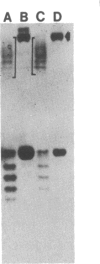
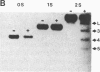
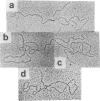
Abstract
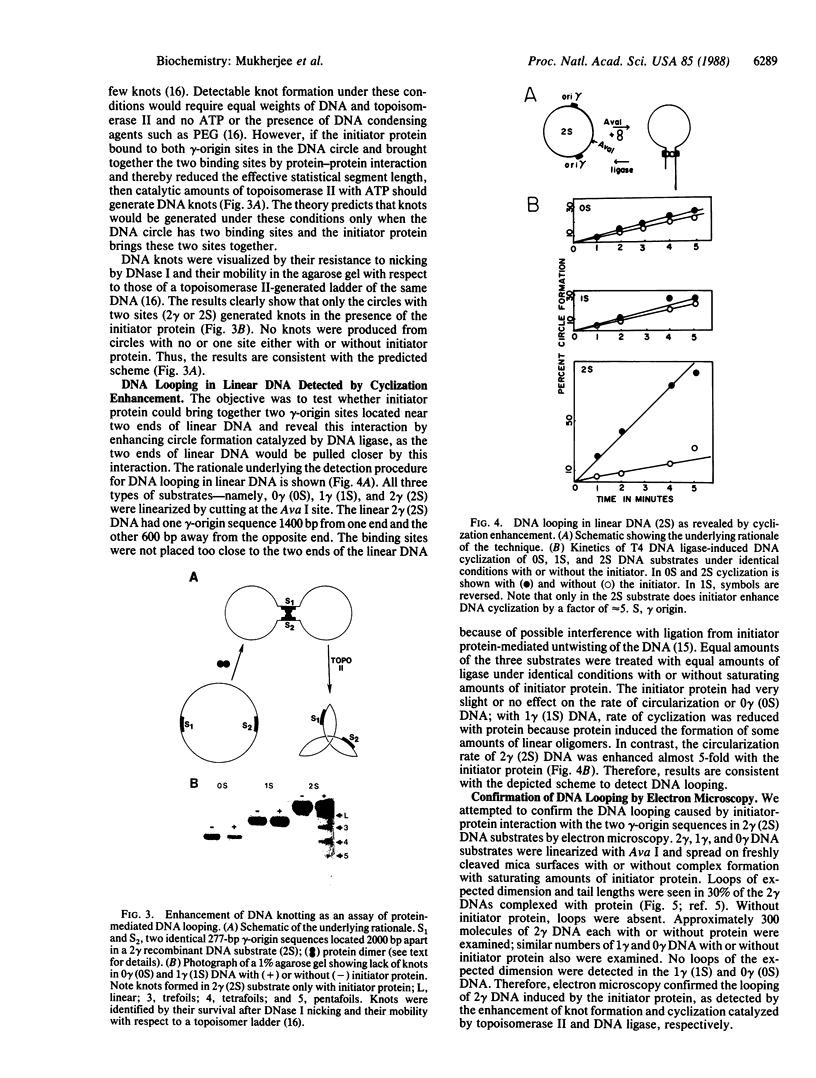
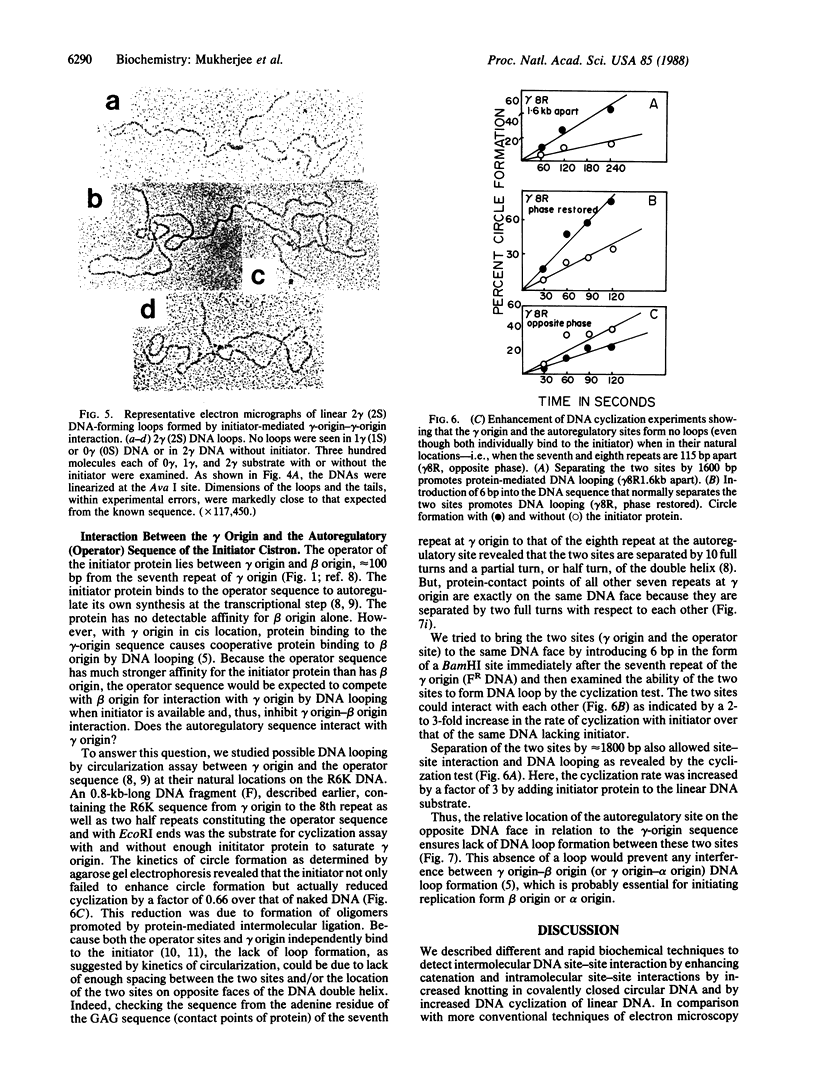
We describe different and relatively rapid biochemical techniques to detect protein-mediated DNA looping. These techniques, based on enhancement of DNA knotting and that of ligase-catalyzed cyclization, were used to show that the replication initiator protein of plasmid R6K can bring together two intramolecular gamma origin of replication sequences located as far apart as 2 kilobases. The site-site interaction causes looping out of the intervening DNA sequence as visualized by electron microscopy. Because the autoregulatory sequence of the initiator cistron also binds initiator protein, we investigated whether the gamma origin-bound protein can participate in autoregulation by interaction of the two sites through a protein bridge. We discovered that the two sites do not interact in vitro at their natural locations when on opposite faces of the double helix. Moving the two sites to the same face of the double helix by introducing a half turn into the intervening sequence allows protein-mediated site-site interaction to occur.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chattoraj D. K., Mason R. J., Wickner S. H. Mini-P1 plasmid replication: the autoregulation-sequestration paradox. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):551–557. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90468-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. Three origins of replication are active in vivo in the R plasmid RSF1040. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11075–11077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filutowicz M., Davis G., Greener A., Helinski D. R. Autorepressor properties of the pi-initiation protein encoded by plasmid R6K. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 11;13(1):103–114. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germino J., Bastia D. Interaction of the plasmid R6K-encoded replication initiator protein with its binding sites on DNA. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germino J., Bastia D. The replication initiator protein of plasmid R6K tagged with beta-galactosidase shows sequence-specific DNA-binding. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):131–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90503-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J., Hochschild A., Ptashne M. DNA loops induced by cooperative binding of lambda repressor. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):750–752. doi: 10.1038/322750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Cooperative binding of lambda repressors to sites separated by integral turns of the DNA helix. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90833-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley W., Bastia D. Replication initiator protein of plasmid R6K autoregulates its own synthesis at the transcriptional step. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2574–2578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Liu C. C., Alberts B. M. Type II DNA topoisomerases: enzymes that can unknot a topologically knotted DNA molecule via a reversible double-strand break. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):697–707. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A., Adhya S. Demonstration of two operator elements in gal: in vitro repressor binding studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6100–6104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K., Huo L., Schleif R. F. The DNA loop model for ara repression: AraC protein occupies the proposed loop sites in vivo and repression-negative mutations lie in these same sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3654–3658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee S., Erickson H., Bastia D. Enhancer-origin interaction in plasmid R6K involves a DNA loop mediated by initiator protein. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):375–383. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee S., Patel I., Bastia D. Conformational changes in a replication origin induced by an initiator protein. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel I., Bastia D. A replication origin is turned off by an origin-"silencer" sequence. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90521-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Transactivation of a bovine papilloma virus transcriptional regulatory element by the E2 gene product. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):183–191. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundin O., Varshavsky A. Terminal stages of SV40 DNA replication proceed via multiply intertwined catenated dimers. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]