Abstract
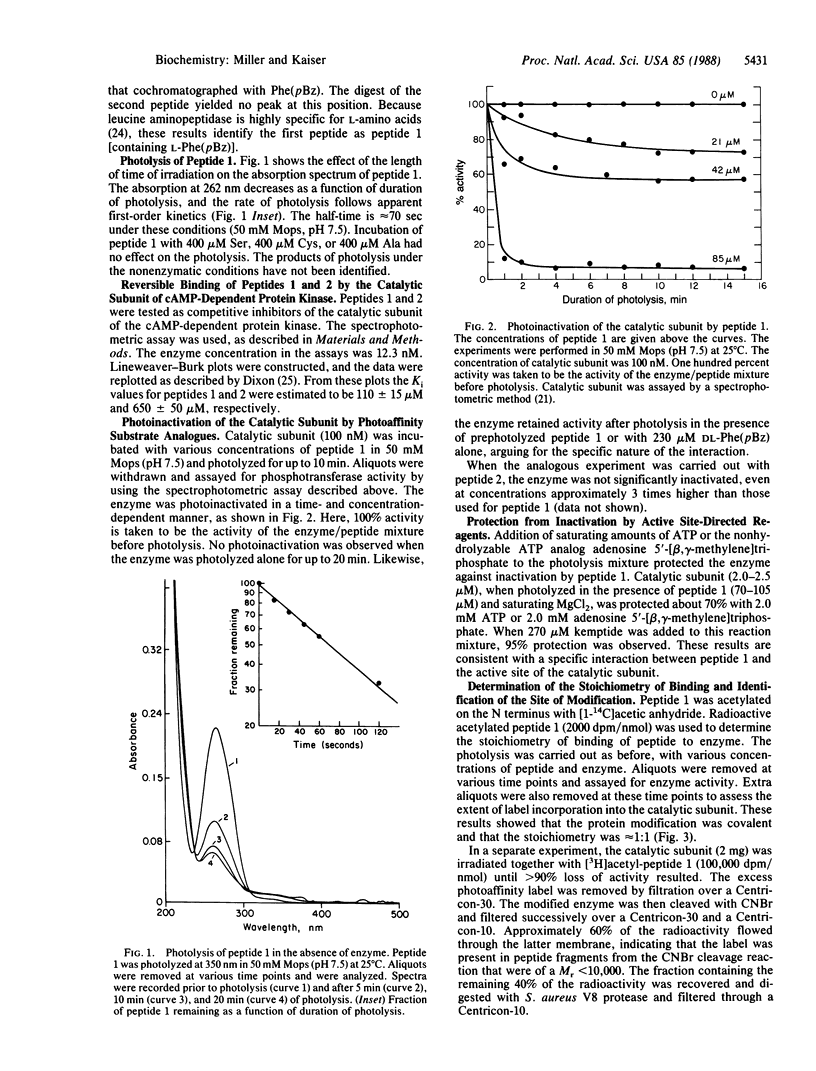
A peptide-based photoaffinity label for the catalytic subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase was prepared from the amino acid p-benzoyl-L-phenylalanine [L-Phe(pBz)]. By using solid-phase peptide synthesis methodology, DL-Phe(pBz) was incorporated into the cAMP-dependent protein kinase substrate Leu-Arg-Arg-Ala-Ser-Leu-Gly in place of the phosphorylatable serine. The diastereomeric peptides were separated by reverse-phase HPLC. The peptide substrate analog containing L-Phe(pBz) had a Ki of approximately 110 microM at pH 7.5. When photolyzed at 350 nm in the presence of the enzyme, this peptide caused time- and concentration-dependent inactivation. Radioactive acetylated L-Phe(pBz) peptide was used to establish the binding stoichiometry of peptide to enzyme; these results, together with protection experiments, showed the photoaffinity labeling to be specific (approximately 1:1). To identify the residues that were modified on the catalytic subunit, the photoinactivated enzyme was cleaved with CNBr and V8 protease (Staphylococcus aureus). The resulting peptide fragments were purified by HPLC and were sequenced; these experiments identified the modified residues as Gly-125 and Met-127. This region of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit contains many residues that are conserved in serine- and tyrosine-protein kinases.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayley H., Knowles J. R. Photoaffinity labeling. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:69–114. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Activation of protein kinase by physiological concentrations of cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3580–3583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake J., Li C. H. The synthesis and biological activity of (165, 182, 189-S-carbamidomethylcysteine)-human growth hormone-(140-191). Int J Pept Protein Res. 1975;7(6):495–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1975.tb02471.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramson H. N., Thomas N., Matsueda R., Nelson N. C., Taylor S. S., Kaiser E. T. Modification of the catalytic subunit of bovine heart cAMP-dependent protein kinase with affinity labels related to peptide substrates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10575–10581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granot J., Mildvan A. S., Bramson H. N., Thomas N., Kaiser E. T. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the conformation and kinetics of the peptide-substrate at the active site of bovine heart protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 3;20(3):602–610. doi: 10.1021/bi00506a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helene C. Phosphorescence of benzophenone in aqueous solution and its quenching by nucleic acid derivatives. Photochem Photobiol. 1972 Dec;16(6):519–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1972.tb06321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson C. S., Krebs E. G. Affinity labeling of catalytic subunit of bovine heart muscle cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase by 5'-p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyladenosine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7509–7514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauer J. C., Erickson-Viitanen S., Wolfe H. R., Jr, DeGrado W. F. p-Benzoyl-L-phenylalanine, a new photoreactive amino acid. Photolabeling of calmodulin with a synthetic calmodulin-binding peptide. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10695–10700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Graves D. J., Benjamini E., Krebs E. G. Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4888–4894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobashery S., Kaiser E. T. Identification of amino acid residues involved in substrate recognition by the catalytic subunit of bovine cyclic AMP dependent protein kinase: peptide-based affinity labels. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3691–3696. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroder L., Hallett A., Wünsch E., Keller O., Wersin G. Di-tert.-butyldicarbonat--ein vorteilhaftes Reagenz zur Eingührung der tert.-Butyloxycarbonyl-Schutzgruppe. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Nov;357(11):1651–1653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEERS E., Jr, CRAVEN G. R., ANFINSEN C. B., BETHUNE J. L. EVIDENCE FOR NONIDENTICAL CHAINS IN THE BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2478–2484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara S., Shimonishi Y., Kishida Y., Okada M., Sugihara H. Use of anhydrous hydrogen fluoride in peptide synthesis. I. Behavior of various protective groups in anhydrous hydrogen fluoride. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1967 Sep;40(9):2164–2167. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.40.2164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Parmelee D. C., Wade R. D., Kumar S., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Long G. L., Demaille J. G., Fischer E. H. Complete amino acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of bovine cardiac muscle cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):848–851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowadski J. M., Nguyen H. X., Anderson D., Taylor S. S. Crystallization studies of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Crystals of catalytic subunit diffract to 3.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):617–620. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90249-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Nelson N. C., Taylor S. S. Affinity labeling of cAMP-dependent protein kinase with p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyl adenosine. Covalent modification of lysine 71. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10837–10842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Taylor S. S. Affinity labeling of the nucleotide binding site of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase using p-fluorosulfonyl-[14C]benzoyl 5'-adenosine. Identification of a modified lysine residue. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8363–8368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


