Abstract
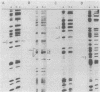
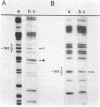
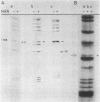
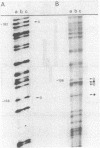
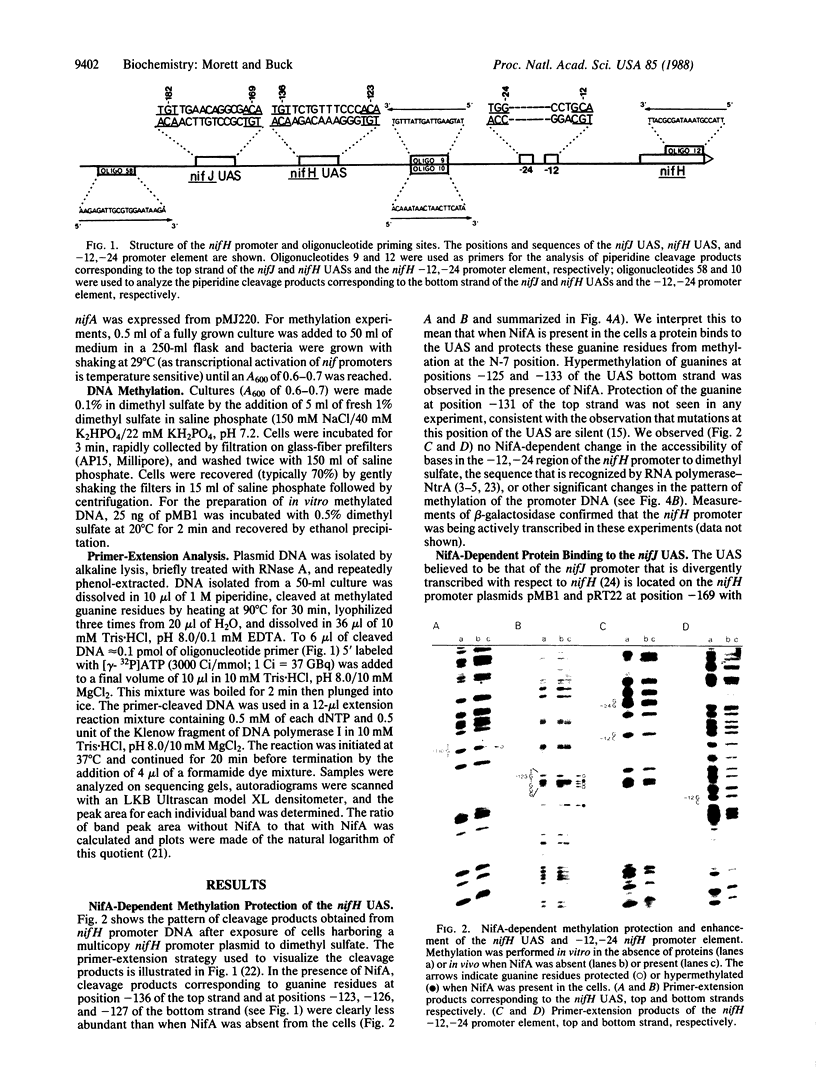
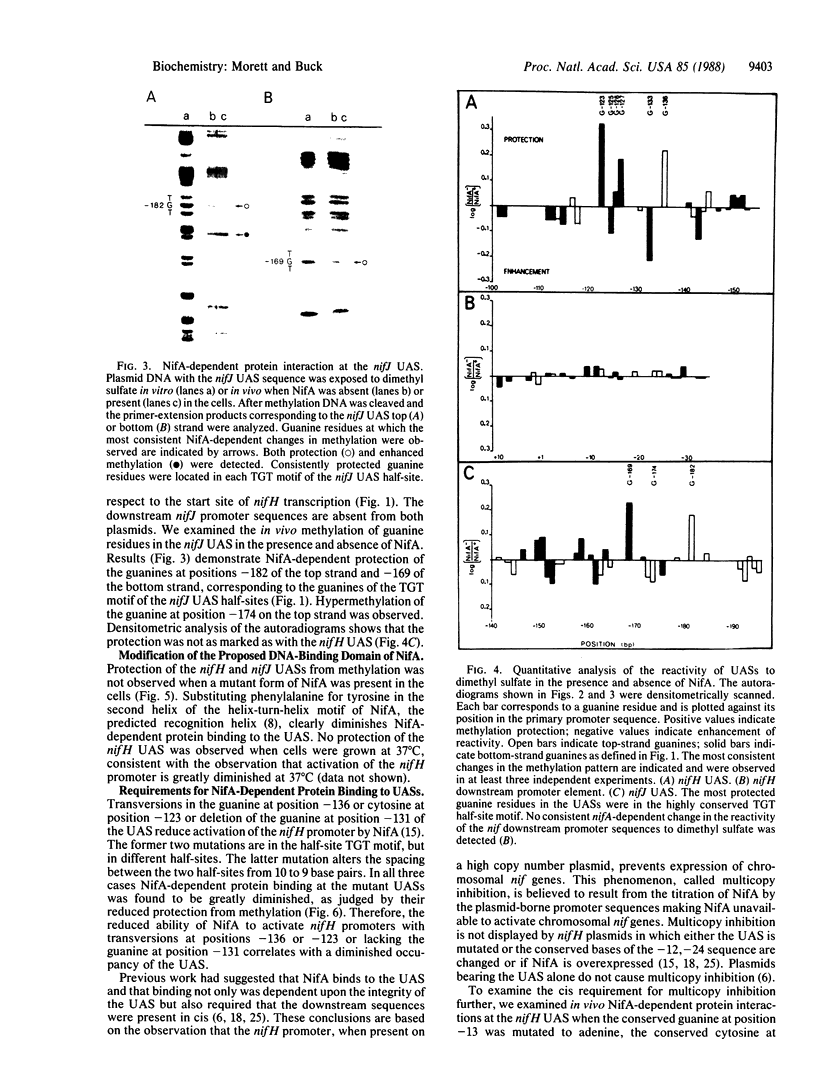
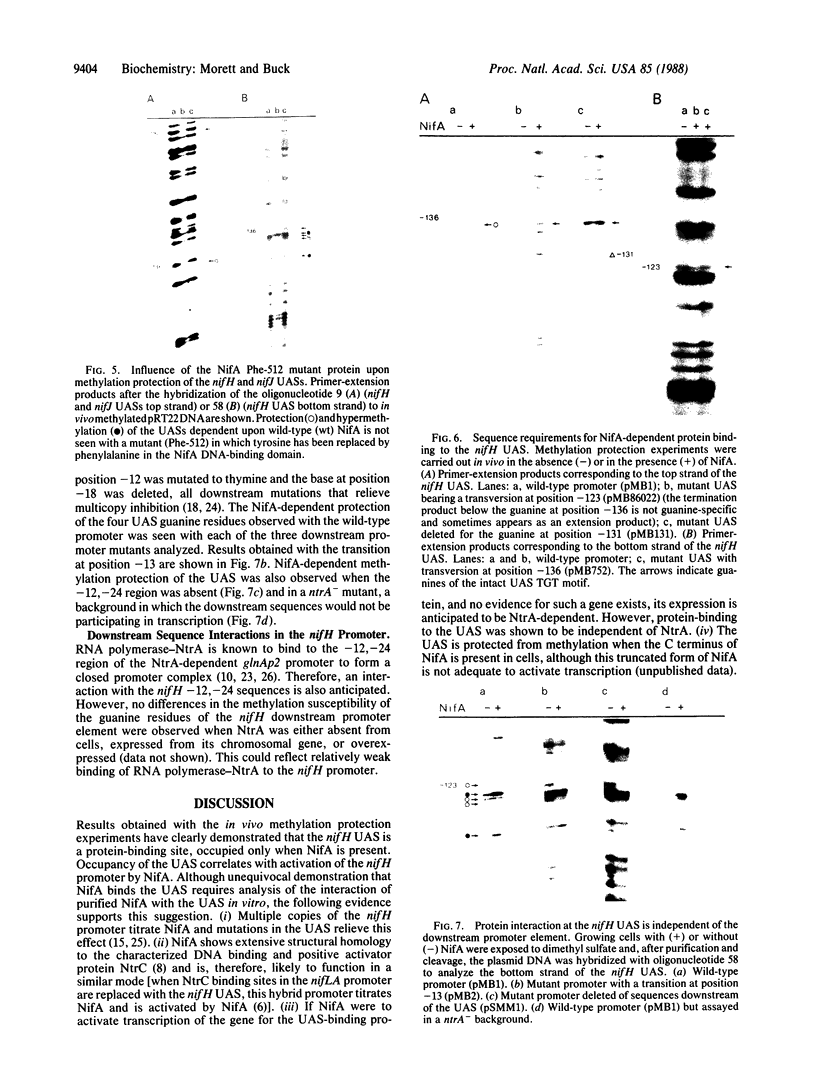
Primer-extension analysis of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifH promoter was used to determine changes in the accessibility of the promoter DNA to methylation after exposure of growing cells to dimethyl sulfate. Four guanine residues present in the nifH upstream activator sequence (UAS), the proposed NifA binding site, were protected from methylation and two guanine residues were hypermethylated when the transcriptional activator protein NifA was present in the cells. The interaction detected at the nifH UAS was independent of the alternative sigma factor NtrA required for transcription of the nifH and other nif promoters. Mutations within the nifH UAS that diminish NifA-dependent transcriptional activation reduced the interaction at the UAS. It seems likely that the pattern of methylation protection observed in the nifH UAS is the result of NifA binding.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin S., Henderson N., Dixon R. Requirements for transcriptional activation in vitro of the nitrogen-regulated glnA and nifLA promoters from Klebsiella pneumoniae: dependence on activator concentration. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Jul;1(1):92–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett L. T., Cannon F., Dean D. R. Nucleotide sequence and mutagenesis of the nifA gene from Azotobacter vinelandii. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):315–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkmann A., Sawers R. G., Böck A. Involvement of the ntrA gene product in the anaerobic metabolism of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(3):535–542. doi: 10.1007/BF00327209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Gralla J. D. High-resolution analysis of lac transcription complexes inside cells. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5051–5057. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Mutations affecting regulation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifH (nitrogenase reductase) promotor. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):143–147. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.143-147.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Cannon W., Woodcock J. Mutational analysis of upstream sequences required for transcriptional activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifH promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9945–9956. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Cannon W., Woodcock J. Transcriptional activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase promoter may involve DNA loop formation. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Sep;1(2):243–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M. Deletion analysis of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase promoter: importance of spacing between conserved sequences around positions -12 and -24 for activation by the nifA and ntrC (glnG) products. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):545–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.545-551.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Khan H., Dixon R. Site-directed mutagenesis of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifL and nifH promoters and in vivo analysis of promoter activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7621–7638. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buikema W. J., Szeto W. W., Lemley P. V., Orme-Johnson W. H., Ausubel F. M. Nitrogen fixation specific regulatory genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Rhizobium meliloti share homology with the general nitrogen regulatory gene ntrC of K. pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4539–4555. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras A., Drummond M. The effect on the function of the transcriptional activator NtrC from Klebsiella pneumoniae of mutations in the DNA-recognition helix. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4025–4039. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Whitty P., Wootton J. Sequence and domain relationships of ntrC and nifA from Klebsiella pneumoniae: homologies to other regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):441–447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro-Luzzi Ames G., Nikaido K. Nitrogen regulation in Salmonella typhimurium. Identification of an ntrC protein-binding site and definition of a consensus binding sequence. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):539–547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03662.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H. M., Bruderer T., Hennecke H. Essential and non-essential domains in the Bradyrhizobium japonicum NifA protein: identification of indispensable cysteine residues potentially involved in redox reactivity and/or metal binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2207–2224. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn B. Overproduction of phage lambda repressor under control of the lac promotor of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Nov 17;148(3):243–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00332898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönger P., Manian S. S., Reiländer H., O'Connell M., Priefer U. B., Pühler A. Organization and partial sequence of a DNA region of the Rhizobium leguminosarum symbiotic plasmid pRL6JI containing the genes fixABC, nifA, nifB and a novel open reading frame. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):31–49. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Regulation of nitrogen fixation genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:567–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes T., Merrick M., Dixon R. Interaction of purified NtrC protein with nitrogen regulated promoters from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(3):492–498. doi: 10.1007/BF00331345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman J., Wong P. K., Sei K., Keener J., Kustu S. Products of nitrogen regulatory genes ntrA and ntrC of enteric bacteria activate glnA transcription in vitro: evidence that the ntrA product is a sigma factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7525–7529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. P., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA by purified Escherichia coli components: core RNA polymerase and the products of glnF, glnG, and glnL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8453–8457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsrud L. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and a lac operon promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5314–5318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNeil T., Roberts G. P., MacNeil D., Tyler B. The products of glnL and glnG are bifunctional regulatory proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(2):325–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00332696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchin S. D., Austin S., Dixon R. A. The role of activator binding sites in transcriptional control of the divergently transcribed nifF and nifLA promoters from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jul;2(4):433–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Initiation of transcription at the bacterial glnAp2 promoter by purified E. coli components is facilitated by enhancers. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1039–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., Gilbert W. DNA-binding site of lac repressor probed by dimethylsulfate methylation of lac operator. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 25;132(4):709–728. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90384-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Bueno R., Cheng W. D., Abrams S. A., Rothstein D. M., Hunt T. P., Tyler B., Magasanik B. Mutations that create new promoters suppress the sigma 54 dependence of glnA transcription in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4279–4284. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4279-4284.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Astwood P. M., Nixon B. T., Ausubel F. M. Deduced products of C4-dicarboxylate transport regulatory genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum are homologous to nitrogen regulatory gene products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7921–7934. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. C., Xue Z. T., Kong Q. I., Wu Q. L. An open reading frame upstream from the nifH gene of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4241–4250. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuli R., Merrick M. J. Over-production and characterization of the nifA gene product of Klebsiella pneumoniae--the transcriptional activator of nif gene expression. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Feb;134(2):425–432. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-2-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Popham D., Keener J., Kustu S. In vitro transcription of the nitrogen fixation regulatory operon nifLA of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2876–2880. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2876-2880.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]