Abstract
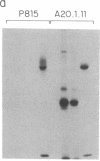
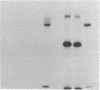
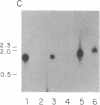
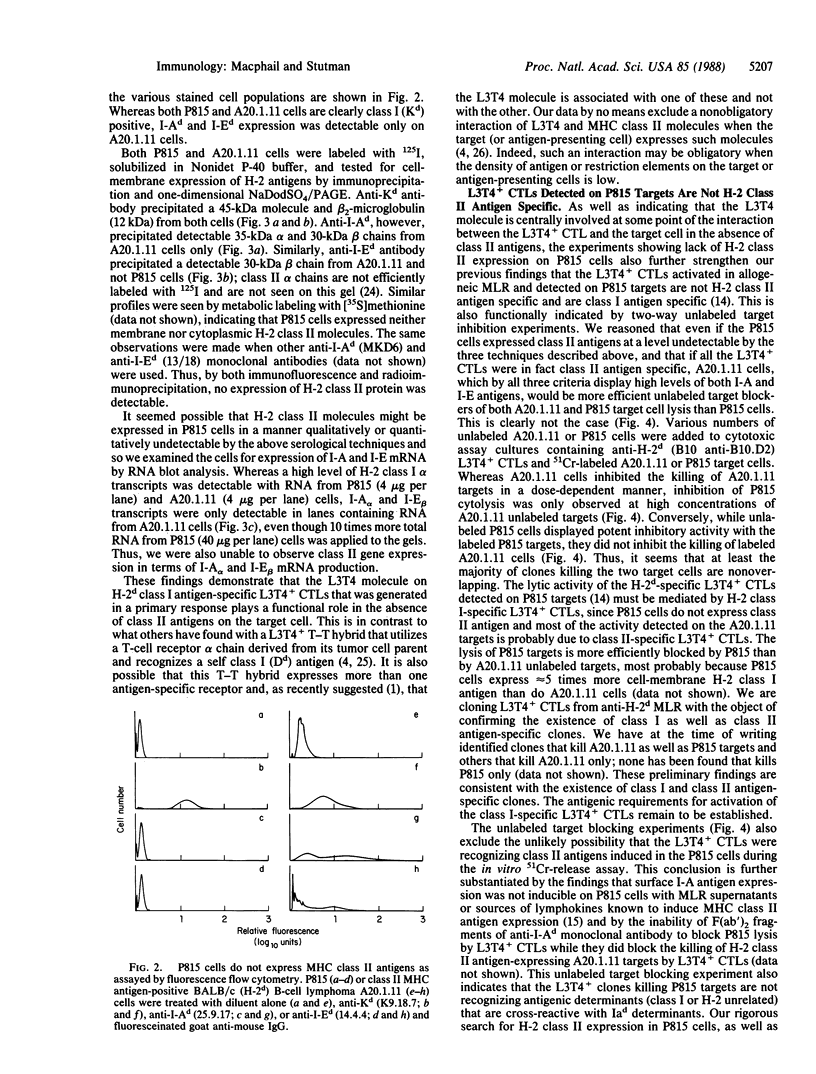
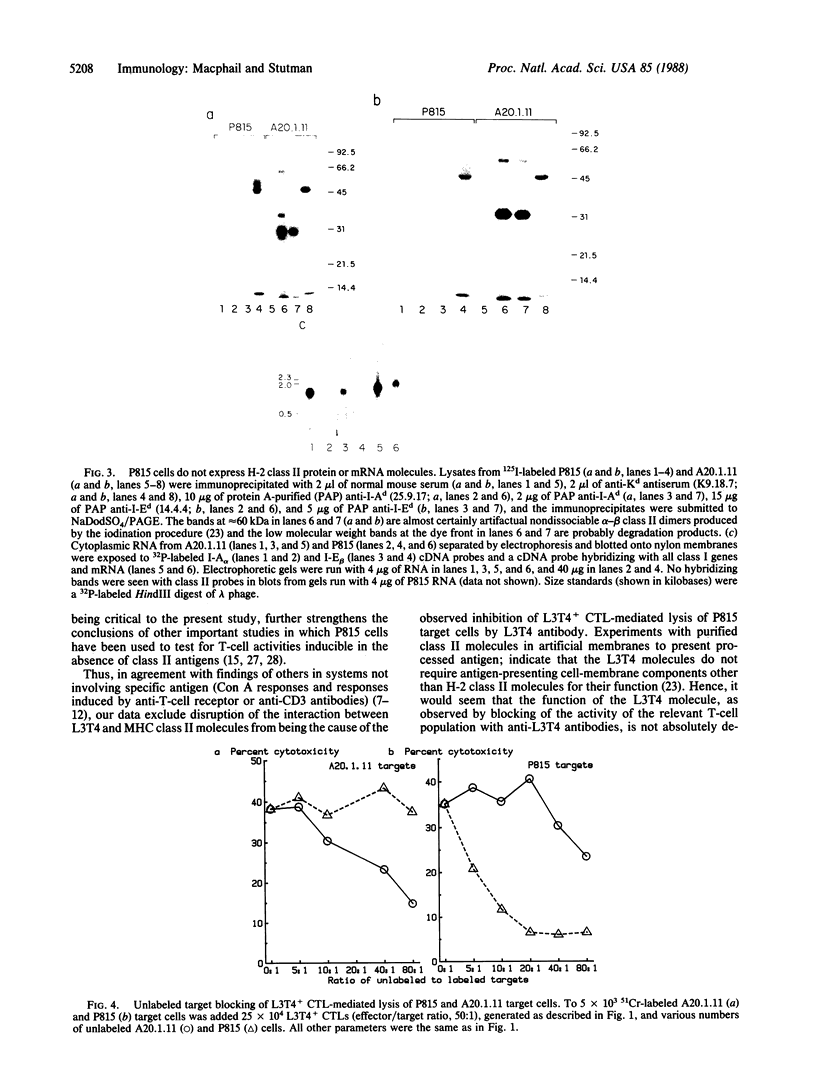
Anti-L3T4 monoclonal antibodies inhibit the cytotoxic activity of L3T4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for H-2 class I antigens. The P815 target cells used to detect this population of murine cytolytic cells are shown by immunofluorescence, radioimmunoprecipitation, and RNA blot analysis not to express H-2 class II protein or mRNA. Contrary to previously proposed models regarding its function, we conclude that the L3T4 molecule is involved at some stage of the lytic interaction between the class I-specific L3T4+ effector cell and its target cell by a mechanism for which there is not an obligatory requirement for H-2 class II antigen expression by the target cell. L3T4 may be an early component of the system that transduces the activation signal from the T-cell receptor complex to the cytoplasm, a cell-surface receptor for a yet undefined natural ligand that delivers a negative signal to the killer T cell, or it may modulate the avidity of the antigen-specific T-cell receptor through a direct physical association with it.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bank I., Chess L. Perturbation of the T4 molecule transmits a negative signal to T cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1294–1303. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekoff M., Kubo R., Grey H. M. Activation requirements for normal T cells: accessory cell-dependent and -independent stimulation by anti-receptor antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1411–1419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C. O., Mathis D. J., Kanter M. R., Williams V. E., 2nd, McDevitt H. O. The murine Ia alpha chains, E alpha and A alpha, show a surprising degree of sequence homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):534–538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman M., Yagüe J., Kubo R., Gay D., Coleclough C., Palmer E., Kappler J., Marrack P. The T cell repertoire may be biased in favor of MHC recognition. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90591-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T-lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. I. The generation of functionally distinct T-cell subclasses is a differentiative process independent of antigen. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1376–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay D., Coeshott C., Golde W., Kappler J., Marrack P. The major histocompatibility complex-restricted antigen receptor on T cells. IX. Role of accessory molecules in recognition of antigen plus isolated IA. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2026–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay D., Maddon P., Sekaly R., Talle M. A., Godfrey M., Long E., Goldstein G., Chess L., Axel R., Kappler J. Functional interaction between human T-cell protein CD4 and the major histocompatibility complex HLA-DR antigen. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):626–629. doi: 10.1038/328626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding H., McCluskey J., Munitz T. I., Germain R. N., Margulies D. H., Singer A. T-cell recognition of a chimaeric class II/class I MHC molecule and the role of L3T4. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):425–427. doi: 10.1038/317425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenstein J. L., Kappler J., Marrack P., Burakoff S. J. The role of L3T4 in recognition of Ia by a cytotoxic, H-2Dd-specific T cell hybridoma. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1213–1224. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenstein J. L., Malissen B., Burakoff S. J. Role of L3T4 in antigen-driven activation of a class I-specific T cell hybridoma. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):369–374. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenstein J. L., Sitkovsky M. V., Burakoff S. J. Distinct roles for L3T4 in T cell activation. Fed Proc. 1987 Feb;46(2):313–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty K. J., Andrus L., Prowse S. J. Role of lymphokine and antigen in the control of specific T cell responses. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:279–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macphail S., Paciucci P. A., Stutman O. Phenotypic heterogeneity of antisyngeneic tumor killer cells (ASTK) generated in allogeneic mixed lymphocyte reactions. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3205–3210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macphail S., Stutman O. L3T4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for class I H-2 antigens are activated in primary mixed lymphocyte reactions. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4007–4015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark W. H., Kimura S., Hämmerling U. Biochemical characterization of murine lymphoid alloantigen Ly-m20.2, a cell surface marker controlled by a gene linked to the Mls locus. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2635–2641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Endres R., Shimonkevitz R., Zlotnik A., Dialynas D., Fitch F., Kappler J. The major histocompatibility complex-restricted antigen receptor on T cells. II. Role of the L3T4 product. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1077–1091. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengle-Gaw L., McDevitt H. O. Predicted protein sequence of the murine I-E-beta S-polypeptide chain from cDNA and genomic clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2910–2914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldwin R. L., Havran W. L., Nau G. J., Lancki D. W., Kim D. K., Fitch F. W. Antibodies to the L3T4 and Lyt-2 molecules interfere with antigen receptor-driven activation of cloned murine T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):657–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens T., Fazekas de St Groth B. Participation of L3T4 in T cell activation in the absence of class II major histocompatibility complex antigens. Inhibition by anti-L3T4 antibodies is a function both of epitope density and mode of presentation of anti-receptor antibody. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2402–2409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani L., Mage M. G. Search for class II major histocompatibility complex molecular involvement in the response of Lyt-2+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte precursors to alloantigen. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Nov;15(11):1125–1130. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830151111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saizawa K., Rojo J., Janeway C. A., Jr Evidence for a physical association of CD4 and the CD3:alpha:beta T-cell receptor. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):260–263. doi: 10.1038/328260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. D., Vitetta E. S., Cullen S. E. Labeling characteristics and separation of Ia antigen subunits. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):671–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J., Schaefer M. Capacity of purified Lyt-2+ T cells to mount primary proliferative and cytotoxic responses to Ia- tumour cells. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):541–544. doi: 10.1038/322541a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dialynas D. P., Fitch F. W., English M. Monoclonal antibody to L3T4 blocks the function of T cells specific for class 2 major histocompatibility complex antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1118–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tite J. P., Sloan A., Janeway C. A., Jr The role of L3T4 in T cell activation: L3T4 may be both an Ia-binding protein and a receptor that transduces a negative signal. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1986;2(4):179–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassmer P., Chan C., Lögdberg L., Shevach E. M. Role of the L3T4-antigen in T cell activation. II. Inhibition of T cell activation by monoclonal anti-L3T4 antibodies in the absence of accessory cells. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2237–2242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]