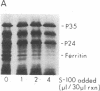
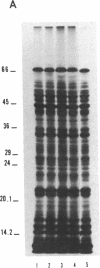
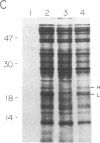
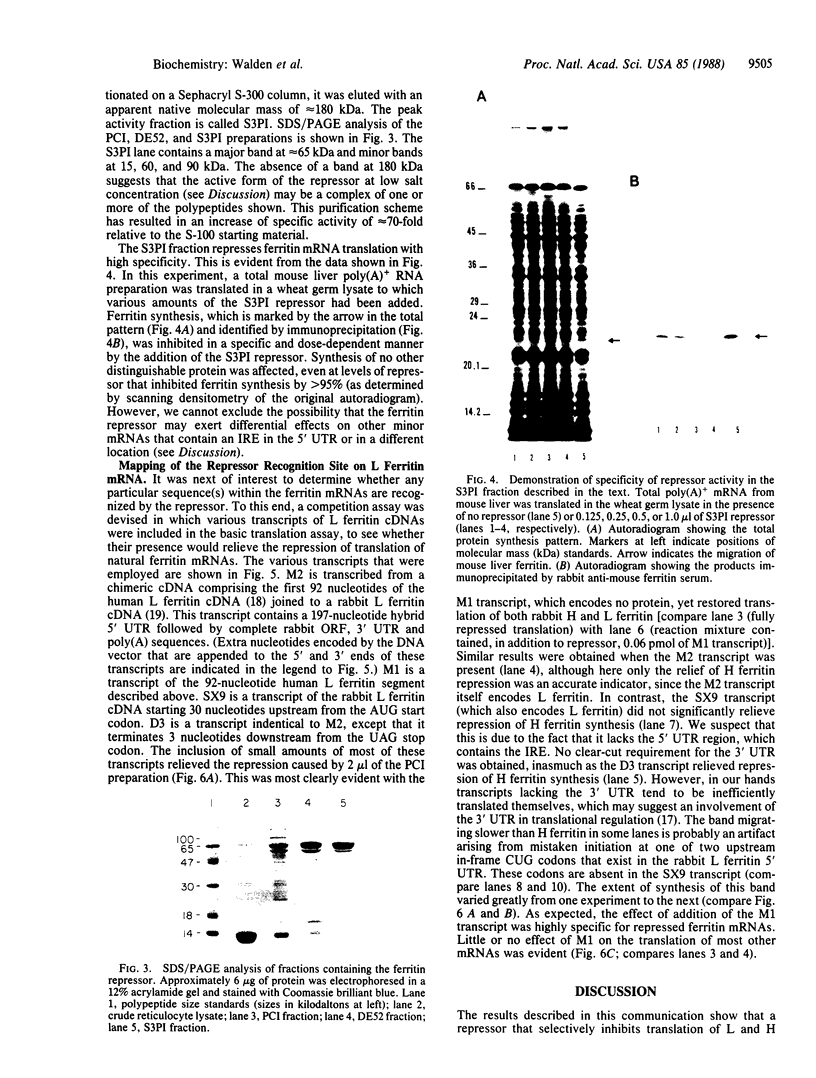
Abstract
Mouse and rabbit ferritin mRNAs translate very poorly in rabbit reticulocyte lysates relative to most other mRNAs. This translational deficiency is not seen in wheat germ lysates, suggesting the presence of an inhibitor in reticulocyte lysate that is specific for ferritin mRNA. A specific repressor of ferritin mRNA translation has been partially purified from rabbit reticulocytes by differential ultracentrifugation, ammonium sulfate fractionation, and chromatography on phosphocellulose, DEAE-cellulose, and Sephacryl S-300. The elution profile from the latter suggests an aggregate molecular mass of approximately 180 kDa for the repressor. The inhibitory activity of this repressor against native ferritin mRNA can be relieved by adding in vitro transcripts of ferritin light-chain RNAs that contain the first 92 nucleotides of the 5' untranslated region. No other sequences appear to be necessary for this effect.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Listowsky I. Iron transport and storage proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:357–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aziz N., Munro H. N. Both subunits of rat liver ferritin are regulated at a translational level by iron induction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):915–927. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aziz N., Munro H. N. Iron regulates ferritin mRNA translation through a segment of its 5' untranslated region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8478–8482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Koeller D. M., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron-responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):924–928. doi: 10.1126/science.2452485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu L. L., Fineberg R. A. On the mechanism of iron-induced synthesis of apoferritin in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 25;244(14):3847–3854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels-McQueen S., Ray A., Walden W. E., Ray B. K., Brown P. H., Thach R. E. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA encoding rabbit ferritin L chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7741–7741. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickey L. F., Wang Y. H., Shull G. E., Wortman I. A., 3rd, Theil E. C. The importance of the 3'-untranslated region in the translational control of ferritin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3071–3074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drysdale J. W., Munro H. N. Regulation of synthesis and turnover of ferritin in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3630–3637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godefroy-Colburn T., Ravelonandro M., Pinck L. Cap accessibility correlates with the initiation efficiency of alfalfa mosaic virus RNAs. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 15;147(3):549–552. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-2956.1985.00549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Barriocanal J. G., Dancis A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Identification of the iron-responsive element for the translational regulation of human ferritin mRNA. Science. 1987 Dec 11;238(4833):1570–1573. doi: 10.1126/science.3685996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Rouault T. A., Caughman S. W., Dancis A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. A cis-acting element is necessary and sufficient for translational regulation of human ferritin expression in response to iron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6730–6734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson T. G., Cladaras M. H., Ray B. K., Lee K. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Discriminatory interaction of purified eukaryotic initiation factors 4F plus 4A with the 5' ends of reovirus messenger RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7266–7276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibold E. A., Munro H. N. Cytoplasmic protein binds in vitro to a highly conserved sequence in the 5' untranslated region of ferritin heavy- and light-subunit mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2171–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Translational control of protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:39–72. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.000351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N., Linder M. C. Ferritin: structure, biosynthesis, and role in iron metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1978 Apr;58(2):317–396. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. T., White K., Munro H. N. Conservation of ferritin heavy subunit gene structure: implications for the regulation of ferritin gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7438–7442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Insertion mutagenesis to increase secondary structure within the 5' noncoding region of a eukaryotic mRNA reduces translational efficiency. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Lawson T. G., Kramer J. C., Cladaras M. H., Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. ATP-dependent unwinding of messenger RNA structure by eukaryotic initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7651–7658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Marone M., Ferrone M., Costanzo F., Colombo M., Minganti C., Cortese R., Silengo L. Cloning of the gene coding for human L apoferritin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2863–2876. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Theil E. C. Translational control of ferritin synthesis by iron in embryonic reticulocytes of the bullfrog. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14187–14191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil E. C. Ferritin: structure, gene regulation, and cellular function in animals, plants, and microorganisms. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:289–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walden W. E., Daniels-McQueen S., Smith L. L., Thach R. E. Procedures for enhancing the utility of the metallothionein promoter for the regulated expression of downstream open reading frames. Gene. 1987;61(3):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walden W. E., Thach R. E. Translational control of gene expression in a normal fibroblast. Characterization of a subclass of mRNAs with unusual kinetic properties. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):2033–2041. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zähringer J., Baliga B. S., Munro H. N. Novel mechanism for translational control in regulation of ferritin synthesis by iron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):857–861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]