Abstract
In vivo "footprints" of the glnA regulatory region under activating conditions demonstrate that the three most upstream activator sequences bind the protein NRI in the cell. Together, protections at these sites span six of seven consecutive major grooves and lie on the same helix face. E sigma 54 protects two major grooves of DNA approximately 60 base pairs downstream at the glnAp2 promoter and primarily on the opposite helix face. Experiments using potassium permanganate to probe open complex formation in vivo demonstrate that NRI is absolutely required for E sigma 54 to open the promoter DNA. Together, the dimethyl sulfate and permanganate studies verify [Reitzer, L. J., Bueno, R., Cheng, W. D., Abrams, S. A., Rothstein, D. M., Hunt, T. P., Tyler, B. & Magasanik, B. (1987) J. Bacteriol. 169, 4279-4284] that E sigma 54 occupies the glnAp2 promoter in a closed complex in vivo even in the presence of excess nitrogen and the absence of NRI. Furthermore, the slow step in transcriptional activation is shown to be an NRI-dependent conformational change in the downstream promoter DNA, which results in DNA melting. These observations place interesting restrictions on models describing the mechanism by which NRI activates transcription from glnAp2 at a distance.
Full text
PDF
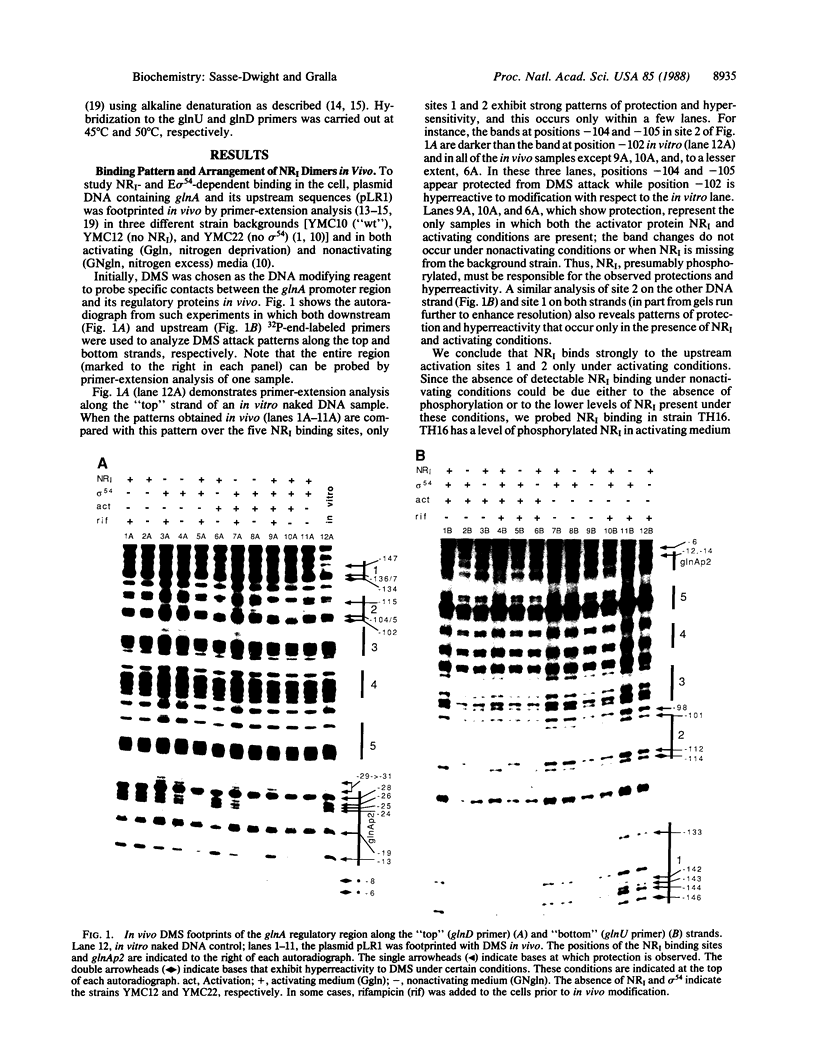



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ausubel F. M. Regulation of nitrogen fixation genes. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90294-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Gralla J. D. High-resolution analysis of lac transcription complexes inside cells. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5051–5057. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Zhang L., Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. DNA supercoiling promotes formation of a bent repression loop in lac DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90513-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias A. A., Bastarrachea F. Nucleotide sequence of the glnA control region of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(1):171–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00330342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. M., Hahn S., Ogden S., Schleif R. F. An operator at -280 base pairs that is required for repression of araBAD operon promoter: addition of DNA helical turns between the operator and promoter cyclically hinders repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5017–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralla J. D. Rapid "footprinting" on supercoiled DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3078–3081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hendrickson W., Schleif R. Transcription of Escherichia coli ara in vitro. The cyclic AMP receptor protein requirement for PBAD induction that depends on the presence and orientation of the araO2 site. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):355–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman J., Wong P. K., Sei K., Keener J., Kustu S. Products of nitrogen regulatory genes ntrA and ntrC of enteric bacteria activate glnA transcription in vitro: evidence that the ntrA product is a sigma factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7525–7529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Cooperative binding of lambda repressors to sites separated by integral turns of the DNA helix. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90833-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. P., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA by purified Escherichia coli components: core RNA polymerase and the products of glnF, glnG, and glnL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8453–8457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer H., Niemöller M., Amouyal M., Revet B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. lac repressor forms loops with linear DNA carrying two suitably spaced lac operators. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1481–1491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magasanik B. Genetic control of nitrogen assimilation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:135–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Magasanik B. Covalent modification of the glnG product, NRI, by the glnL product, NRII, regulates the transcription of the glnALG operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5909–5913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Initiation of transcription at the bacterial glnAp2 promoter by purified E. coli components is facilitated by enhancers. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1039–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T., Sturtevant J. M., Ptashne M. The lambda repressor contains two domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1608–1612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Bueno R., Cheng W. D., Abrams S. A., Rothstein D. M., Hunt T. P., Tyler B., Magasanik B. Mutations that create new promoters suppress the sigma 54 dependence of glnA transcription in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4279–4284. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4279-4284.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Expression of glnA in Escherichia coli is regulated at tandem promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1979–1983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Isolation of the nitrogen assimilation regulator NR(I), the product of the glnG gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5554–5558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA in E. coli is stimulated by activator bound to sites far from the promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. Probing co-operative DNA-binding in vivo. The lac O1:O3 interaction. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 5;202(1):107–119. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90523-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Halpern Y. S., Magasanik B. Genetic and metabolic control of enzymes responsible for histidine degradation in Salmonella typhimurium. 4-imidazolone-5-propionate amidohydrolase and N-formimino-L-glutamate formiminohydrolase. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3320–3329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]