Abstract
Nitrate reductase activity in barley (Hordeum vulgare L. cv. Himalaya) aleurone layers has been determined in the intact tissue, using two different methods. The first method measures the rate of appearance of H218O produced during the reduction of KN18O3. The second assay measures excreted nitrite resulting from nitrate reduction under anaerobic conditions. Nitrite production in this anaerobic, intact-tissue assay was dependent upon the presence of phosphate (pH 7.5) and was increased by ethanol and bisulfite.
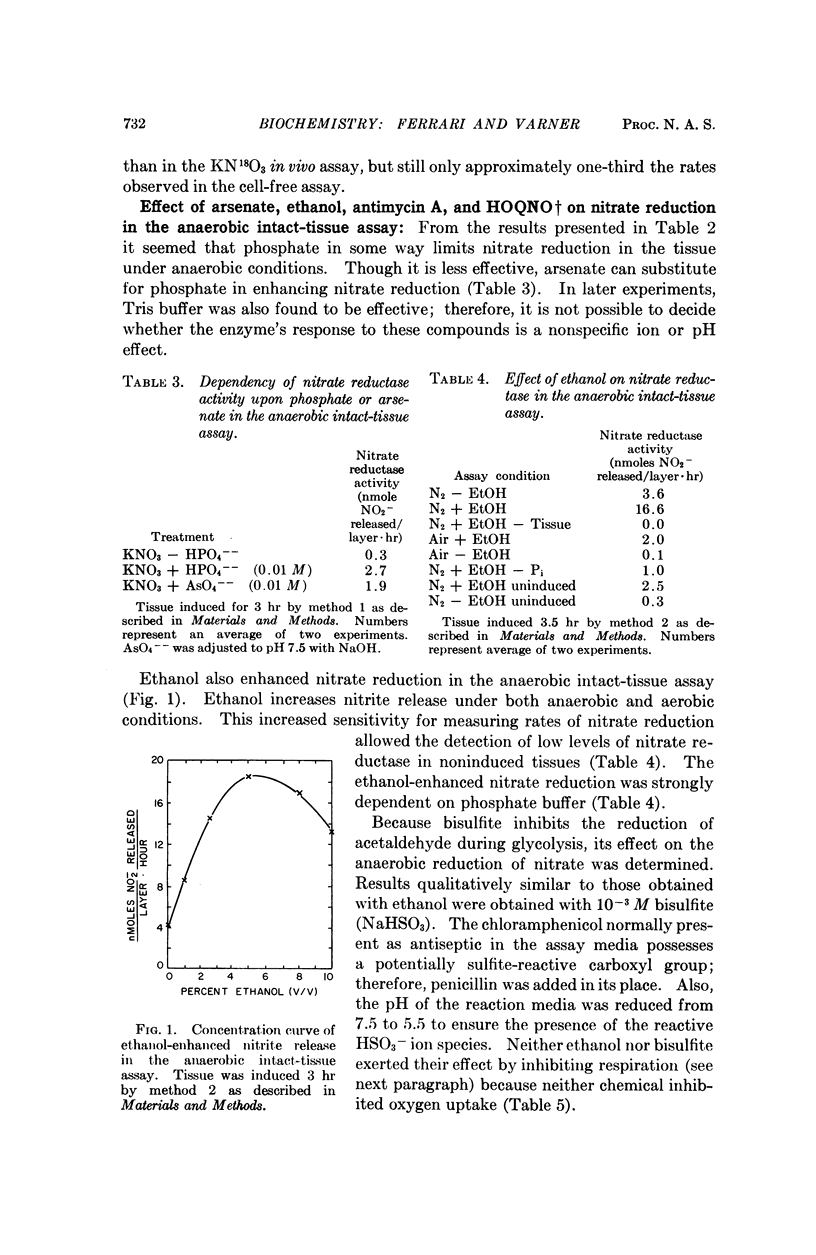
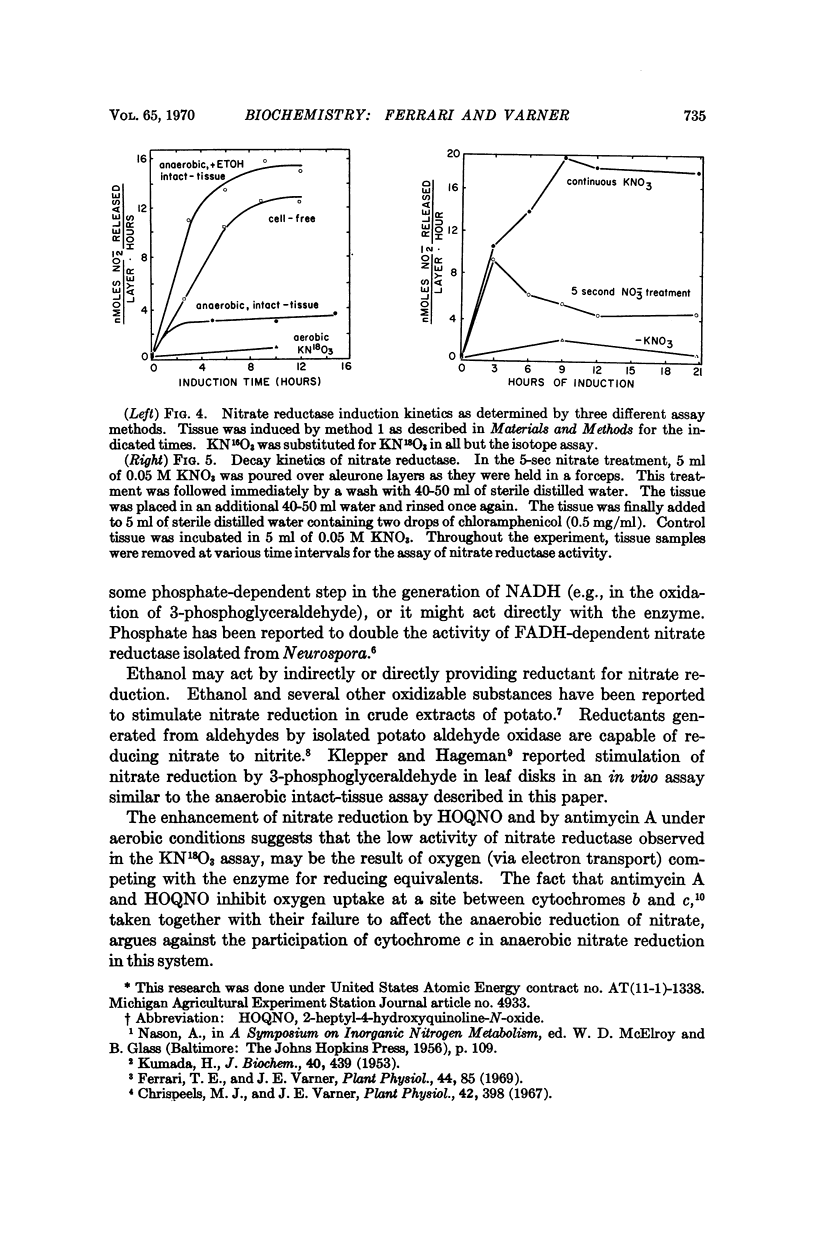
After ten hours of nitrate induction, nitrate reductase activities measured by the KN18O3 assay are one-sixth, and those measured by the anaerobic intact-tissue assay are one-third, of those observed in cell-free extracts of aleurone layers. Addition of ethanol to the anaerobic intact-tissue medium increased the rate of nitrate reduction to a level greater than that found in the cell-free assay.
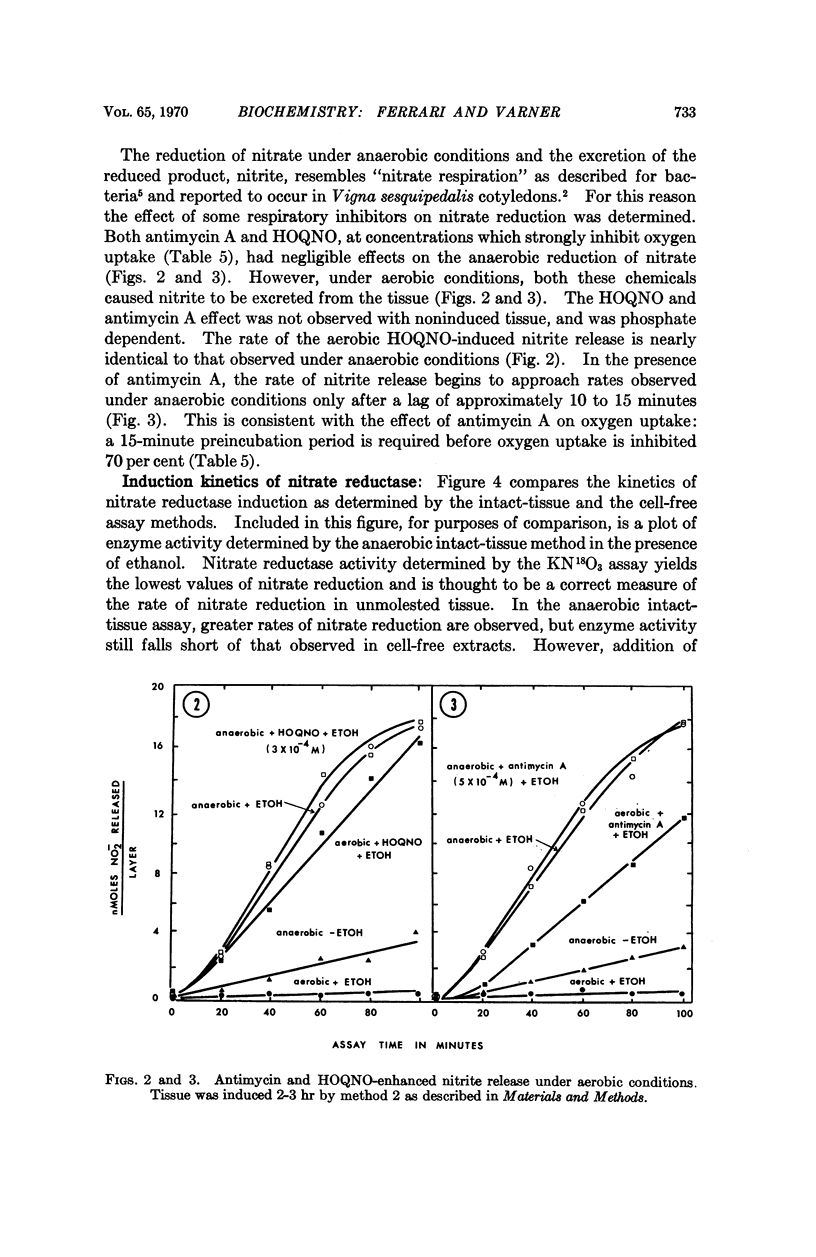
Oxygen inhibited nitrite release in the anaerobic intact-tissue assay. However, under aerobic conditions and in the presence of 2-heptyl-4-hydroxyquinoline-N-oxide or antimycin A, nitrate reduction increased to rates comparable to those observed under anaerobiosis. Neither of these electron transport inhibitors affected anaerobic nitrate reduction, though they were effective in inhibiting oxygen uptake in separate experiments.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernheim F. The aldehyde oxidase of the potato. Biochem J. 1928;22(2):344–352. doi: 10.1042/bj0220344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrispeels M. J., Varner J. E. Gibberellic Acid-enhanced synthesis and release of alpha-amylase and ribonuclease by isolated barley and aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1967 Mar;42(3):398–406. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.3.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari T. E., Varner J. E. Substrate induction of nitrate reductase in barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1969 Jan;44(1):85–88. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINSKY S. C., McELROY W. D. Neurospora nitrate reductase: the role of phosphate flavine and cytochrome c reductase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Feb;73(2):466–483. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


