Abstract
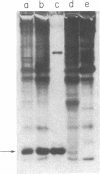
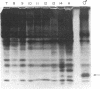
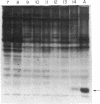
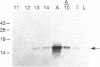
cDNA encoding pheromone-binding protein (PBP), the major soluble protein in olfactory sensilla of male moths, has been cloned from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. A study of the developmental time course of PBP reveals that it is first synthesized just prior to eclosion and that the percentage of antennal mRNA encoding PBP shifts from zero to about 20% at that time. PBP is also found in sensilla from female M. sexta antennae. No amino acid sequence homology is observed between PBP and the vertebrate odorant-binding protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignetti E., Cavaggioni A., Pelosi P., Persaud K. C., Sorbi R. T., Tirindelli R. Purification and characterisation of an odorant-binding protein from cow nasal tissue. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):227–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckh J., Kaissling K. E., Schneider D. Insect olfactory receptors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:263–280. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrbach S. E., Truman J. W. Mechanisms for programmed cell death in the nervous system of a moth. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;126:65–81. doi: 10.1002/9780470513422.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godovac-Zimmermann J. The structural motif of beta-lactoglobulin and retinol-binding protein: a basic framework for binding and transport of small hydrophobic molecules? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):64–66. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hishinuma A., Hockfield S., McKay R., Hildebrand J. G. Monoclonal antibodies reveal cell-type-specific antigens in the sexually dimorphic olfactory system of Manduca sexta. II. Expression of antigens during postembryonic development. J Neurosci. 1988 Jan;8(1):308–315. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-01-00308.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden H. M., Rypniewski W. R., Law J. H., Rayment I. The molecular structure of insecticyanin from the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta L. at 2.6 A resolution. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1565–1570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaissling K. E. Chemo-electrical transduction in insect olfactory receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:121–145. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Wells R. G., Reed R. R. Isolation of an olfactory cDNA: similarity to retinol-binding protein suggests a role in olfaction. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1053–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.3493528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papiz M. Z., Sawyer L., Eliopoulos E. E., North A. C., Findlay J. B., Sivaprasadarao R., Jones T. A., Newcomer M. E., Kraulis P. J. The structure of beta-lactoglobulin and its similarity to plasma retinol-binding protein. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):383–385. doi: 10.1038/324383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pervaiz S., Brew K. Homology of beta-lactoglobulin, serum retinol-binding protein, and protein HC. Science. 1985 Apr 19;228(4697):335–337. doi: 10.1126/science.2580349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner J., Reed R. R., Feinstein P. G., Snyder S. H. Molecular cloning of odorant-binding protein: member of a ligand carrier family. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):336–339. doi: 10.1126/science.3388043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner J., Sklar P. B., Snyder S. H. Odorant-binding protein: localization to nasal glands and secretions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4942–4946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner J., Trifiletti R. R., Strittmatter S. M., Snyder S. H. Isolation and characterization of an olfactory receptor protein for odorant pyrazines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Hildebrand J. G., Prescott D. J. Differentiation of insect sensory neurons in the absence of their normal synaptic targets. Dev Biol. 1976 Aug;52(1):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Hildebrand J. G. Structure and development of antennae in a moth, Manduca sexta. Dev Biol. 1976 Jul 15;51(2):280–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer L. Protein structure. One fold among many. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):659–659. doi: 10.1038/327659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. Insect olfaction: deciphering system for chemical messages. Science. 1969 Mar 7;163(3871):1031–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3871.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer E. S., Sanes J. R., Hildebrand J. G. Ontogeny of electroantennogram responses in the moth, Manduca sexta. J Insect Physiol. 1976;22(7):955–960. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(76)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J. L. Production of antisera with small doses of immunogen: multiple intradermal injections. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]