Abstract
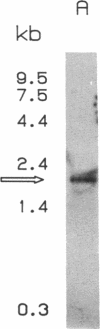
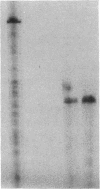
Incubation of DDT1 MF-2 hamster vas deferens cells with beta-adrenergic agonists results in a time- and concentration-dependent decreases in both beta-adrenergic receptor (beta AR) responsiveness and receptor number. Receptor mRNA levels were quantified by DNA-excess solution hybridization by using a 170-nucleotide single-stranded probe derived from the hamster beta 2AR cDNA. RNA blot analysis of poly(A)+-selected RNA with the solution probe revealed a 2.2-kilobase species. Digestion of the RNA/solution probe mixture with S1 endonuclease revealed a single species of RNA (170 bases) that was protected by the solution probe. DDT1 MF-2 cells were found to contain 0.38 pg of beta AR mRNA per microgram of total cellular RNA. Incubation (16 hr) with isoproterenol decreased beta AR mRNA levels in cells by 40%. This agonist-induced decrease in receptor mRNA levels was found to be dependent on the time of incubation and the dose of agonist. The decrease in beta AR mRNA was half-maximal at 0.1-0.5 microM isoproterenol. The beta-adrenergic antagonists CGP 20712A (beta 1-selective) and ICI 118,551 (beta 2-selective) blocked in a dose-dependent fashion the ability of isoproterenol to effect receptor mRNA levels. The beta 2-adrenergic antagonist displayed a potency 25-fold greater than that of the beta 1-adrenergic antagonist, in agreement with the subtype of receptor (beta 2) expressed by these cells. For down-regulated cells in which receptor mRNA levels declined in response to agonist, the addition of the antagonist ligand (-)-propranolol (1 microM) was able to restore receptor mRNA levels to 90% of the control value within 12 hr. Full recovery of steady-state beta AR mRNA was achieved within 60 hr. These studies provide a molecular explanation for the down-regulation of GTP-binding regulatory protein (G protein)-linked cell-surface receptors that accompanies desensitization.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahouth S. W., Malbon C. C. Human beta-adrenergic receptors. Simultaneous purification of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic-receptor peptides. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):557–566. doi: 10.1042/bj2480557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung F. Z., Lentes K. U., Gocayne J., Fitzgerald M., Robinson D., Kerlavage A. R., Fraser C. M., Venter J. C. Cloning and sequence analysis of the human brain beta-adrenergic receptor. Evolutionary relationship to rodent and avian beta-receptors and porcine muscarinic receptors. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):200–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81436-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Ishii S., Richert N., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Epidermal growth factor regulates the expression of its own receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8374–8378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Drogula C., Krönke M., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Interleukin 2 (IL-2) augments transcription of the IL-2 receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4230–4234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Kobilka B. K., Strader D. J., Benovic J. L., Dohlman H. G., Frielle T., Bolanowski M. A., Bennett C. D., Rands E., Diehl R. E. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):75–79. doi: 10.1038/321075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doss R. C., Perkins J. P., Harden T. K. Recovery of beta-adrenergic receptors following long term exposure of astrocytoma cells to catecholamine. Role of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12281–12286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser C. M., Venter J. C. The synthesis of beta-adrenergic receptors in cultured human lung cells: induction by glucocorticoids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):390–397. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80233-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K. Agonist-induced desensitization of the beta-adrenergic receptor-linked adenylate cyclase. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Mar;35(1):5–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. J., Insel P. A. Agonist-mediated regulation of alpha 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptor metabolism in a muscle cell line, BC3H-1. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;29(6):521–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Frielle T., Dohlman H. G., Bolanowski M. A., Dixon R. A., Keller P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Delineation of the intronless nature of the genes for the human and hamster beta 2-adrenergic receptor and their putative promoter regions. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7321–7327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., MacGregor C., Daniel K., Kobilka T. S., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Functional activity and regulation of human beta 2-adrenergic receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15796–15802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Pugh E. N., Jr ATP mediates rapid reversal of cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase activation in visual receptor membranes. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):734–736. doi: 10.1038/287734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma P. T., Yamamoto T., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Increased mRNA for low density lipoprotein receptor in livers of rabbits treated with 17 alpha-ethinyl estradiol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):792–796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan L. C., Koachman A. M., Insel P. A. Genetic analysis of beta-adrenergic receptor internalization and down-regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):129–133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan L. C., McKernan R. M., Insel P. A. Metabolism of alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors in vitro and in vivo. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987;27:215–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.27.040187.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moylan R. D., Barovsky K., Brooker G. N6,O2'-Dibutyryl cyclic AMP and cholera toxin-induced beta-adrenergic receptor loss in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4947–4950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. The subunits of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Resolution of the activated 45,000-dalton (alpha) subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11369–11376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oron Y., Straub R. E., Traktman P., Gershengorn M. C. Decreased TRH receptor mRNA activity precedes homologous downregulation: assay in oocytes. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1406–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.2825350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Protein phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:831–887. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpace P. J., Baresi L. A., Sanford D. A., Abrass I. B. Desensitization and resensitization of beta-adrenergic receptors in a smooth muscle cell line. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Dec;28(6):495–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to postmeiotic male germ cells and the neural tube of mid-gestational embryos. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90665-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelness G. S., Williams D. L. Apolipoprotein II messenger RNA. Transcriptional and splicing heterogeneity yields six 5'-untranslated leader sequences. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9929–9935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Molecular mechanisms of receptor desensitization using the beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase system as a model. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):124–129. doi: 10.1038/317124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver B. J., Bokar J. A., Virgin J. B., Vallen E. A., Milsted A., Nilson J. H. Cyclic AMP regulation of the human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene is mediated by an 18-base-pair element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2198–2202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Blake A. D., Cheung A. H., Register R. B., Rands E., Zemcik B. A., Candelore M. R., Dixon R. A. The carboxyl terminus of the hamster beta-adrenergic receptor expressed in mouse L cells is not required for receptor sequestration. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):855–863. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90623-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser R. H., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-agonist- and prostaglandin E1-induced translocation of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: evidence that the kinase may act on multiple adenylate cyclase-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6362–6366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su Y. F., Harden T. K., Perkins J. P. Catecholamine-specific desensitization of adenylate cyclase. Evidence for a multistep process. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7410–7419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toews M. L. Comparison of agonist-induced changes in beta- and alpha 1-adrenergic receptors of DDT1 MF-2 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;31(1):58–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L., Newman T. C., Shelness G. S., Gordon D. A. Measurement of apolipoprotein mRNA by DNA-excess solution hybridization with single-stranded probes. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:671–689. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]