Abstract
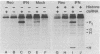
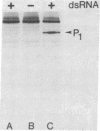
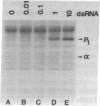
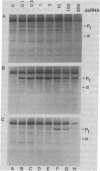
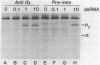
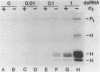
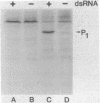
In this report we demonstrate that reovirus serotype 1-infected cells contain an inhibitor of the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-dependent protein kinase. We provide evidence that suggests that the virus-encoded sigma 3 protein is likely responsible for this kinase inhibitory activity. We could not detect activation of the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase in extracts prepared from either interferon-treated or untreated reovirus serotype 1-infected mouse L cells under conditions that led to activation of the kinase in extracts prepared from either interferon-treated or untreated, uninfected cells. Extracts from reovirus-infected cells blocked activation of kinase in extracts from interferon-treated cells when the two were mixed prior to assay. The kinase inhibitory activity in extracts of reovirus-infected cells could be overcome by adding approximately 100-fold excess of dsRNA over the amount required to activate kinase in extracts of uninfected cells. Kinase inhibitory activity in extracts of interferon-treated, virus-infected cells could be overcome with somewhat less dsRNA (approximately 10-fold excess). Most of the inhibitory activity in the extracts could be removed by adsorption with immobilized anti-reovirus sigma 3 serum or immobilized dsRNA, suggesting that the dsRNA-binding sigma 3 protein is necessary for kinase inhibitory activity. Purified sigma 3 protein, when added to reaction mixtures containing partially purified kinase, inhibited enzyme activation. Control of activation of this kinase, which can modify eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor 2, may be relevant to the sensitivity of reovirus replication to treatment of cells with interferon and to the shutoff of host protein synthesis in reovirus-infected cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Huismans H., Joklik W. K. Reovirus-coded polypeptides in infected cells: isolation of two native monomeric polypeptides with affinity for single-stranded and double-stranded RNA, respectively. Virology. 1976 Apr;70(2):411–424. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Joklik W. K. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. I. Patterns of gene expression by mutants of groups C, D, and E. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., DeCorato D., Safer B., Galabru J., Hovanessian A. G. Adenovirus VAI RNA complexes with the 68 000 Mr protein kinase to regulate its autophosphorylation and activity. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):689–697. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A., Zilberstein A., Schmidt A., Shulman L., Revel M. The interferon-induced protein kinase PK-i from mouse L cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9846–9853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajewski J., Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA antagonizes the antiviral action of interferon by preventing activation of the interferon-induced eIF-2 alpha kinase. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny A., Safer B. Purification of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2-eukaryotic initiation factor 2B complex and characterization of its guanine nucleotide exchange activity during protein synthesis initiation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3402–3408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebleu B., Sen G. C., Shaila S., Cabrer B., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3107–3111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Hayes E. C., Joklik W. K. Characterization of anti-reovirus immunoglobulins secreted by cloned hybridoma cell lines. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):134–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90533-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux R., Lemay G., Millward S. The viral protein sigma 3 participates in translation of late viral mRNA in reovirus-infected L cells. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2472–2479. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2472-2479.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Jacobs B. L., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Effect of double-stranded RNA and the 5'-O-monophosphate form of 2',5'-oligoadenylate on the inhibition of reovirus mRNA translation in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15232–15237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Interferon-mediated inhibition of reovirus mRNA translation in the absence of detectable mRNA degradation but in the presence of protein phosphorylation. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):461–475. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90313-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides. Multiplication rate but not yield of reovirus serotypes 1 and 3 correlates with the level of virus-mediated inhibition of cellular protein synthesis. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. W., Florini J. R. A rapid method for desalting small volumes of solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Sep;55(1):328–330. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paez E., Esteban M. Resistance of vaccinia virus to interferon is related to an interference phenomenon between the virus and the interferon system. Virology. 1984 Apr 15;134(1):12–28. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Duncan R., Hershey J. W., Kerr I. M. Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase and 2-5A system are both activated in interferon-treated, encephalomyocarditis virus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):894–898. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.894-898.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Kerr I. M. Interferon-mediated, double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase is inhibited in extracts from vaccinia virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):229–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.229-236.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Hovanessian A., Brown R. E., Clemens M. J., Kerr I. M. Interferon-mediated protein kinase and low-molecular-weight inhibitor of protein synthesis. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):477–480. doi: 10.1038/264477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E., Duncan R., Knutson G. S., Hershey J. W. Mechanism of interferon action. Increased phosphorylation of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 alpha in interferon-treated, reovirus-infected mouse L929 fibroblasts in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13451–13457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E., Knutson G. S., Berry M. J., Atwater J. A., Lasky S. R. Purification of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase from mouse fibroblasts. Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:499–516. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)19070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E., Knutson G. S., Berry M. J., Atwater J. A., Lasky S. R. Purification of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase from mouse fibroblasts. Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:499–516. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)19070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Procedures for measurement of phosphorylation of ribosome-associated proteins in interferon-treated cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):168–178. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Impact of virus infection on host cell protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:317–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Taira H., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Characteristics of a double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase system partially purified from interferon treated Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5915–5921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. Reovirus inhibition of cellular RNA and protein synthesis: role of the S4 gene. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker-Dowling P., Youngner J. S. Characterization of a specific kinase inhibitory factor produced by vaccinia virus which inhibits the interferon-induced protein kinase. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker-Dowling P., Youngner J. S. Vaccinia rescue of VSV from interferon-induced resistance: reversal of translation block and inhibition of protein kinase activity. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):128–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90539-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebe M. E., Joklik T. W. The mechanism of inhibition of reovirus replication by interferon. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90193-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Federman P., Shulman L., Revel M. Specific phosphorylation in vitro of a protein associated with ribosomes of interferon-treated mouse L cells. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80418-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]