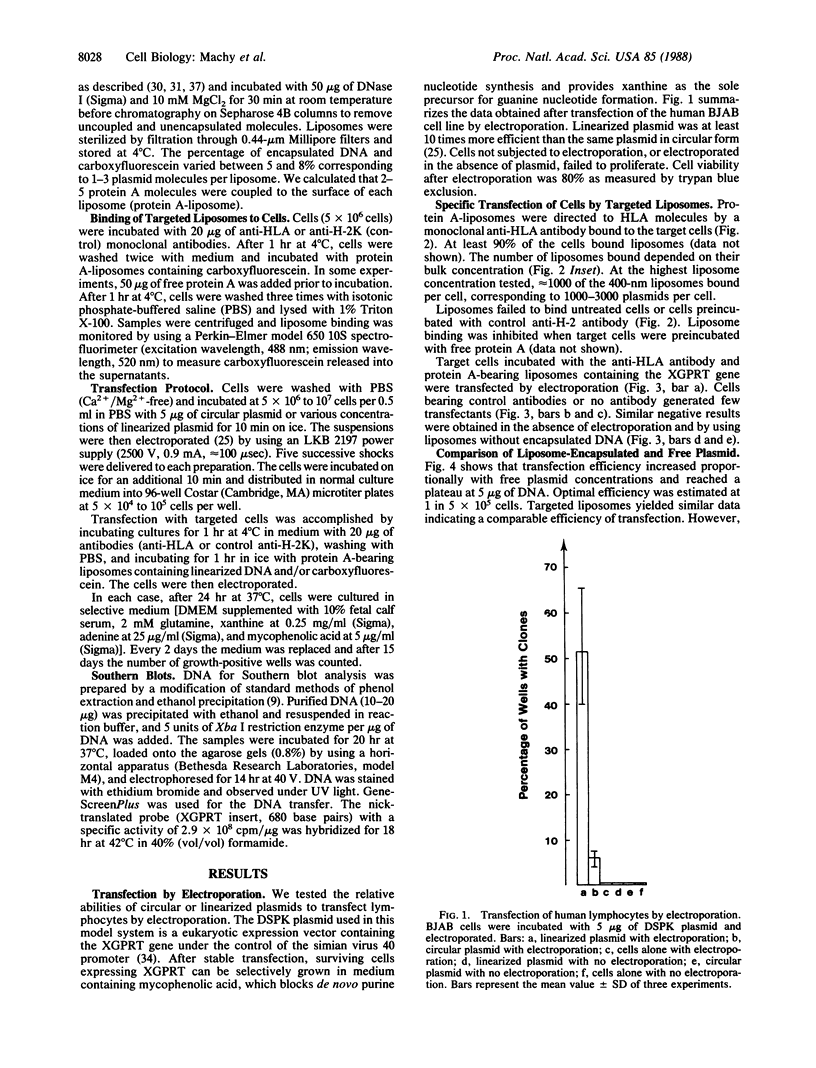
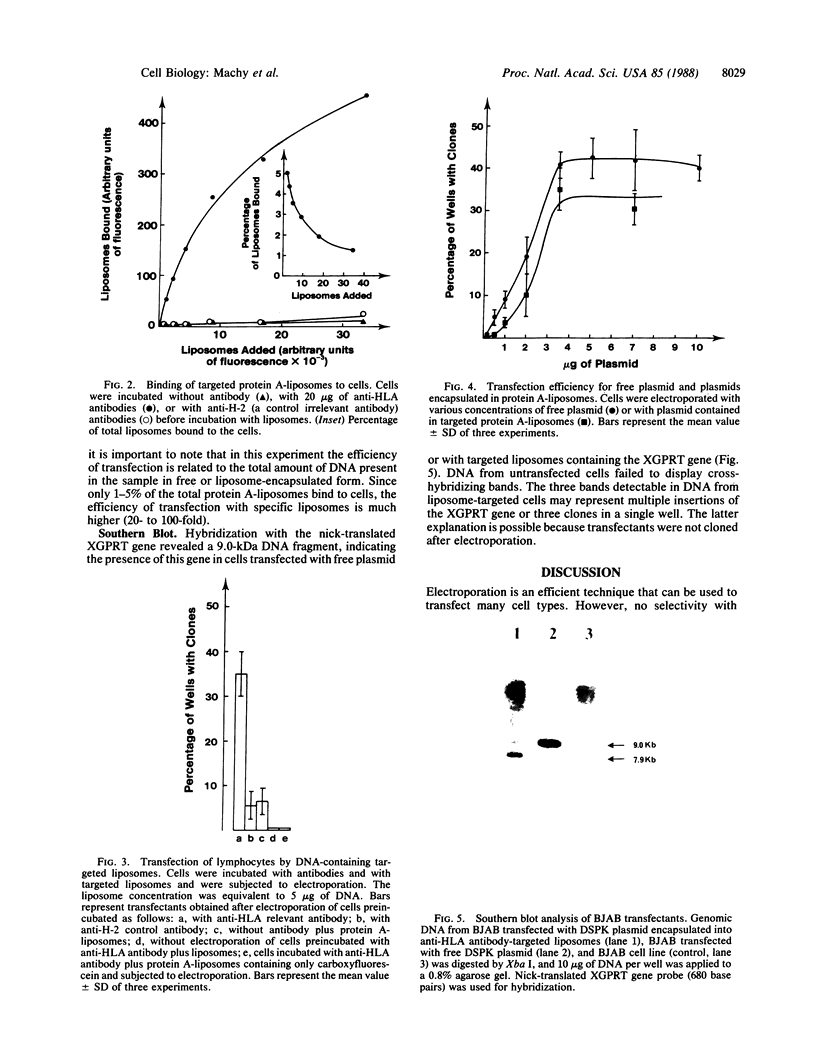
Abstract
Large unilamellar liposomes, coated with protein A and encapsulating the gene that confers resistance to mycophenolic acid, were used as a model system to demonstrate gene transfer into specific lymphoid cells. Protein A, which selectively recognizes mouse IgG2a antibodies, was coupled to liposomes to target them specifically to defined cell types coated with IgG2a antibody. Protein A-coated liposomes bound human B lymphoblastoid cells preincubated with a mouse IgG2a anti-HLA monoclonal antibody but failed to adhere to cells challenged with an irrelevant (anti-H-2) antibody of the same isotype or to cells incubated in the absence of antibody. Transfection of target cells bound to protein A-coated liposomes was achieved by electroporation. This step was essential since only electroporated cells survived in a selective medium containing mycophenolic acid. Transfection efficiency with electroporation and targeted liposomes was as efficient as conventional procedures that used unencapsulated plasmids free in solution but, in the latter case, cell selectivity is not possible. This technique provides a methodology for introducing defined biological macromolecules into specific cell types.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbet J., Machy P., Leserman L. D. Monoclonal antibody covalently coupled to liposomes: specific targeting to cells. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;16(3):243–258. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.1981.380160305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. High efficiency transformation by direct microinjection of DNA into cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):479–488. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90358-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Sharp P. A. SV40 DNA transfection of cells in suspension: analysis of efficiency of transcription and translation of T-antigen. Gene. 1981 Mar;13(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diacumakos E. G. Methods for micromanipulation of human somatic cells in culture. Methods Cell Biol. 1973;7:287–311. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61783-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber F. E., Melnick J. L., Butel J. S. Optimal conditions for uptake of exogenous DNA by Chinese hamster lung cells deficient in hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 16;390(3):298–311. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraley R., Subramani S., Berg P., Papahadjopoulos D. Introduction of liposome-encapsulated SV40 DNA into cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10431–10435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furusawa M., Yamaizumi M., Nishimura T., Uchida T., Okada Y. Use of erythrocyte ghosts for injection of substances into animal cells by cell fusion. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;14:73–80. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60469-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey W., Doe B., Wofsy L. Immunospecific vesicle targeting facilitates microinjection into lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2267–2271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Use of staphylococcal protein A as an immunological reagent. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:241–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Leder P. Splicing and the formation of stable RNA. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1299–1302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanspal M., Ralston G. B. Purification of a trypsin-insensitive fragment of spectrin from human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 28;669(2):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath T. D., Lopez N. G., Papahadjopoulos D. The effects of liposome size and surface charge on liposome-mediated delivery of methotrexate-gamma-aspartate to cells in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 24;820(1):74–84. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonak Z. L., Braman V., Kennett R. H. Production of continuous mouse plasma cell lines by transfection with human leukemia DNA. Hybridoma. 1984 Summer;3(2):107–118. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1984.3.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke H., Hämmerling G. J., Hämmerling U. Fine specificity analysis with monoclonal antibodies of antigens controlled by the major histocompatibility complex and by the Qa/TL region in mice. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:175–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leserman L. D., Barbet J., Kourilsky F., Weinstein J. N. Targeting to cells of fluorescent liposomes covalently coupled with monoclonal antibody or protein A. Nature. 1980 Dec 11;288(5791):602–604. doi: 10.1038/288602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis W. H., Srinivasan P. R., Stokoe N., Siminovitch L. Parameters governing the transfer of the genes for thymidine kinase and dihydrofolate reductase into mouse cells using metaphase chromosomes or DNA. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 May;6(3):333–347. doi: 10.1007/BF01542787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo M. M., Tsong T. Y., Conrad M. K., Strittmatter S. M., Hester L. D., Snyder S. H. Monoclonal antibody production by receptor-mediated electrically induced cell fusion. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):792–794. doi: 10.1038/310792a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyter A., Scangos G. A., Ruddle F. H. Mechanisms of DNA uptake by mammalian cells: fate of exogenously added DNA monitored by the use of fluorescent dyes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):422–426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyter A., Scangos G., Juricek D., Keene D., Ruddle F. H. Mechanisms of DNA entry into mammalian cells. II. Phagocytosis of calcium phosphate DNA co-precipitate visualized by electron microscopy. Exp Cell Res. 1982 May;139(1):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90336-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyter A., Tomasi M., Gitman A. G., Etinger L., Nussbaum O. The use of specific antibodies to mediate fusion between Sendai virus envelopes and living cells. Ciba Found Symp. 1984;103:163–180. doi: 10.1002/9780470720844.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machy P., Barbet J., Leserman L. D. Differential endocytosis of T and B lymphocyte surface molecules evaluated with antibody-bearing fluorescent liposomes containing methotrexate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4148–4152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machy P., Leserman L. D. Small liposomes are better than large liposomes for specific drug delivery in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 5;730(2):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90348-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machy P., Pierres M., Barbet J., Leserman L. D. Drug transfer into lymphoblasts mediated by liposomes bound to distinct sites on H-2 encoded I-A, I-E, and K molecules. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2098–2102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machy P., Truneh A., Gennaro D., Hoffstein S. Endocytosis and de novo expression of major histocompatibility complex encoded class I molecules: kinetic and ultrastructural studies. Eur J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;45(1):126–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthay K. K., Heath T. D., Papahadjopoulos D. Specific enhancement of drug delivery to AKR lymphoma by antibody-targeted small unilamellar vesicles. Cancer Res. 1984 May;44(5):1880–1886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Howard B. H., Berg P. Synthesis of rabbit beta-globin in cultured monkey kidney cells following infection with a SV40 beta-globin recombinant genome. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):108–114. doi: 10.1038/277108a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsuji T., Inoko H., Ando A., Sato T., Koide Y., Tadakuma T., Yoshida T. O., Tsuji K. The role of transfected HLA-DQ genes in the mixed lymphocyte reaction-like condition. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00768826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann E., Schaefer-Ridder M., Wang Y., Hofschneider P. H. Gene transfer into mouse lyoma cells by electroporation in high electric fields. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):841–845. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolau C., Le Pape A., Soriano P., Fargette F., Juhel M. F. In vivo expression of rat insulin after intravenous administration of the liposome-entrapped gene for rat insulin I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1068–1072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada C. Y., Rechsteiner M. Introduction of macromolecules into cultured mammalian cells by osmotic lysis of pinocytic vesicles. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson F., Hunt C. A., Szoka F. C., Vail W. J., Papahadjopoulos D. Preparation of liposomes of defined size distribution by extrusion through polycarbonate membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):9–23. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90085-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano J. S. Biologic activity of isolated viral nucleic acids. Prog Med Virol. 1970;12:1–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfarr D. S., Sathe G., Reff M. E. A highly modular cloning vector for the analysis of eukaryotic genes and gene regulatory elements. DNA. 1985 Dec;4(6):461–467. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Papahadjopoulos D., Vail W. J. Lipid vesicles as carriers for introducing biologically active materials into cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;14:33–71. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H., Weir L., Leder P. Enhancer-dependent expression of human kappa immunoglobulin genes introduced into mouse pre-B lymphocytes by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7161–7165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebaï N., Malissen B. Structural and genetic analyses of HLA class I molecules using monoclonal xenoantibodies. Tissue Antigens. 1983 Aug;22(2):107–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1983.tb01176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Goldin A. L., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. High-frequency transfer of cloned herpes simplex virus type 1 sequences to mammalian cells by protoplast fusion. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;1(8):743–752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.8.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer-Ridder M., Wang Y., Hofschneider P. H. Liposomes as gene carriers: efficient transformation of mouse L cells by thymidine kinase gene. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):166–168. doi: 10.1126/science.7053567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Dijkstra J., Legrand A., Spanjer H., Londos-Gagliardi D., Roerdink F., Scherphof G., Nicolau C. Targeted and nontargeted liposomes for in vivo transfer to rat liver cells of a plasmid containing the preproinsulin I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7128–7131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus S. E., Raskas H. J. Transfection of KB cells by polyethylene glycol-induced fusion with erythrocyte ghosts containing adenovirus type 2 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1980 May;48(1):241–245. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-48-1-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F., Jr, Papahadjopoulos D. Procedure for preparation of liposomes with large internal aqueous space and high capture by reverse-phase evaporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4194–4198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao W., Wilkinson J., Stanbridge E. J., Berns M. W. Direct gene transfer into human cultured cells facilitated by laser micropuncture of the cell membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4180–4184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teissie J., Knutson V. P., Tsong T. Y., Lane M. D. Electric pulse-induced fusion of 3T3 cells in monolayer culture. Science. 1982 Apr 30;216(4545):537–538. doi: 10.1126/science.7071601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teissie J., Tsong T. Y. Electric field induced transient pores in phospholipid bilayer vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 17;20(6):1548–1554. doi: 10.1021/bi00509a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Huang L. Plasmid DNA adsorbed to pH-sensitive liposomes efficiently transforms the target cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 30;147(3):980–985. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80166-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Huang L. pH-sensitive immunoliposomes mediate target-cell-specific delivery and controlled expression of a foreign gene in mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7851–7855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. K., Nicolau C., Hofschneider P. H. Appearance of beta-lactamase activity in animal cells upon liposome-mediated gene transfer. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann U. Electric field-mediated fusion and related electrical phenomena. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 30;694(3):227–277. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]