Abstract
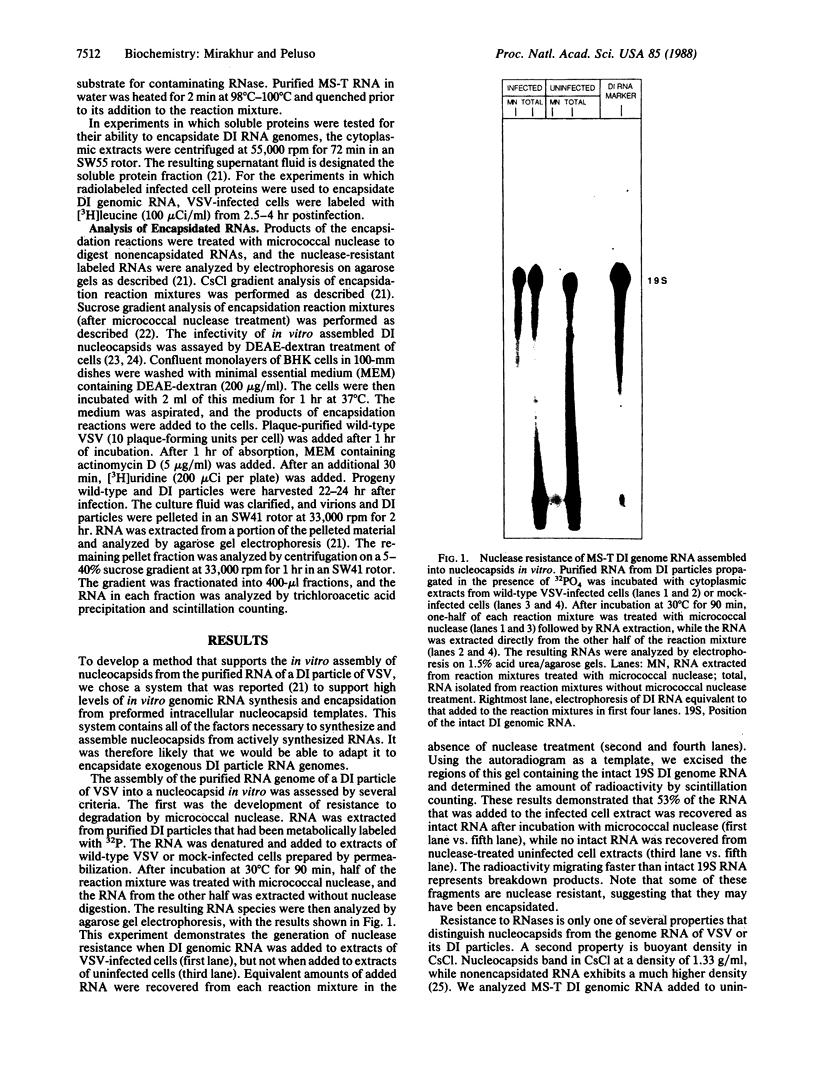
The template for transcription and replication of negative-stranded RNA viruses is a ribonucleoprotein structure, the nucleocapsid. We have developed a system that supports assembly of the negative-stranded RNA genome of a defective interfering (DI) particle of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) into a nucleocapsid in vitro. This system uses extracts from wild-type VSV-infected cells as a source of proteins to encapsidate the RNA. In vitro assembled nucleocapsids were compared to in vivo-derived nucleocapsids by the following characteristics: nuclease resistance of the encapsidated RNA, CsCl density banding of labeled RNA in a position coincident with nucleocapsids, correct sedimentation rate in sucrose gradients, the presence of the nucleocapsid protein on the nucleocapsids, and the infectivity of the in vitro assembled nucleocapsids. We conclude that the system we present is capable of assembling the isolated genome of a rhabdovirus DI particle into nucleocapsids indistinguishable from those produced during the course of intracellular DI replication.
Full text
PDF

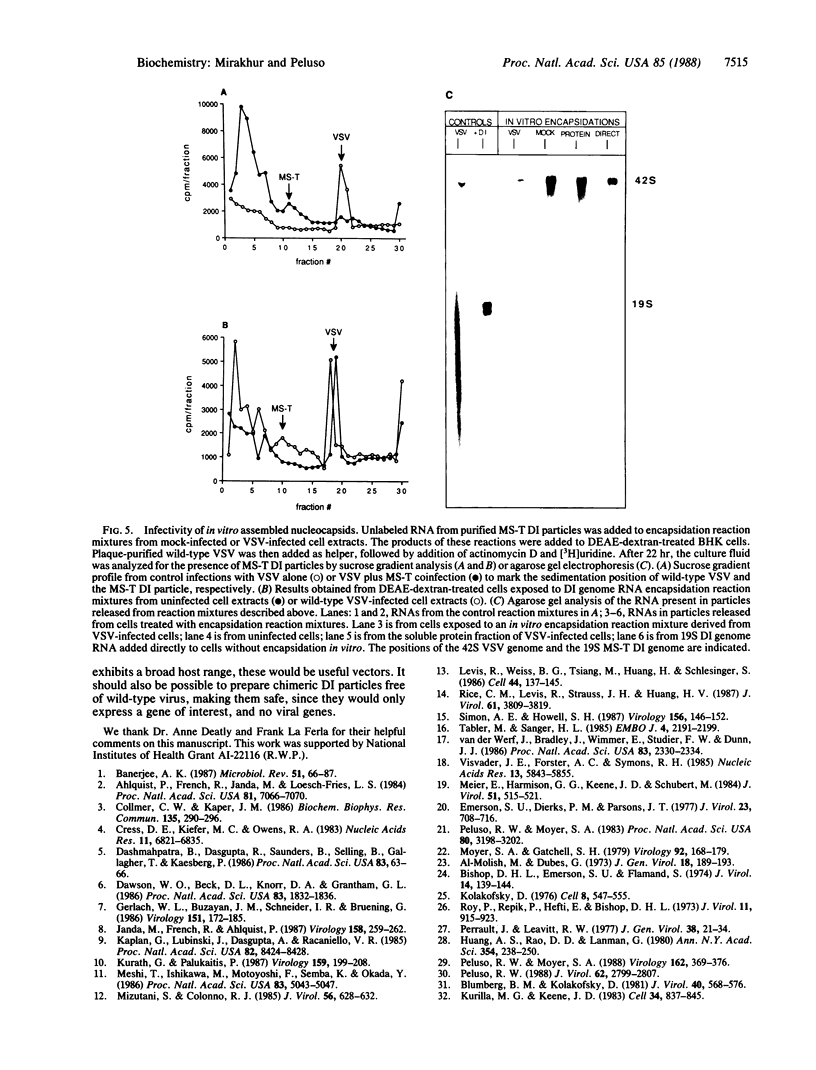
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlquist P., French R., Janda M., Loesch-Fries L. S. Multicomponent RNA plant virus infection derived from cloned viral cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7066–7070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K. Transcription and replication of rhabdoviruses. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):66–87. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.66-87.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Emerson S. U., Flamand A. Reconstitution of infectivity and transcriptase activity of homologous and heterologous viruses: vesicular stomatitis (Indiana serotype), Chandipura, vesicular stomatitis (New Jersey serotype), and Cocal viruses. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):139–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.139-144.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. M., Kolakofsky D. Intracellular vesicular stomatitis virus leader RNAs are found in nucleocapsid structures. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):568–576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.568-576.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collmer C. W., Kaper J. M. Infectious RNA transcripts from cloned cDNAs of cucumber mosaic viral satellites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 26;135(1):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90975-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cress D. E., Kiefer M. C., Owens R. A. Construction of infectious potato spindle tuber viroid cDNA clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6821–6835. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasmahapatra B., Dasgupta R., Saunders K., Selling B., Gallagher T., Kaesberg P. Infectious RNA derived by transcription from cloned cDNA copies of the genomic RNA of an insect virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):63–66. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson W. O., Beck D. L., Knorr D. A., Grantham G. L. cDNA cloning of the complete genome of tobacco mosaic virus and production of infectious transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1832–1836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Dierks P. M., Parsons J. T. In vitro synthesis of a unique RNA species by a T particle of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.708-716.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Rao D. D., Lanman G. Defective interfering particles of vesicular stomatitis virus: structure-function relationships. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:238–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Lubinski J., Dasgupta A., Racaniello V. R. In vitro synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8424–8428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolakofsky D. Isolation and characterization of Sendai virus DI-RNAs. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90223-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurilla M. G., Keene J. D. The leader RNA of vesicular stomatitis virus is bound by a cellular protein reactive with anti-La lupus antibodies. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90541-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Weiss B. G., Tsiang M., Huang H., Schlesinger S. Deletion mapping of Sindbis virus DI RNAs derived from cDNAs defines the sequences essential for replication and packaging. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90492-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier E., Harmison G. G., Keene J. D., Schubert M. Sites of copy choice replication involved in generation of vesicular stomatitis virus defective-interfering particle RNAs. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):515–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.515-521.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meshi T., Ishikawa M., Motoyoshi F., Semba K., Okada Y. In vitro transcription of infectious RNAs from full-length cDNAs of tobacco mosaic virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5043–5047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani S., Colonno R. J. In vitro synthesis of an infectious RNA from cDNA clones of human rhinovirus type 14. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):628–632. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.628-632.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer S. A., Gatchell S. H. Intracellular events in the replication of defective interfering particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):168–179. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peluso R. W. Kinetic, quantitative, and functional analysis of multiple forms of the vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsid protein in infected cells. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2799–2807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2799-2807.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peluso R. W., Moyer S. A. Initiation and replication of vesicular stomatitis virus genome RNA in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peluso R. W., Moyer S. A. Viral proteins required for the in vitro replication of vesicular stomatitis virus defective interfering particle genome RNA. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):369–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90477-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrault J., Leavitt R. W. Characterization of snap-back RNAs in vesicular stomatitis defective interfering virus particles. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jan;38(1):21–34. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Levis R., Strauss J. H., Huang H. V. Production of infectious RNA transcripts from Sindbis virus cDNA clones: mapping of lethal mutations, rescue of a temperature-sensitive marker, and in vitro mutagenesis to generate defined mutants. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3809–3819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3809-3819.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy P., Repik P., Hefti E., Bishop D. H. Complementary RNA species isolated from vesicular stomatitis (HR strain) defective virions. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):915–925. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.915-925.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon A. E., Howell S. H. Synthesis in vitro of infectious RNA copies of the virulent satellite of turnip crinkle virus. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):146–152. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90445-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabler M., Sänger H. L. Infectivity studies on different potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTV) RNAs synthesized in vitro with the SP6 transcription system. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2191–2199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03914.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvader J. E., Forster A. C., Symons R. H. Infectivity and in vitro mutagenesis of monomeric cDNA clones of citrus exocortis viroid indicates the site of processing of viroid precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 26;13(16):5843–5856. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.16.5843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Moslih M. I., Dubes G. R. The kinetics of DEAE-dextran-induced cell sensitization to transfection. J Gen Virol. 1973 Feb;18(2):189–193. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-2-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





