Abstract
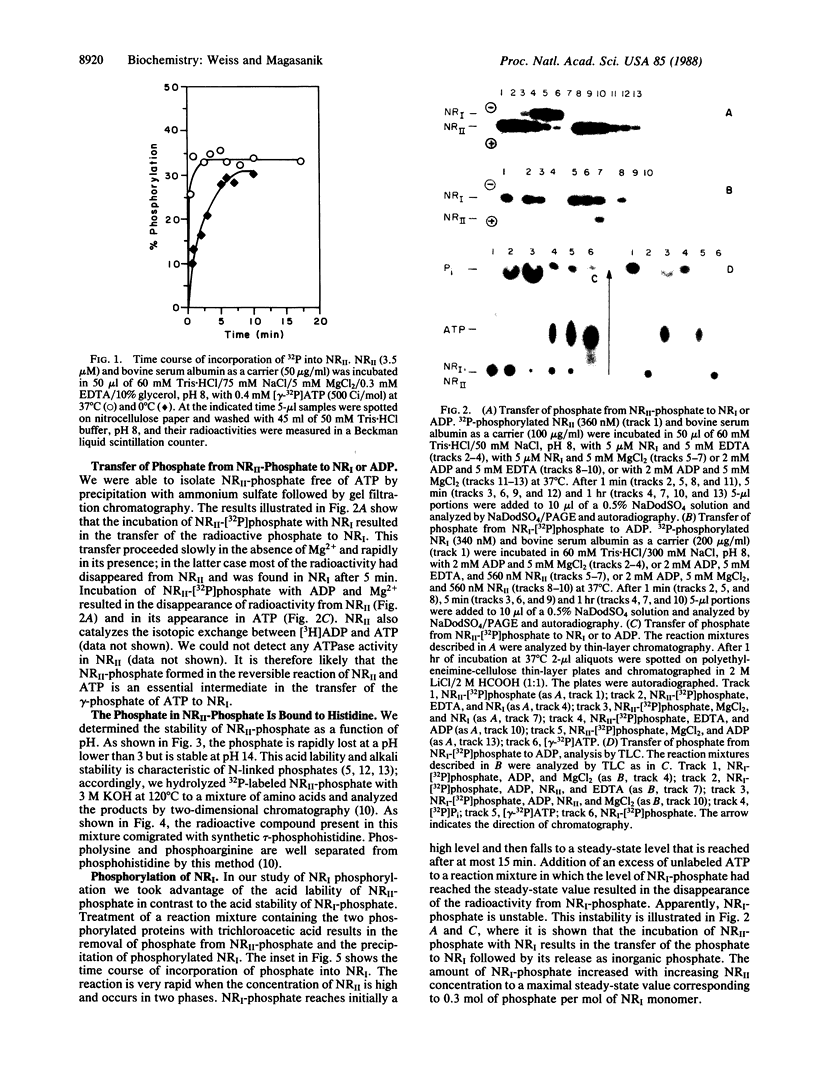
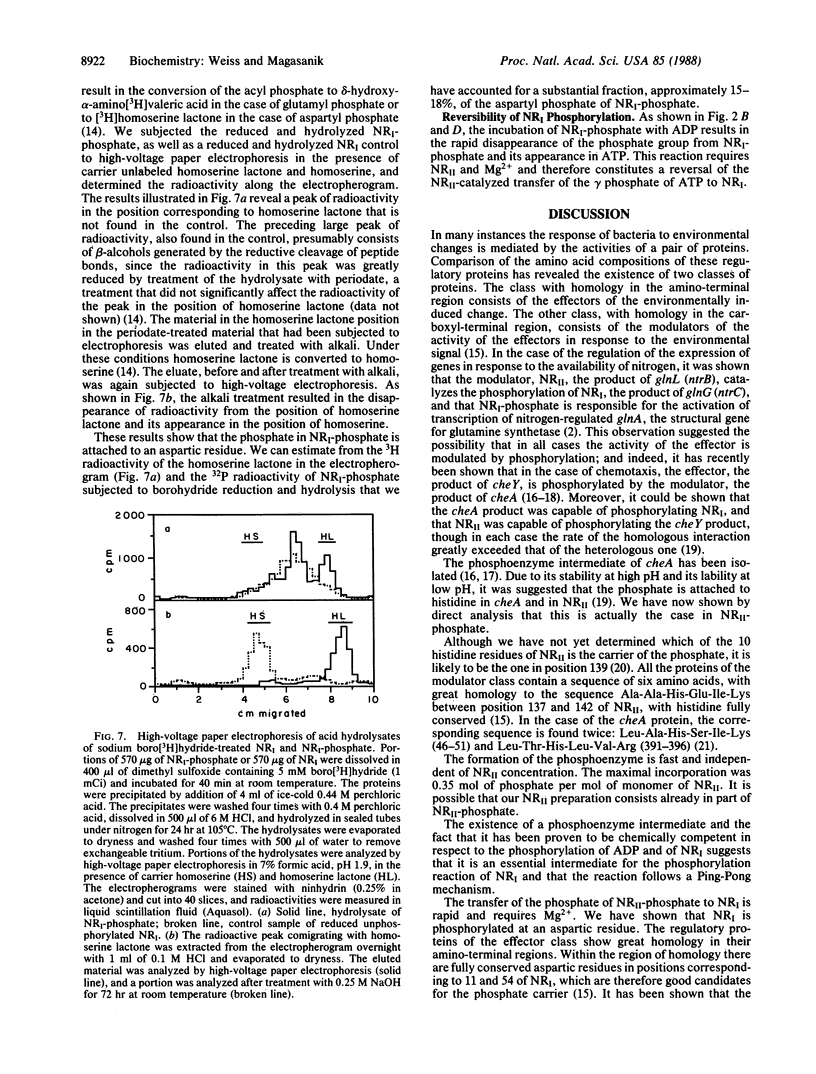
It has previously been shown that phosphorylated nitrogen regulator I (NRI-phosphate) is the activator responsible for increasing the transcription of glnA, the structural gene for glutamine synthetase, and that NRII catalyzes the transfer of the gamma-phosphate of ATP to NRI. We have now shown that the reaction of ATP with NRII results in the reversible transfer of the gamma-phosphate of ATP to a histidine residue of NRII. In turn, NRII-phosphate transfers its phosphate reversibly to an aspartic residue of NRI. NRI-phosphate is hydrolyzed to NRI and inorganic phosphate in a divalent cation-requiring autocatalytic reaction.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bueno R., Pahel G., Magasanik B. Role of glnB and glnD gene products in regulation of the glnALG operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):816–822. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.816-822.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degani C., Boyer P. D. A borohydride reduction method for characterization of the acyl phosphate linkage in proteins and its application to sarcoplasmic reticulum adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 10;248(23):8222–8226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujitaki J. M., Smith R. A. Techniques in the detection and characterization of phosphoramidate-containing proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:23–36. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Oosawa K., Kaplan N., Simon M. I. Phosphorylation of three proteins in the signaling pathway of bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90489-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Oosawa K., Matsumura P., Simon M. I. Protein phosphorylation is involved in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7609–7613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultquist D. E., Moyer R. W., Boyer P. D. The preparation and characterization of 1-phosphohistidine and 3-phosphohistidine. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):322–331. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultquist D. E. The preparation and characterization of phosphorylated derivatives of histidine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 12;153(2):329–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. P., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA by purified Escherichia coli components: core RNA polymerase and the products of glnF, glnG, and glnL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8453–8457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keener J., Kustu S. Protein kinase and phosphoprotein phosphatase activities of nitrogen regulatory proteins NTRB and NTRC of enteric bacteria: roles of the conserved amino-terminal domain of NTRC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):4976–4980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.4976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martensen T. M. Chemical properties, isolation, and analysis of O-phosphates in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:3–23. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda-Ríos J., Sánchez-Pescador R., Urdea M., Covarrubias A. A. The complete nucleotide sequence of the glnALG operon of Escherichia coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2757–2770. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Magasanik B. Covalent modification of the glnG product, NRI, by the glnL product, NRII, regulates the transcription of the glnALG operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5909–5913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Ninfa E. G., Lupas A. N., Stock A., Magasanik B., Stock J. Crosstalk between bacterial chemotaxis signal transduction proteins and regulators of transcription of the Ntr regulon: evidence that nitrogen assimilation and chemotaxis are controlled by a common phosphotransfer mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5492–5496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Ueno-Nishio S., Hunt T. P., Robustell B., Magasanik B. Purification of nitrogen regulator II, the product of the glnL (ntrB) gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):1002–1004. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.1002-1004.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishigaki I., Chen F. T., Hokin L. E. Studies on the characterization of the sodium-potassium transport adenosine triphosphatase. XV. Direct chemical characterization of the acyl phosphate in the enzyme as an aspartyl beta-phosphate residue. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4911–4916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon B. T., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Two-component regulatory systems responsive to environmental stimuli share strongly conserved domains with the nitrogen assimilation regulatory genes ntrB and ntrC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7850–7854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post R. L., Kume S. Evidence for an aspartyl phosphate residue at the active site of sodium and potassium ion transport adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):6993–7000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Isolation of the nitrogen assimilation regulator NR(I), the product of the glnG gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5554–5558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Halpern R. M., Bruegger B. B., Dunlap A. K., Fricke O. Chromosomal protein phosphorylation on basic amino acids. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;19:153–159. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock A., Chen T., Welsh D., Stock J. CheA protein, a central regulator of bacterial chemotaxis, belongs to a family of proteins that control gene expression in response to changing environmental conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1403–1407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wylie D., Stock A., Wong C. Y., Stock J. Sensory transduction in bacterial chemotaxis involves phosphotransfer between Che proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 15;151(2):891–896. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80365-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]