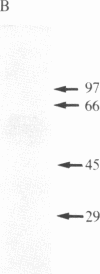Abstract
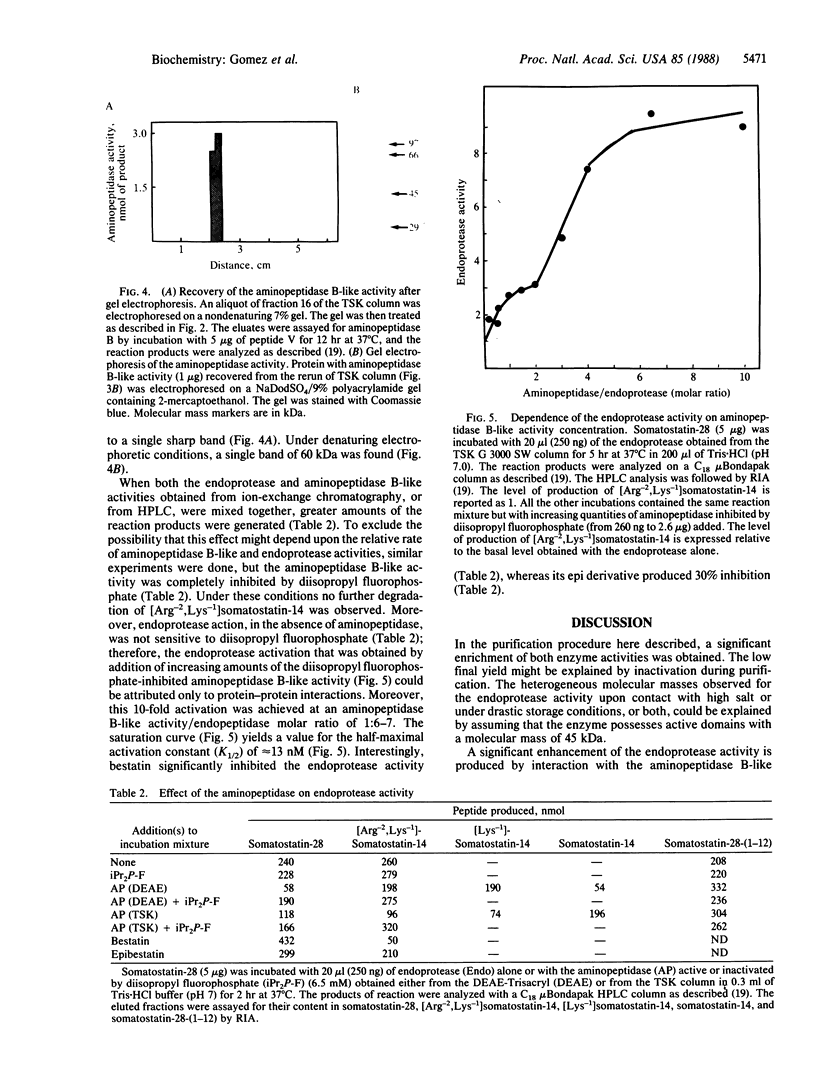
The somatostatin-28 convertase activity involved in vitro in the processing of somatostatin-28 into the neuropeptides somatostatin-28-(1-12) and somatostatin-14 is composed of an endoprotease and a basic aminopeptidase. We report herein on the purification to apparent homogeneity of these two constituents and on their functional interrelationship. In particular we observed that after various physicochemical treatments, the 90-kDa endoprotease activity was recovered both at this molecular mass and as a 45-kDa entity. Moreover, the production of [Arg-2,Lys-1]somatostatin-14 from somatostatin-28 by the action of the endoprotease was activated in a cooperative manner by the aminopeptidase B-like enzyme. A 10-fold activation occurred when the exopeptidase was inhibited by 6.5 mM diisopropyl fluorophosphate and allowed the determination of a half-maximal activation constant (K1/2) of approximately equal to 13 nM. These observations strongly suggest that both enzymes act in a concerted manner in vitro and that they may form a complex in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoit R., Böhlen P., Ling N., Briskin A., Esch F., Brazeau P., Ying S. Y., Guillemin R. Presence of somatostatin-28-(1-12) in hypothalamus and pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):917–921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cha T. A., Alberts B. M. Studies of the DNA helicase-RNA primase unit from bacteriophage T4. A trinucleotide sequence on the DNA template starts RNA primer synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):7001–7010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamagirand C., Creminon C., Fahy C., Boussetta H., Cohen P. Partial purification and functional properties of an endoprotease from bovine neurosecretory granules cleaving proocytocin/neurophysin peptides at the basic amino acid doublet. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6018–6023. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. Proteolytic events in the post-translational processing of polypeptide hormone precursors. Biochimie. 1987 Feb;69(2):87–89. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90239-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devi L., Goldstein A. Dynorphin converting enzyme with unusual specificity from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty K., Steiner D. F. Post-translational proteolysis in polypeptide hormone biosynthesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:625–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluschankof P., Cohen P. Proteolytic enzymes in the post-translational processing of polypeptide hormone precursors. Neurochem Res. 1987 Oct;12(10):951–958. doi: 10.1007/BF00966318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluschankof P., Gomez S., Morel A., Cohen P. Enzymes that process somatostatin precursors. A novel endoprotease that cleaves before the arginine-lysine doublet is involved in somatostatin-28 convertase activity of rat brain cortex. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9615–9620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluschankof P., Morel A., Benoit R., Cohen P. The somatostatin-28 convertase of rat brain cortex generates both somatostatin-14 and somatostatin-28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1051–1057. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluschankof P., Morel A., Gomez S., Nicolas P., Fahy C., Cohen P. Enzymes processing somatostatin precursors: an Arg-Lys esteropeptidase from the rat brain cortex converting somatostatin-28 into somatostatin-14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6662–6666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
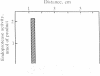
- Gomez S., Gluschankof P., Morel A., Cohen P. The somatostatin-28 convertase of rat brain cortex is associated with secretory granule membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10541–10545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh Y. P., Chang T. L. Pro-opiocortin converting activity in rat intermediate and neural lobe secretory granules. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jan 11;137(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80314-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Van Keuren M. L. Silver staining methods for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:230–239. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Kojima M., Matsuo H. A putative prohormone processing protease in bovine adrenal medulla specifically cleaving in between Lys-Arg sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):884–891. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90129-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Matsuo H. A novel protease from yeast with specificity towards paired basic residues. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):558–560. doi: 10.1038/309558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel A., Nicolas P., Cohen P. Evidence for a predominant form of Mr = 15,000 prosomatostatin in the mouse hypothalamus. Relationship with somatostatin-14 and -28. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8273–8276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg F., Nordström K., Terenius L. Endopeptidase in human cerebrospinal fluid which cleaves proenkephalin B opioid peptides at consecutive basic amino acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Sep 30;131(3):1069–1074. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90199-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish D. C., Tuteja R., Altstein M., Gainer H., Loh Y. P. Purification and characterization of a paired basic residue-specific prohormone-converting enzyme from bovine pituitary neural lobe secretory vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14392–14397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradayrol L., Jörnvall H., Mutt V., Ribet A. N-terminally extended somatostatin: the primary structure of somatostatin-28. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 1;109(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81310-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rholam M., Nicolas P., Cohen P. Precursors for peptide hormones share common secondary structures forming features at the proteolytic processing sites. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. P., Rutter W. J. Sequence of the human somatostatin I gene. Science. 1984 Apr 13;224(4645):168–171. doi: 10.1126/science.6142531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soda K., Tanizawa K. Kynureninases: enzymological properties and regulation mechanism. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1979;49:1–40. doi: 10.1002/9780470122945.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavianini M. A., Hayes T. E., Magazin M. D., Minth C. D., Dixon J. E. Isolation, characterization, and DNA sequence of the rat somatostatin gene. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11798–11803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vishwanatha J. K., Coughlin S. A., Wesolowski-Owen M., Baril E. F. A multiprotein form of DNA polymerase alpha from HeLa cells. Resolution of its associated catalytic activities. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6619–6628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]