(3):333–335. doi: 10.1007/BF00331009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper J. Gene order and co-transduction in the leu-ara-fol-pyrA region of the Salmonella typhimurium linkage map. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):94–99. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.94-99.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Macnab R. M., DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Inversion of a behavioral response in bacterial chemotaxis: explanation at the molecular level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4150–4154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Macnab R. M. The steady-state counterclockwise/clockwise ratio of bacterial flagellar motors is regulated by protonmotive force. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):563–597. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kier L. D., Weppelman R. M., Ames B. N. Regulation of nonspecific acid phosphatase in Salmonella: phoN and phoP genes. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):155–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.155-161.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kier L. D., Weppelman R., Ames B. N. Regulation of two phosphatases and a cyclic phosphodiesterase of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):420–428. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.420-428.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kier L. D., Weppelman R., Ames B. N. Resolution and purification of three periplasmic phosphatases of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):399–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.399-410.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsman A. J., Smith D. A., Hulanicka M. D. Genetic instability in auxotrophs of Salmonella typhimurium requiring cysteine or methionine and resistant to inhibition by 1,2,4-triazole. Genetics. 1978 Jul;89(3):419–437. doi: 10.1093/genetics/89.3.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsman A. J., Smith D. A. The nature of genetic instability in auxotrophs of Salmonella typhimurium requiring cysteine or methionine and resistant to inhibition by 1,2,4-triazole. Genetics. 1978 Jul;89(3):439–451. doi: 10.1093/genetics/89.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsman A. J. The structure of the cysCDHIJ region in unstable cysteine or methionine requiring mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Nov 18;156(3):327–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00267189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinney D. M., Foster J. W., Moat A. G. Pyridine nucleotide cycle of Salmonella typhimurium: in vitro demonstration of nicotinamide mononucleotide deamidase and characterization of pnuA mutants defective in nicotinamide mononucleotide transport. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):607–611. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.607-611.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Reichardt K., Botstein D. Inversions and deletions of the Salmonella chromosome generated by the translocatable tetracycline resistance element Tn10. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 5;127(1):89–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90461-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Roth J., Botstein D. Genetic engineering in vivo using translocatable drug-resistance elements. New methods in bacterial genetics. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 15;116(1):125–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Steele D. A., Reichardt K., Botstein D. Specificity of insertion by the translocatable tetracycline-resistance element Tn10. Genetics. 1979 Aug;92(4):1023–1040. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.4.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koduri R. K., Bedwell D. M., Brenchley J. E. Characterization of a HindIII-generated DNA fragment carrying the glutamine synthetase gene of Salmonella typhimurium. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koduri R. K., Bedwell D. M., Brenchley J. E. Characterization of a HindIII-generated DNA fragment carrying the glutamine synthetase gene of Salmonella typhimurium. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno T., Gray W. R. Chemical and genetic studies on L-histidinol dehydrogenase of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and structure of the tryptic peptides. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 15;147(3):451–464. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90495-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno T., Roth J. R. A Salmonella frameshift suppressor that acts at runs of A residues in the messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 25;126(1):37–52. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90278-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno T., Roth J. Electrolyte effects on the activity of mutant enzymes in vivo and in vitro. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1386–1392. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondratiev Y. S., Brukhansky G. V., Andreeva I. V., Skavronskaya A. G. UV-sensitivity and repair of UV-damages in Salmonella of wild type. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Dec 30;158(2):211–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00268315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenevskaya N. F., Andreeva I. V., Kiryushkina A. A., Lichoded L. Y., Kondratiev Y. S., Skavronskaya A. G. Intergeneric mating: transfer of polA gene from E. coli to S. typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1977 Dec;45(3):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(77)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozdroj H., Kłopotowski T. The smoB mutation suppressing cell filamentation and ability to support the multiplication of phage P22 in Salmonella typhimurium. Acta Biochim Pol. 1979;26(1-2):135–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajewska E., Shugar D. Pyrimidine nucleoside analogues as inducers of pyrimidine nucleoside catabolizing enzymes in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Biol Rep. 1975 Dec;2(4):295–301. doi: 10.1007/BF00357016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S. G., McFarland N. C., Hui S. P., Esmon B., Ames G. F. Nitrogen control of Salmonella typhimurium: co-regulation of synthesis of glutamine synthetase and amino acid transport systems. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):218–234. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.218-234.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Burton D., Garcia E., McCarter L., McFarland N. Nitrogen control in Salmonella: regulation by the glnR and glnF gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4576–4580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Iino T. A trans-acting factor mediates inversion of a specific DNA segment in flagellar phase variation of Salmonella. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):479–481. doi: 10.1038/284479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Iino T., Komeda Y., Yamaguchi S. Functional homology of fla genes between Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Apr;178(1):59–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00267213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Suzuki T., Yamaguchi S., Iino T. Role of gene flaFV on flagellar hook formation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):267–275. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.267-275.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwoh D. Y., Kemper J. Bacteriophage P22-mediated specialized transduction in Salmonella typhimurium: high frequency of aberrant prophage excision. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):519–534. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.519-534.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwoh D. Y., Kemper J. Bacteriophage P22-mediated specialized transduction in Salmonella typhimurium: identification of different types of specialized transducing particles. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):535–550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.535-550.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaScolea L. J., Jr, Dooley M. M., Torget R., Balbinder E. A mutation to 5-methyltryptophan dependence in the trp operon of Salmonella typhimurium. III. Correlation between phenotype and the properties of the second enzyme for tryptophan biosynthesis in a 5-methyltryptophan dependent mutant and several 5-methyltryptophan-independent revertants. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 4;165(2):145–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00269902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampel K. A., Riley M. Discontinuity of homology of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium DNA in the lac region. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(1):82–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00422916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley D., Guest J. R. Biochemical and genetic characterics of deletion and other mutant strains of Salmonella typhimurium LT2 lacking alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex activities,. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jun;82(2):319–335. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laszlo D. J., Taylor B. L. Aerotaxis in Salmonella typhimurium: role of electron transport. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):990–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.990-1001.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeVine S. M., Ardeshir F., Ames G. F. Isolation and Characterization of acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase mutants of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):1081–1085. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.1081-1085.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg E. M., Cohen S. N. Transformation of Salmonella typhimurium by plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):1072–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.1072-1074.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Peng F. C., Hermodson M. A., Kohlhaw G. B. Transaminase B from Escherichia coli: quaternary structure, amino-terminal sequence, substrate specificity, and absence of a separate valine-alpha-ketoglutarate activity. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):339–345. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.339-345.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. H., Al-Zarban S., Wilcox G. Genetic characterization of the araE gene in Salmonella typhimurium lt2. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):298–304. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.298-304.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. H., Heffernan L., Wilcox G. Isolation of ara-lac gene fusions in Salmonella typhimurium LT2 by using transducing bacteriophage Mu d (Apr lac). J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1325–1331. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1325-1331.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann V., Redmond J., Egan A., Minner I. The acceptor for polar head groups of the lipid A component of Salmonella lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May 16;86(2):487–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann V., Rupprecht E. Microheterogeneity in lipid A demonstrated by a new intermediate in the biosynthesis of 3-deozy-D-manno-octulosonic-acid--lipid A. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec;81(3):443–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann V., Rupprecht E., Osborn M. J. Isolation of mutants conditionally blocked in the biosynthesis of the 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic-acid--lipid-A part of lipopolysaccharides derived from Salmonella typhimurium. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 1;76(1):41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner A. F., Hill C. W. Involvement of ribosomal ribonucleic acid operons in Salmonella typhimurium chromosomal rearrangements. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):492–498. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.492-498.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemoine V. R., Rowbury R. J. An effect of F-like plasmids on the maintenance of Flac in a dnaC mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Nov 18;156(3):313–318. doi: 10.1007/BF00267187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenny A. B., Margolin P. Locations of the opp and supX genes of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):747–752. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.747-752.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. E., Saier M. H., Jr Genetic dissection of catalytic activities of the Salmonella typhimurium mannitol enzyme II. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1106–1109. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1106-1109.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew H. C., Nikaido H., Mäkelä P. H. Biosynthesis of uridine diphosphate N-acetylmannosaminuronic acid in rff mutants of Salmonella tryphimurium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):227–233. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.227-233.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P., Mättänen P. L., Palva E. T. Cloning of the regulatory locus ompB of Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. I. Isolation of the ompR gene and identification of its gene product. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(2):184–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00332673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P., Mättänen P. L., Palva E. T. Cloning of the regulatory locus ompB of Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. II. Identification of the envZ gene product, a protein involved in the expression of the porin proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(2):190–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00332674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Hellerqvist C. G. Rough mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: immunochemical and structural analysis of lipopolysaccharides from rfaH mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jan;116(1):25–32. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G., Foster J., Manlapaz-Ramos P., Olivera B. M. Nucleoside salvage pathway for NAD biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1111–1116. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1111-1116.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lounatmaa K. Ultrastructure of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium bacteriocin-resistant mutants deficient in the 33K protein. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):646–651. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.646-651.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyman M. B., Stocker B. A., Roantree R. J. Evaluation of the immune response directed against the Salmonella antigenic factors O4,5 and O9. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):956–965. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.956-965.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Stendahl O., Tagesson C., Edebo L., Johansson G. The tendency of smooth and rough Salmonella typhimurium bacteria and lipopolysaccharide to hydrophobic and ionic interaction, as studied in aqueous polymer two-phase systems. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Jun;85(3):212–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makover S., Telep E. The antibacterial potential of a phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system blocking agent. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Mar;31(3):237–238. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy S. R., Nunn W. D. Selection for loss of tetracycline resistance by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1110–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1110-1111.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuck B. A., Ho C. High-resolution proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies of histidine-binding proteins J of Salmonella typhimurium. An investigation of substrate and membrane interaction sites. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):566–573. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May S. G., Old D. C. Meso-tartrate resistance and phylogenetic relationships of biotypes of Salmonella typhimurium. Genet Res. 1980 Dec;36(3):327–337. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300019935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland N., McCarter L., Artz S., Kustu S. Nitrogen regulatory locus "glnR" of enteric bacteria is composed of cistrons ntrB and ntrC: identification of their protein products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2135–2139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel R., Roth J. Identification and mapping of a second proline permease Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1064–1070. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1064-1070.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel R., Roth J. Purification of the putA gene product. A bifunctional membrane-bound protein from Salmonella typhimurium responsible for the two-step oxidation of proline to glutamate. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9755–9761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel R., Roth J. Regulation of the genes for proline utilization in Salmonella typhimurium: autogenous repression by the putA gene product. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 5;148(1):21–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mijica-a T., Garcia E., Ascaso C. Mutants of coliphage BF23 able to propagate on smooth strains of Salmonella typhimurium. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1976 Apr;84(2):402–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G. Gentic mapping of Salmonella typhimurium peptidase mutations. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):171–176. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.171-176.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Green L. Degradation of abnormal proteins in peptidase-deficient mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):925–930. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.925-930.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Green L. Degradation of proline peptides in peptidase-deficient strains of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):350–356. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.350-356.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Green L., Schultz R. Salmonella typhimurium mutations affecting utilization of L-leucine beta-naphthylamide. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(2):228–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00331854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton N., Gunn J., Beacham I. R. Nucleoside diphosphate sugar hydrolase gene of Salmonella typhimurium: chromosomal location determined by intergeneric crosses. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1428–1429. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1428-1429.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miozzari G. F., Yanofsky C. Gene fusion during the evolution of the tryptophan operon in enterobacteriaceae. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):486–489. doi: 10.1038/277486a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mojica T. Transduction by phage P1CM clr-100 in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1975;138(2):113–126. doi: 10.1007/BF02428116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortlock R. P., Old D. C. Utilization of D-xylose by wild-type strains of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):173–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.173-178.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowbray S. L., Petsko G. A. Preliminary X-ray data for the ribose binding protein from Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 25;160(3):545–547. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90313-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulford C. A., Osborn M. J. An intermediate step in translocation of lipopolysaccharide to the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1159–1163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L., Rick P. D. Size heterogeneity of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides in outer membranes and culture supernatant membrane fragments. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):630–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.630-640.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murooka Y., Harada T. Regulation of derepressed synthesis of arylsulfatase by tyramine oxidase in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):796–802. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.796-802.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murooka Y., Takizawa N., Harada T. Introduction of bacteriophage Mu into bacteria of various genera and intergeneric gene transfer by RP4::Mu. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):358–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.358-368.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphey-Corb M., Kong H. L., Murray M. L. Interaction of mutagenic spermidine-nitrous acid reaction products with uvr- and recA-dependent repair systems in Salmonella. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):191–195. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.191-195.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers D. E., Stocker B. A., Roantree R. J. Mapping of genes determining penicillin-resistance and serum-sensitivity in Salmonella enteritidis. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jun;118(2):367–376. doi: 10.1099/00221287-118-2-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N., Heine H. G., Boos W. Cloning of mglB, the structural gene for the galactose-binding protein of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):473–480. doi: 10.1007/BF00334143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagelkerke F., Postma P. W. 2-deoxygalactose, a specific substrate of the Salmonella typhiimurium galactose permease: its use for the isolation of galP mutants. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):607–613. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.607-613.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Pirtle R. M., Inouye M. Homology of the gene coding for outer membrane lipoprotein within various Gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):595–604. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.595-604.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S. O., Scholte B. J., Postma P. W. Phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system-mediated regulation of carbohydrate metabolism in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):604–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.604-615.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. P., Blumenberg M., Yanofsky C. Comparison of the nucleoside sequence of trpA and sequences immediately beyond the trp operon of Klebsiella aerogenes. Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1743–1755. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. P., Miozzari G. F., van Cleemput M., Bennett G. N., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequences of the trpG regions of Escherichia coli, Shigella dysenteriae, Salmonella typhimurium and Serratia marcescens. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 5;142(4):503–517. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90260-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. P., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequences of trpA of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: an evolutionary comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5244–5248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. P., van Cleemput M., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli trpE. Anthranilate synthetase component I contains no tryptophan residues. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 15;146(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90365-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Song S. A., Shaltiel L., Nurminen M. Outer membrane of Salmonella XIV. Reduced transmembrane diffusion rates in porin-deficient mutants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 23;76(2):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90728-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Takeuchi Y., Ohnishi S. I., Nakae T. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Electron spin resonance studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 14;465(1):152–164. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90363-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyman K., Plosila M., Howden L., Mäkelä P. H. Genetic determination of lipopolysaccharide: locus of O-specific unit polymerase in group E of salmonella. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1979 Apr;243(2-3):355–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old D. C., Dawes P. F., Barker R. M. Transduction of inositol-fermenting ability demonstrating phylogenetic relationships among strains of Salmonella typhimurium. Genet Res. 1980 Apr;35(2):215–224. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300014063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim D. S., Bennett G. N., Yanofsky C. Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and trp repressor interaction with the promoter-operator region of the tryptophan operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 5;144(2):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim D. S., Yanofsky C. Functional analysis of wild=type and altered tryptophan operon promoters of Salmonella typhimurium in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 5;144(2):143–161. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orbach M. J., Jackson E. N. Transfer of chimeric plasmids among Salmonella typhimurium strains by P22 transduction. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):985–994. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.985-994.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Rick P. D., Rasmussen N. S. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Translocation and integration of an incomplete mutant lipid A into the outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4246–4251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostapchuk P., Anilionis A., Riley M. Conserved genes in enteric bacteria are not identical. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(2):475–477. doi: 10.1007/BF00425864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski J., Hulanicka D. Constitutive mutation of cysJIH operon in a cysB deletion strain of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Sep;175(2):145–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00425530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski J., Hulanicka D. Effect of DNA gyrase inhibitors on gene expression of the cysteine regulon. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(3):363–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00425612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeeke N., Van Scharrenburg G., Lugtenberg B. Antigenic relationships between pore proteins of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Sep;110(1):247–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbye K. M., Margolin P. Role of the supX gene in ultraviolet light-induced mutagenesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):170–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.170-178.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. T., Blum P. H., Artz S. W. Effects of the hisT mutation of Salmonella typhimurium on translation elongation rate. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):357–363. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.357-363.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Liljeström P., Harayama S. Cosmid cloning and transposon mutagenesis in Salmonella typhimurium using phage lambda vehicles. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(2):153–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00268420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T. Major outer membrane protein in Salmonella typhimurium induced by maltose. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):286–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.286-294.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Salmonella typhimurium analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey N. K., Switzer R. L. Mutant strains of Salmonella typhimurium with defective phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase activity. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Aug;128(8):1863–1871. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-8-1863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang P. P., Walker G. C. Identification of the uvrD gene product of Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1172–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1172-1179.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postgate J. R., Krishnapillai V. Expression of Klebsiella nif and his genes in Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Feb;98(2):379–385. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-2-379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W. Defective enzyme II-BGlc of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system leading to uncoupling of transport and phosphorylation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):382–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.382-389.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Schuitema A., Kwa C. Regulation of methyl beta-galactoside permease activity in pts and crr mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(4):448–453. doi: 10.1007/BF00428734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Stock J. B. Enzymes II of the phosphotransferase system do not catalyze sugar transport in the absence of phosphorylation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):476–484. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.476-484.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primakoff P., Artz S. W. Positive control of lac operon expression in vitro by guanosine 5'-diphosphate 3'-diphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1726–1730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primerano D. A., Burns R. O. Metabolic basis for the isoleucine, pantothenate or methionine requirement of ilvG strains of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1202–1211. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1202-1211.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primerano D. A., Burns R. O. Role of acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase in biosynthesis of pantothenic acid in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):259–269. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.259-269.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard D. G., Nivas S. C., York M. D., Pomeroy B. S. Effects of Gal-E-mutant of Salmonella typhimurium on experimental salmonellosis in chickens. Avian Dis. 1978 Oct-Dec;22(4):562–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pueyo C. Forward mutations to arabinose resistance in Salmonella typhimurium strains: a sensitive assay for mutagenicity testing. Mutat Res. 1978 Dec;54(3):311–321. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(78)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pueyo C., Lopez-Barea J. The L-arabinose-resistance test with Salmonella typhimurium strain SV3 selects forward mutations at several ara genes. Mutat Res. 1979 Aug;64(4):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(79)90094-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Conrard D. J., Schnaitman C. A., Gregg T. I. In vivo effects of local anesthetics on the production of major outer membrane proteins by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 20;599(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdonikas L. E. Poluchenie i kharakteristika glitserinovykh mutantov S. typhimurium. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1976;(12):29–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rephaeli A. W., Saier M. H., Jr Regulation of genes coding for enzyme constituents of the bacterial phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):658–663. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.658-663.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades M., MacHattie L. A., Thomas C. A., Jr The P22 bacteriophage DNA molecule. I. The mature form. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):21–40. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick P. D., Young D. A. Isolation and characterization of a temperature-sensitive lethal mutant of Salmonella typhimurium that is conditionally defective in 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonate-8-phosphate synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):447–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.447-455.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick P. D., Young D. A. Relationship between cell death and altered lipid A synthesis in a temperature-sensitive lethal mutant of Salmonella typhimurium that is conditionally defective in 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonate-8-phosphate synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):456–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.456-464.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle D. L., Carbon J. Frameshift suppression: a nucleotide addition in the anticodon of a glycine transfer RNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 25;242(121):230–234. doi: 10.1038/newbio242230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzino A., Mastanduno M., Freundlich M. Partial derepression of the isoleucine-valine enzymes during methionine starvation is Salmonella typhimurium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 18;475(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez S. B., Ingraham J. L. Location on the Salmonella typhimurium chromosome of the gene encoding nucleoside diphosphokinase (ndk). J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1101–1103. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1101-1103.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. A., Brenchley J. E. Bacteriophage P1 as a vehicle for Mu mutagenesis of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):848–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.848-851.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. A., Brenchley J. E. Regulation of nitrogen utilization of hisT mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):801–808. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.801-808.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. A., Brenchley J. Rapid methods for generalized transduction of Salmonella typhimurium mutants. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):261–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.261-263.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. A., Dendinger S. M., Murphy C. H., Brenchley J. E. Genetic characterization of the glutamate dehydrogenase gene (gdhA) of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):795–803. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.795-803.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. R., Antón D. N., Hartman P. E. Histidine regulatory mutants in Salmonella typhimurium. I. Isolation and general properties. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):305–323. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Vázquez R., Pueyo C., Cerdá-Olmedo E. A mutagen assay detecting forward mutations in an arabinose-sensitive strain of Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1978 Oct;54(2):121–129. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(78)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERSON K. E., DEMEREC M. THE LINKAGE MAP OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Genetics. 1965 Jun;51:897–913. doi: 10.1093/genetics/51.6.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr Bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase systems: structural, functional, and evolutionary interrelationships. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Dec;41(4):856–871. doi: 10.1128/br.41.4.856-871.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Bromberg F. G., Roseman S. Characterization of constitutive galactose permease mutants in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):512–514. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.512-514.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Feucht B. U., Mora W. K. Sugar phosphate: sugar transphosphorylation and exchange group translocation catalyzed by the enzyme 11 complexes of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):8899–8907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Straud H., Massman L. S., Judice J. J., Newman M. J., Feucht B. U. Permease-specific mutations in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli that release the glycerol, maltose, melibiose, and lactose transport systems from regulation by the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1358–1367. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1358-1367.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sales M., Brenchley J. E. The regulation of the ammonia assimilatory enzymes in Rel+ and Rel- strains of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(2):263–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00331860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Hall C. A. F-prime factors of Salmonella typhimurium and an inversion between S. typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1970 Feb;64(2):215–228. doi: 10.1093/genetics/64.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Hartman P. E. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition V. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):471–519. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.471-519.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Janzer J., Head J. Influence of lipopolysaccharide and protein in the cell envelope on recipient capacity in conjugation of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):283–293. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.283-293.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition IV. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):558–586. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.558-586.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E. Revised linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):354–372. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.354-372.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Ross H., Ziegler L., Mäkelä P. H. F + , Hfr, and F' strains of Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella abony. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):608–637. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.608-637.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Saeed Y. A. P22-mediated transduction analysis of the rough A (rfa) region of the chromosome of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):58–63. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.58-63.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Stocker B. A. Gene rfaH, which affects lipopolysaccharide core structure in Salmonella typhimurium, is required also for expression of F-factor functions. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):535–541. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.535-541.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvas M., Malinen M., Nurminen M., Mäkelä P. H. T2 lipopolysaccharide antigen of Salmonella: comparison of the properties of T2 and mucoid forms. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):839–842. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.839-842.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Yura T. Chromosomal location and expression of the structural gene for major outer membrane protein Ia of Escherichia coli K-12 and of the homologous gene of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):468–477. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.468-477.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaife J. G., Heilig J. S., Rowen L., Calendar R. Gene for the RNA polymerase sigma subunit mapped in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli by cloning and deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6510–6514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlecht S., Ferber E., Fromme I. Untersuchungen zur Fettsäurezusammensetzung von Lipiden bei Salmonella typhimurium-S- und R-Formen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1979 Dec;245(4):476–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlecht S., Fromme I., Ferber E., Müller W., Gmeiner J. Chemische und biologische Eigenschaften von Revertanten aus einer Salmonella typhimurium-Rd1-Mutante. Zentralbl Bakteriol A. 1980 Jun;247(1):50–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid M., Roth J. R. Circularization of transduced fragments: a mechanism for adding segments to the bacterial chromosome. Genetics. 1980 Jan;94(1):15–29. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieger H. A method for detection of phage mutants with altered transducing ability. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;110(4):378–381. doi: 10.1007/BF00438281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieger H., Backhaus H. The origin of DNA in transducing particles in P22-mutants with increased transduction-frequencies (HT-mutants). Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Jan 24;120(2):181–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00267246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. P., Nichols B. P., Yanofsky C. Procedure for production of hybrid genes and proteins and its use in assessing significance of amino acid differences in homologous tryptophan synthetase alpha polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2169–2173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholte B. J., Postma P. W. Competition between two pathways for sugar uptake by the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system in Salmonella typhimurium. Eur J Biochem. 1981;114(1):51–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholte B. J., Postma P. W. Mutation in the crp gene of Salmonella typhimurium which interferes with inducer exclusion. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):751–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.751-757.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholte B. J., Schuitema A. R., Postma P. W. Characterization of factor IIIGLc in catabolite repression-resistant (crr) mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):576–586. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.576-586.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholte B. J., Schuitema A. R., Postma P. W. Isolation of IIIGlc of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent glucose phosphotransferase system of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):257–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.257-264.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann W., Bade E. G. A Salmonella typhimurium endonuclease that converts native DNA to fragments of about 8 X 10(5) daltons. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Aug;101(2):319–325. doi: 10.1099/00221287-101-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of the trpC-trpB intercistronic region from Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1979 May 15;130(2):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90422-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamanna D. K., Sanderson K. E. Genetics and regulation of D-xylose utilization in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):71–79. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.71-79.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamanna D. K., Sanderson K. E. Uptake and catabolism of D-xylose in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):64–70. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.64-70.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanabruch W. G., Behlau I., Walker G. C. Spontaneous mutators of salmonella typhimurium LT2 generated by insertion of transposable elements. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):827–835. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.827-835.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanabruch W. G., Rein R. P., Behlau I., Walker G. C. Mutagenesis, by methylating and ethylating agents, in mutH, mutL, mutS, and uvrD mutants of Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):33–44. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.33-44.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw K. J., Berg C. M., Sobol T. J. Salmonella typhimurium mutants defective in acetohydroxy acid synthases I and II. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1258–1263. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1258-1263.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw K. J., Berg C. M. Substrate channeling: alpha-ketobutyrate inhibition of acetohydroxy acid synthase in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1509–1512. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1509-1512.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakihara Y., Wakabayashi T. Three-dimensional image reconstruction of straight flagella from a mutant Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 5;131(3):485–507. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva D. O., Dobrogosz W. J. Proton efflux associated with melibiose permease activity in Salmonella typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 14;81(3):750–755. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91415-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Phase variation: genetic analysis of switching mutants. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):845–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Zieg J., Hilmen M., Simon M. Phase variation in Salmonella: genetic analysis of a recombinational switch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):391–395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Zieg J., Simon M. Flagellar-phase variation: isolation of the rh1 gene. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):517–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.517-523.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sledziewska E., Hulanicka D. Method of isolation of cysteine constitutive mutants of the cysteine regulon in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 24;165(3):289–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00332529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Levine M. A phage P22 gene controlling integration of prophage. Virology. 1967 Feb;31(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. M., Kelln R. A., O'Donovan G. A. Repression and derepression of the enzymes of the pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway in Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Nov;121(1):27–38. doi: 10.1099/00221287-121-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somers J. M., Sweet G. D., Kay W. W. Flurorcitrate resistant tricarboxylate transport mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(3):338–345. doi: 10.1007/BF00425608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Rowbury R. J. The plasmid of Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Mar 19;121(4):347–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00433233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinson D. B., Gollub E. G., Hu R. C., Liu K. P. Regulation of tyrosine and phenylalanine biosynthesis in Salmonella. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1976;23(2):167–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Specific inactivator of flagellar reversal in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):442–447. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.442-447.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stan-Lotter H., Gupta M., Sanderson K. E. The influence of cations on the permeability of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium and other gram-negative bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Apr;25(4):475–485. doi: 10.1139/m79-070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples M. A., Houston L. L. Proteolytic degradation of imidazoleglycerolphosphate dehydratase-histidinol phosphatase from Salmonella typhimurium and the isolation of a resistant bifunctional core enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1395–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staskawicz B. J., Panopoulos N. J. Phaseolotoxin transport in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium via the oligopeptide permease. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):474–479. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.474-479.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetter D. W., Middleton R. B. Tryptophan-requiring parental strains yield Salmonella typhimurium x Escherichia coli hybrid recombinants with functional tryptophan operons. Can J Genet Cytol. 1979 Jun;21(2):255–259. doi: 10.1139/g79-029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr A protein methylesterase involved in bacterial sensing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker B. A., Males B. M., Takano W. Salmonella typhimurium mutants of RfaH-phenotype: genetics and antibiotic sensitivities. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jan;116(1):17–24. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker B. A., Mäkelä P. H. Genetics of the (gram-negative) bacterial surface. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978 Jun 5;202(1146):5–30. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1978.0055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker B. A., Nurminen M., Mäkelä P. H. Mutants defective in the 33K outer membrane protein of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):376–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.376-383.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuttard C. Location of trpR mutations in the serB-thr region of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1972 Aug;111(2):368–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.2.368-374.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Iino T. Role of the flaR gene in flagellar hook formation in Salmonella spp. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):973–979. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.973-979.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet G. D., Somers J. M., Kay W. W. Purification and properties of a citrate-binding transport component, the C protein of Salmonella typhimurium. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):710–715. doi: 10.1139/o79-089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekely E., Simon M. Homology between the invertible deoxyribonucleic acid sequence that controls flagellar-phase variation in Salmonella sp. and deoxyribonucleic acid sequences in other organisms. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):829–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.829-836.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szwacka M., Cieśla Z., Kłopotowski T. Azide-induced mutagenesis in gram-negative bacteria is recA-and lexA-independent. Mutat Res. 1979 Sep;62(2):221–225. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(79)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Săsărman A., Desrochers M., Sonea S., Sanderson K. E., Surdeanu M. Porphobilinogen-accumulating mutants of Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jun;94(2):359–366. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-2-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanemura S., Bauerle R. Conditionally expressed missense mutations: the basis for the unusual phenotype of an apparent trpD nonsense mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1980 Jul;95(3):545–559. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.3.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanemura S., Bauerle R. Suppression of a deletion mutation in the glutamine amidotransferase region of the Salmonella typhimurium trpD gene by mutations in pheA and tyrA. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):573–582. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.573-582.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L., Miller J. B., Warrick H. M., Koshland D. E., Jr Electron acceptor taxis and blue light effect on bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):567–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.567-573.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomulka K. W., Gots J. S. Isolation and characterization of purine regulatory mutants of Salmonella typhimurium with an episomal purE-lac fusion. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):153–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.153-161.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga H., Tokunaga M., Nakae T. Characterization of porins from the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. 1. Chemical analysis. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):433–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga M., Tokunaga H., Okajima Y., Nakae T. Characterization of porins from the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. 2. Physical properties of the functional oligomeric aggregates. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):441–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuno S., Roth L., Weinberger C., Gough M. Effect of mutant host RNA polymerase on the bifunctional activities of P22 gene c1. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jun 8;153(2):205–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00264737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T., Iwashita S., Kanegasaki S. Role of cell surface mobility on bacteriophage infection: translocation of Salmonella phages to membrane adhesions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 6;73(3):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90881-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trucksis M., Depew R. E. Identification and localization of a gene that specifies production of Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2164–2168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trucksis M., Golub E. I., Zabel D. J., Depew R. E. Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium supX genes specify deoxyribonucleic acid topoisomerase I. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):679–681. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.679-681.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueki T., Mitsui T., Nikaido H. X-ray diffraction studies of outer membranes of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biochem. 1979 Jan;85(1):173–182. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uerkvitz W., Beck C. F. Periplasmic phosphatases in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. A biochemical, physiological, and partial genetic analysis of three nucleoside monophosphate dephosphorylating enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):382–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M. Increased outer membrane resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate and cations in novel lipid A mutants. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):426–434. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.426-434.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Jensen M., Helander I., Nurminen M., Rietschel E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from the polymyxin-resistant pmrA mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 29;129(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Outer membrane permeability barrier disruption by polymyxin in polymyxin-susceptible and -resistant Salmonella typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):578–583. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Sarvas M. Decreased binding of polymyxin by polymyxin-resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):664–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.664-667.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., Green L., Miller C. G. Oligopeptidase-deficient mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1259–1265. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1259-1265.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., Miller C. G. Dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase-deficient mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1252–1258. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1252-1258.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voll M. J., Cohen L. A., Germida J. J. his-Linked hydrogen sulfide locus of Salmonella typhimurium and its expression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):1082–1084. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.1082-1084.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voll M. J., Shiller L. M., Castrilli J. His-linked hydrogen sulfide locus in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):902–905. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.902-905.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walenga R. W., Osborn M. J. Biosynthesis of lipid A. In vivo formation of an intermediate containing 3-deoxy-D-mannoctulosonate in a mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4252–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Receptor structure in the bacterial sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7157–7161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Clegg D. O., Koshland D. E., Jr Molecular cloning and amplification of the adenylate cyclase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4684–4688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. A., Walsh C. T., Botstein D. Two alanine racemase genes in Salmonella typhimurium that differ in structure and function. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1439–1450. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1439-1450.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Hashimoto H., Mitsuhashi S. Salmonella typhimurium LT2 mutation affecting the deletion of resistance determinants on R plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):145–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.145-152.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Arai T., Hattori T. Effects of cell wall polysaccharide on the mating ability of Salmonella typhimurium. Nature. 1970 Jan 3;225(5227):70–71. doi: 10.1038/225070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei G. R., Kustu S. Glutamine auxotrophs with mutations in a nitrogen regulatory gene, ntrC, that is near glnA. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(2):392–399. doi: 10.1007/BF00270646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weppelman R., Kier L. D., Ames B. N. Properties of two phosphatases and a cyclic phosphodiesterase of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.411-419.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S. R., Calvo J. M. Control of leu operon expression in Escherichia coli by a transcription attenuation mechanism. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):579–597. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90348-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West T. P., O'Donovan G. A. Repression of cytosine deaminase by pyrimidines in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):1171–1174. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.1171-1174.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiater A., Filutowicz M., Hulanicka D. A new class of mutants of the cysB regulatory gene for cysteine biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Aug;128(8):1785–1790. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-8-1785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiater A., Hulanicka D. The regulatory cysK mutant of S. typhimurium. Acta Biochim Pol. 1978;25(3):281–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild J., Filutowicz M., Kłopotowski T. Utilization of D-amino acids by dadR mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Jul;118(1):71–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00406077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G., Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Non-smooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: differentiation by phage sensitivity and genetic mapping. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):527–554. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Lee C. E., Wild J. R. Genetic and biochemical characterization of distinct transport systems for uracil, uridine and cytidine in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Apr;178(1):121–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00267220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield S. L., Falkinham J. O., 3rd Effect of recA and polA mutations on gene duplication in Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1981 Jan;91(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(81)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler M. E., Yanofsky C. Pausing of RNA polymerase during in vitro transcription of the tryptophan operon leader region. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3738–3744. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Botstein D. Control of lysogenization by phage P22. I. The P22 cro gene. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):209–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Botstein D., Miller J. H. Characterization of amber and ochre suppressors in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):433–439. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.433-439.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollin R., Creeger E. S., Rothfield L. I., Stocker B. A., Lindberg A. A. Salmonella typhimurium mutants defective in UDP-D-galactose:lipopolysaccharide alpha 1,6-D-galactosyltransferase. Structural, immunochemical, and enzymologic studies of rfaB mutants. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3769–3774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray C., Sojka W. J., Morris J. A., Brinley Morgan W. J. The immunization of mice and calves with gal E mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Aug;79(1):17–24. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400052803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T. A model for three-point analysis of random general transduction. Genetics. 1966 Aug;54(2):405–410. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Davies J. A genetic and biochemical study of streptomycin- and spectinomycin-resistance in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;110(3):197–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00337833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Murooka Y., Harada T. Comparative immunological studies on arylsulfatase in bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae: occurrence of latent arylsulfatase protein regulated by sulfur compounds and tyramine. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):536–541. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.536-541.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata H., Nakamura K., Inouye M. Comparison of the lipoprotein gene among the Enterobacteriaceae. DNA sequence of Erwinia amylovora lipoprotein gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2194–2198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N. Somatic O-1 antigen conversion of Salmonella typhimurium by a type B phage P221dis, hybrid between P22 and Fels 1 phages. J Gen Virol. 1978 Nov;41(2):367–376. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-2-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Breeding S. A., Lankford C. E. Enterochelin (enterobactin): virulence factor for Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):174–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.174-180.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. L., Becker J. M., Naider F. Transport of [14C]Gly-Pro in a proline peptidase mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 15;471(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90401-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C., vanCleemput M. Nucleotide sequence of trpE of Salmonella typhimurium and its homology with the corresponding sequence of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):235–246. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen C., Green L., Miller C. G. Degradation of intracellular protein in Salmonella typhimurium peptidase mutants. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 15;143(1):21–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen C., Green L., Miller C. G. Peptide accumulation during growth of peptidase deficient mutants. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 15;143(1):35–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young B. S., Wright A. Multiple effects of an RNA polymerase beta' mutation on in vitro transcription. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Oct 20;155(2):191–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00393159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel D. J., Trucksis M., Depew R. E. Salmonella typhimurium mutants with reduced levels of transfer ribonucleic acid-inhibitable endodeoxyribonucleolytic activity. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):173–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.173-178.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak V. L., Kelln R. A. 5-Fluoroorotate-resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Nov;24(11):1339–1345. doi: 10.1139/m78-216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak V. L., Kelln R. A. A Salmonella typhimurium mutant dependent upon carbamyl aspartate for resistance to 5-fluorouracil is specifically affected in ubiquinone biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1095–1098. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1095-1098.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Hilmen M., Simon M. Regulation of gene expression by site-specific inversion. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90098-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Simon M. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of an invertible controlling element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4196–4200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zyskind J. W., Deen L. T., Smith D. W. Isolation and mapping of plasmids containing the Salmonella typhimurium origin of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3097–3101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zyskind J. W., Smith D. W. Nucleotide sequence of the Salmonella typhimurium origin of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2460–2464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



