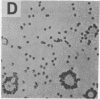
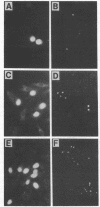
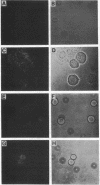
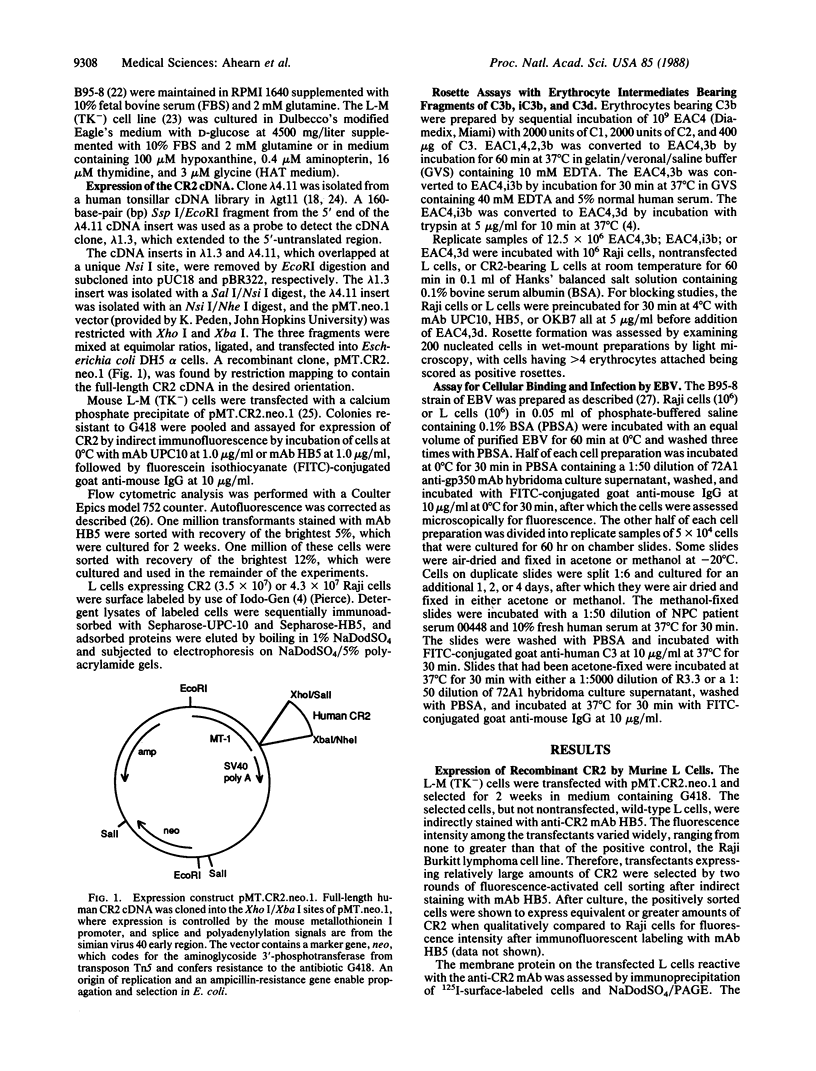
Abstract
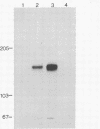
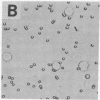
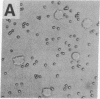
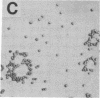
The normal host range of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is limited to primate B lymphocytes and certain epithelial cells that express the C3d/EBV receptor [complement receptor 2 (CR2, CD21)]. In the present study, expansion of the tissue tropism of EBV has been accomplished by stably transfecting the murine fibroblast L cell line with pMT.CR2. neo.1, a eukaryotic expression vector promoting the transcription of a complementary DNA insert encoding human CR2. High CR2-expressing transfected L cells were selected by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. The recombinant CR2 was shown to have the same molecular weight as wild-type CR2 from Raji cells and to mediate the binding by the transfectants of particles bearing the iC3b and C3d fragments of the third component of complement. All CR2-expressing L cells, but not nontransfected controls, also bound EBV, as assessed by indirect immunofluorescence. After a 60-hr culture, approximately 0.5% of the CR2-expressing cells preincubated with EBV demonstrated immunofluorescent staining of EBV nuclear antigen with serum from a patient with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. No fluorescent staining of cells was seen with monoclonal antibodies to the early antigen complex or to gp350/220, indicating that the infection was predominantly latent. Infected cells cultured for up to 4 weeks remained EBV nuclear antigen-positive. The capacity of recombinant human CR2 to confer on murine L cells susceptibility to stable latent infection by EBV indicates that this receptor is a primary determinant of the tissue tropism of EBV and may facilitate studies of cell-specific factors that regulate the viral growth cycle.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti S., Parks D. R., Herzenberg L. A. A single laser method for subtraction of cell autofluorescence in flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1987 Mar;8(2):114–119. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990080203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calender A., Billaud M., Aubry J. P., Banchereau J., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induces expression of B-cell activation markers on in vitro infection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Alicot E. M., Katzman P. J., Klickstein L. B., Smith J. A., Fearon D. T. Organization of the genes encoding complement receptors type 1 and 2, decay-accelerating factor, and C4-binding protein in the RCA locus on human chromosome 1. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1271–1280. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho M. S., Milman G., Hayward S. D. A second Epstein-Barr virus early antigen gene in BamHI fragment M encodes a 48- to 50-kilodalton nuclear protein. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):860–866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.860-866.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. H., Fischer E., Kazatchkine M. D., Lenoir G. M., Lefevre-Delvincourt C., Revillard J. P. Expression of CR1 and CR2 complement receptors following Epstein-Barr virus infection of Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Jun;25(6):587–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb01085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolyniuk M., Pritchett R., Kieff E. Proteins of Epstein-Barr virus. I. Analysis of the polypeptides of purified enveloped Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):935–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.935-949.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Identification of the membrane glycoprotein that is the C3b receptor of the human erythrocyte, polymorphonuclear leukocyte, B lymphocyte, and monocyte. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):20–30. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingeroth J. D., Weis J. J., Tedder T. F., Strominger J. L., Biro P. A., Fearon D. T. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4510–4514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan J. S., Greenspan D., Lennette E. T., Abrams D. I., Conant M. A., Petersen V., Freese U. K. Replication of Epstein-Barr virus within the epithelial cells of oral "hairy" leukoplakia, an AIDS-associated lesion. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 19;313(25):1564–1571. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512193132502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Walling M. Regulation in vivo of a cloned mammalian gene: cadmium induces the transcription of a mouse metallothionein gene in SV40 vectors. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):273–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman G. J., Lazarowitz S. G., Hayward S. D. Monoclonal antibody against a 250,000-dalton glycoprotein of Epstein-Barr virus identifies a membrane antigen and a neutralizing antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2979–2983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida K., Nadler L., Nussenzweig V. Identification of the membrane receptor for the complement fragment C3d by means of a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1021–1033. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Klein G., Oldstone M. B., Bokish V., Yefenof E. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. VIII. Association between complement and Epstein-Barr virus receptors on human lymphoid cells. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(4):401–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. F., Shurin S., Abramowsky C., Tubbs R. R., Sciotto C. G., Wahl R., Sands J., Gottman D., Katz B. Z., Sklar J. T-cell lymphomas containing Epstein-Barr viral DNA in patients with chronic Epstein-Barr virus infections. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 24;318(12):733–741. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803243181203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R., PIEKARSKI L. J., HSU T. C. DELETION OF THYMIDINE KINASE ACTIVITY FROM L CELLS RESISTANT TO BROMODEOXYURIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Aug;31:297–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. D., Cooper N. R., Tack B. F., Nemerow G. R. Molecular cloning of the cDNA encoding the Epstein-Barr virus/C3d receptor (complement receptor type 2) of human B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9194–9198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., Mold C., Schwend V. K., Tollefson V., Cooper N. R. Identification of gp350 as the viral glycoprotein mediating attachment of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) to the EBV/C3d receptor of B cells: sequence homology of gp350 and C3 complement fragment C3d. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1416–1420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1416-1420.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., Wolfert R., McNaughton M. E., Cooper N. R. Identification and characterization of the Epstein-Barr virus receptor on human B lymphocytes and its relationship to the C3d complement receptor (CR2). J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):347–351. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.347-351.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., Vroman B., Chase B., Sculley T., Hummel M., Kieff E. Identification of polypeptide components of the Epstein-Barr virus early antigen complex with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):193–201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.193-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey-Campos J., Rubinstein P., Rodriguez de Cordoba S. A physical map of the human regulator of complement activation gene cluster linking the complement genes CR1, CR2, DAF, and C4BP. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):664–669. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynes M., Aubert J. P., Cohen J. H., Audouin J., Tricottet V., Diebold J., Kazatchkine M. D. Human follicular dendritic cells express CR1, CR2, and CR3 complement receptor antigens. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2687–2694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro I. M., Volsky D. J. Infection of normal human epithelial cells by Epstein-Barr virus. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1225–1228. doi: 10.1126/science.6298935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Davis D. S., Young L. S., Hutt-Fletcher L., Tedder T. F., Rickinson A. B. Human epithelial cell expression of an Epstein-Barr virus receptor. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):805–811. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Nedrud J. G., Raab-Traub N., Hanes R. A., Pagano J. S. Epstein-Barr virus replication in oropharyngeal epithelial cells. N Engl J Med. 1984 May 10;310(19):1225–1230. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405103101905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Vesterinen E. H., Nedrud J. G., Raab-Traub N., Walton L. A., Pagano J. S. Replication of Epstein-Barr virus in human epithelial cells infected in vitro. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):480–483. doi: 10.1038/306480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J., Weis J., Fearon D., Whang Y., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus gp350/220 binding to the B lymphocyte C3d receptor mediates adsorption, capping, and endocytosis. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):203–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Weis J. J., Clement L. T., Fearon D. T., Cooper M. D. The role of receptors for complement in the induction of polyclonal B-cell proliferation and differentiation. J Clin Immunol. 1986 Jan;6(1):65–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00915366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volsky D. J., Shapiro I. M., Klein G. Transfer of Epstein-Barr virus receptors to receptor-negative cells permits virus penetration and antigen expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5453–5457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. J., Fearon D. T., Klickstein L. B., Wong W. W., Richards S. A., de Bruyn Kops A., Smith J. A., Weis J. H. Identification of a partial cDNA clone for the C3d/Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes: homology with the receptor for fragments C3b and C4b of the third and fourth components of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5639–5643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. J., Fearon D. T. The identification of N-linked oligosaccharides on the human CR2/Epstein-Barr virus receptor and their function in receptor metabolism, plasma membrane expression, and ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13824–13830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. J., Tedder T. F., Fearon D. T. Identification of a 145,000 Mr membrane protein as the C3d receptor (CR2) of human B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):881–885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. J., Toothaker L. E., Smith J. A., Weis J. H., Fearon D. T. Structure of the human B lymphocyte receptor for C3d and the Epstein-Barr virus and relatedness to other members of the family of C3/C4 binding proteins. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1047–1066. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]