Abstract
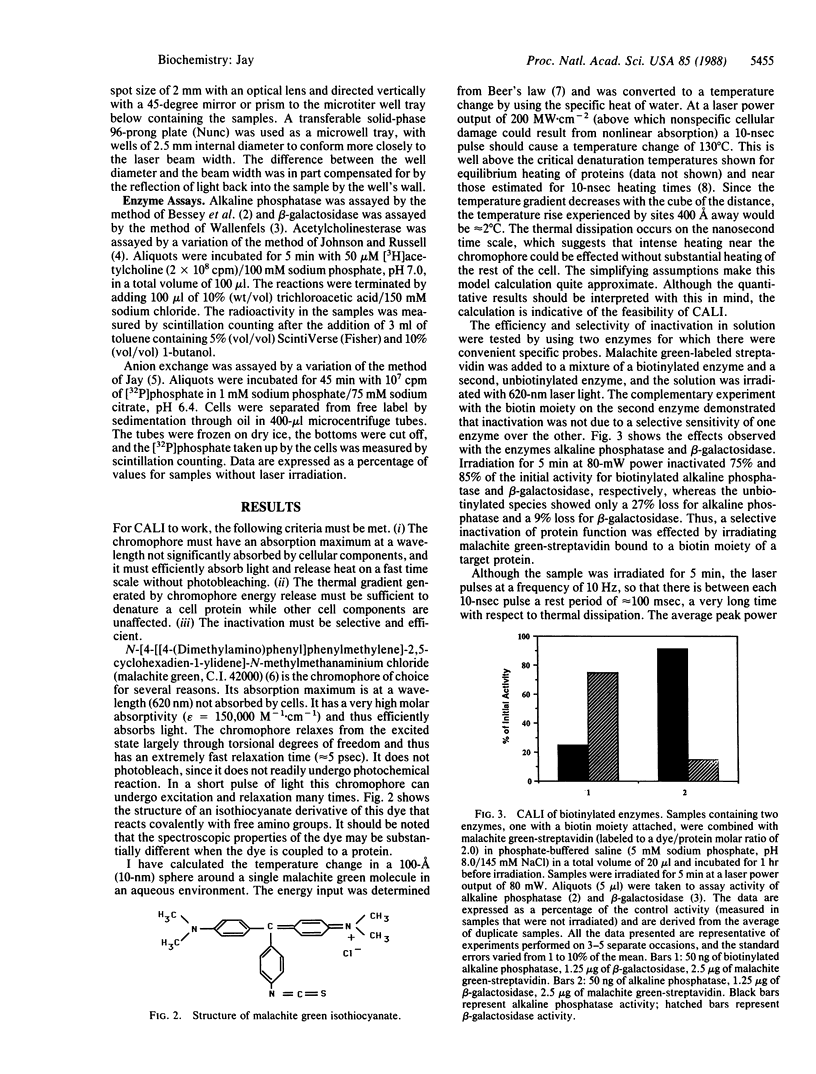
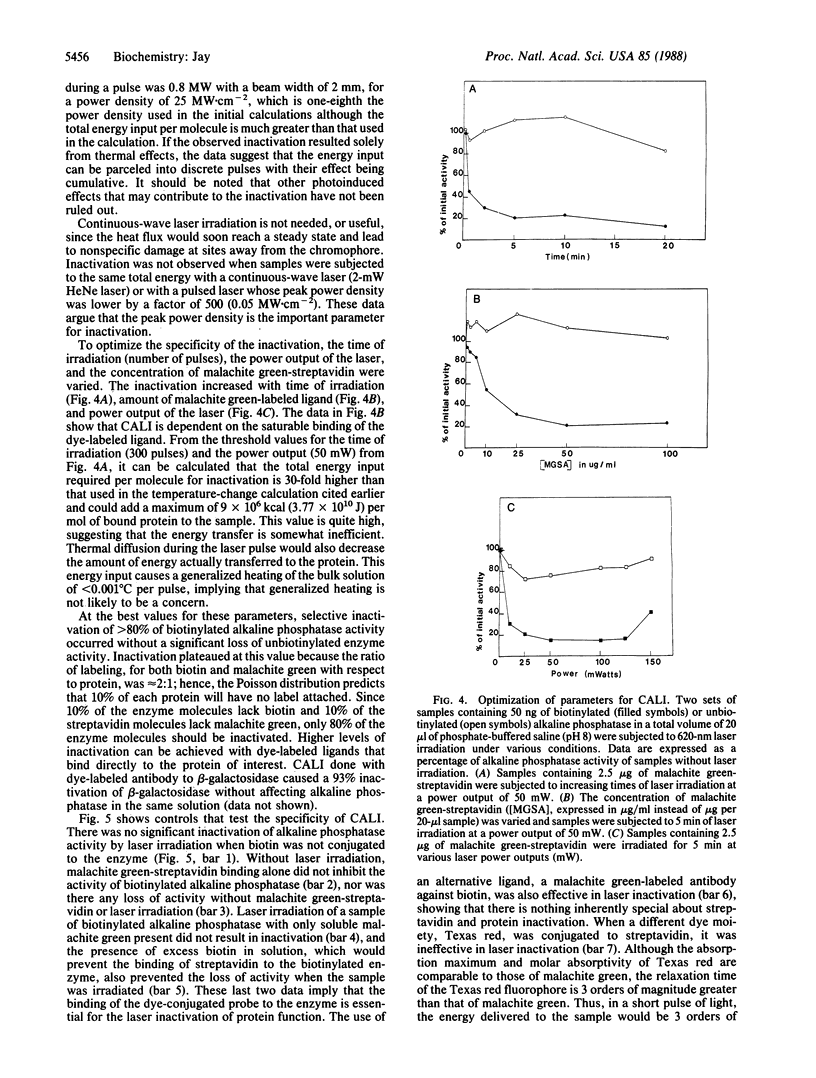
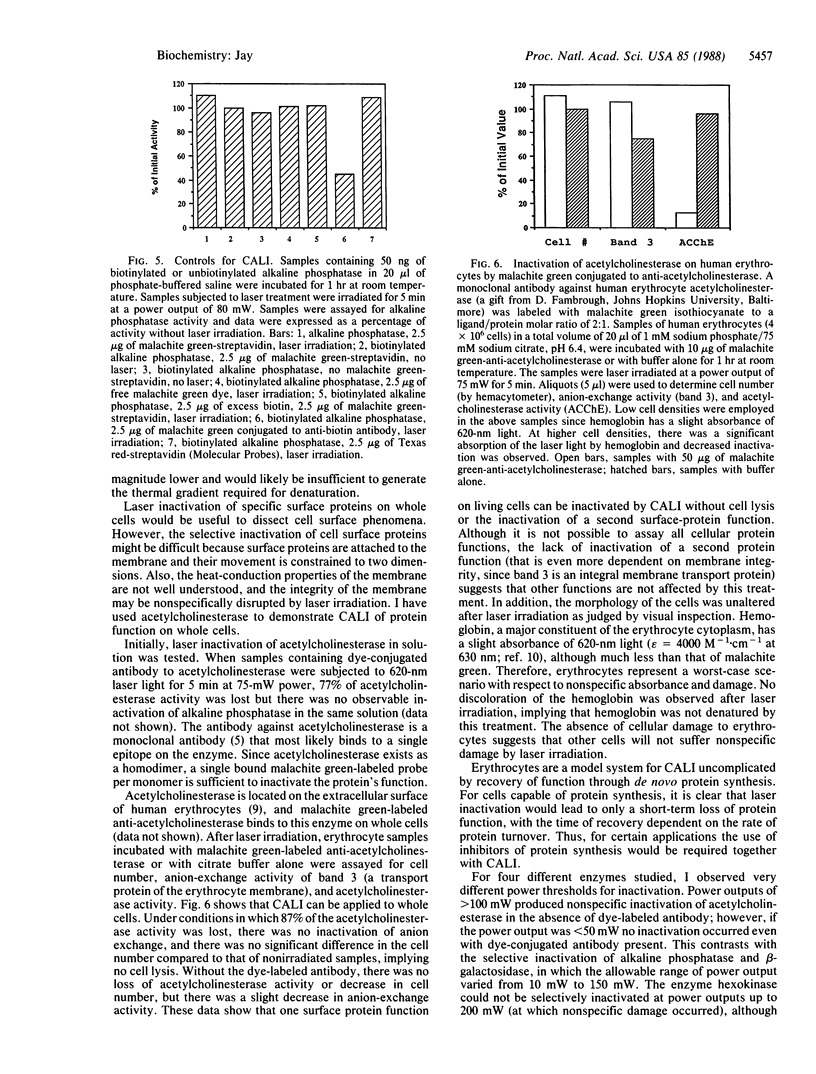
Chromophore-assisted laser inactivation of protein function has been achieved. After a protein binds a specific ligand or antibody conjugated with malachite green (C.I. 42,000), it is selectively inactivated by laser irradiation at a wavelength of light absorbed by the dye but not significantly absorbed by cellular components. Ligand-bound proteins in solution and on the surfaces of cells can be denatured without other proteins in the same samples being affected. Chromophore-assisted laser inactivation can be used to study cell surface phenomena by inactivating the functions of single proteins on living cells, a molecular extension of cellular laser ablation. It has an advantage over genetics and the use of specific inhibitors in that the protein function of a single cell within the organism can be inactivated by focusing the laser beam.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. R., Parrish J. A. Selective photothermolysis: precise microsurgery by selective absorption of pulsed radiation. Science. 1983 Apr 29;220(4596):524–527. doi: 10.1126/science.6836297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Engel A. G., Rosenberry T. L. Acetylcholinesterase of human erythrocytes and neuromuscular junctions: homologies revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1078–1082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay D. G. Characterization of the chicken erythrocyte anion exchange protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9431–9436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. D., Russell R. L. A rapid, simple radiometric assay for cholinesterase, suitable for multiple determinations. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. P., Selverston A. Rapid killing of single neurons by irradiation of intracellularly injected dye. Science. 1979 Nov 9;206(4419):702–704. doi: 10.1126/science.386514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


